Cadim Grammar: Difference between revisions
m (Cadim moved to Cadim Grammar) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The plural endings do not change the original stress of the word: '''neko''', cat... '''nekom''' cats, '''muj''', man... '''mujat''', men. Note that adjectives do not agree with plural nouns. | The plural endings do not change the original stress of the word: '''neko''', cat... '''nekom''' cats, '''muj''', man... '''mujat''', men. Note that adjectives do not agree with plural nouns. | ||
If there are other words (such as ''' | If there are other words (such as '''cok(a)''' (much/many) or numbers) that indicate plurality, the plural ending may be omitted. | ||
Gender is not indicated in most nouns. For animals, use '''muj''' and ''' | Gender is not indicated in most nouns. For animals, use '''muj''' and '''nekeb''' as adjectives after the noun. | ||
* Adjectives do not change when they are plural. But when an adjective is used in place of a noun, it can be pluralized: ''al | * Adjectives do not change when they are plural. But when an adjective is used in place of a noun, it can be pluralized: '''al segu''' "the following (ones)". | ||
=Articles= | =Articles= | ||
Revision as of 05:38, 21 September 2008
Nouns
Nouns and adjectives
Adjectives indicating quantities precede the noun; adjectives indicating qualities follow it. But tayeb "good" and mala "bad" usually precede the noun.
- -t/-at for most words
- -m/-em for words ending in front vowels other than [a] or when the word ends with a coronal plosive
The plural endings do not change the original stress of the word: neko, cat... nekom cats, muj, man... mujat, men. Note that adjectives do not agree with plural nouns.
If there are other words (such as cok(a) (much/many) or numbers) that indicate plurality, the plural ending may be omitted.
Gender is not indicated in most nouns. For animals, use muj and nekeb as adjectives after the noun.
- Adjectives do not change when they are plural. But when an adjective is used in place of a noun, it can be pluralized: al segu "the following (ones)".
Articles
Cadim only has a definite article.
- the -- al
The preposition de or man (of/from/about) is used without an article to express the partitive sense, e.g. icub de kahua... a cup of coffee, al darab de yuga... the piece of cake.
No article is used when a word is being used in a generic sense, e.g. amu kahua, yuga ilha tayeb... I like coffee, cake is good.
It is always permissible to drop articles after prepositions.
No article is necessary before names, words used as names, abstract nouns (-(e)ya), or infinitives (-ek/-mak).
Determiners
The following words precede the noun and often substitute for la or un and add a degree of precision:
- this -- hada
- e.g. this thing, these things -- hada ceya, hada ceyat
- as a pronoun: this, these -- hada, hadam
- that -- sela
- e.g. that thing, those things -- sela ceya, sela ceyat
- as a pronoun: that, those -- sela, selat
- all -- kul(u)
- e.g. all things, everything -- kul ceyat
- as a pronoun: all, everyone -- kulu
- each, every -- kada
- e.g. each thing, everything -- kada ceya
- as a pronoun: each one, every one -- kularen (persons only)
- some -- nej
- e.g. something, somethings -- nej ceya, nej ceyat
- as a pronoun: someone -- nejaren (persons only)
- no -- ne , la
- e.g. nothing, no one -- nul, neren
- as a pronoun: none, no one -- neren (persons only)
The following (when adjectives) require an article unless plural:
- many -- zida
- e.g. ceyat zida... many things
- e.g. al zida ceyat... the many things
- few -- cua
- e.g. ceyat cua... few things
- e.g. al ceyat cua... the few things
- same -- ista
- e.g. al ceya ista, al ceyat ista... the same thing, the same things
- other, else -- otra
- e.g. al ceya otra, al ceyat otra... the other things, the other thing
- e.g. ceya otra, ceyat otra... another thing, other things.
The preceding particles are often followed by...
- thing -- ceya
- person -- aren
- time -- ura (time, hour of the day)
- ima (occasion)
- place -- omra (area)
- lu (location)
- amount, quantity -- anza
- manner, way, how -- mod
- case, situation, circumstance -- mika
Others:
- both -- bada
- bada ceyat
- enough -- bas
- bas ceyat
- such -- tan
- tan ceyat
- certain -- tok
- tok ceya, tok ceyat
- sole, only -- nur(a)
- al nura ceya, nur ceya
Pronouns
- this -- hada
- as a pronoun: this, these -- hada, hadam
- that -- sela
- as a pronoun: that, those -- sela, selat
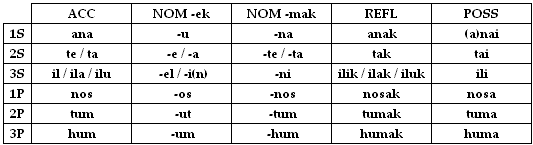
Accusative
- te The polite/formal form.
- il, neuter | ila, feminine | ilu, masculine.
Possessive
- nai is more common than anai.
Nominative
- -el is the formal form of the 3rd person singular.
- -te The polite/formal form of 2nd person singular.
Prepositions
Spacial -- de ruma
- at, to -- ela
- in front of -- anta
- behind -- ba'ad
- from, out of -- de
- in, into -- be
- outside -- bara
- above, over, on -- ala
- below, under -- tahet
- between, among -- bayan
- by, beside, up to -- janiba
- toward -- ela
- along -- alat
- across, through -- kebra
- around -- hula
- opposite -- aksa
Temporal -- de zaman
- at, to -- ala
- before -- anta
- after -- ba'ad
- since -- mun
- in (hence) -- talha
- during -- dum
- until -- gayet
Relational -- de suhed
- of -- man
- about, concerning -- beka
- for, in order to, benefiting, on behalf of -- heyara
- by (actor, author) -- beya
- with, in company of, using -- mita
- without, except -- ona
- opposite, against, in spite of -- aksa
- approximately, around, close to -- hula