Syrunian: Difference between revisions
m (clean-up of table format) |
m (Fixed some transliteration inconsistencies) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| | {{Language | ||
| | |English = Syrunian | ||
| | |native= h-lez sirunyya : הלעז סירוניא | ||
| | |country=Syria (formerly, Roman Province of Syria) | ||
| | |universe=Alternate | ||
|- | |speakers=ca. 6,000 | ||
| | |headingbg=#c9ffd9 | ||
| | |family=Indo-European | ||
|branch=Italic-Romance | |||
|- | |subbranch=Levantine | ||
| | |wordorder=VSO | ||
|alignment=Nominative-Accusative | |||
|writing=a Hebrew-derived alphabet, historically also the Aramaic/Syriac abjads | |||
| | |author=[[User:Culmaer|Culmær]] | ||
| | |date=December 2010 | ||
| | |type=inflecting | ||
| | |width=275px | ||
| | }} | ||
<!-- / həlaʕz sirʊˈniːja / Written in: ||a Hebraic alphabet and the Latin alphabet Historically also written in: ||the Hebrew, Arabic and Syriac abjads Relevant admired<br />projects : || [[Carrajina]]; [[Bâzrâmani]] //--> | |||
||a Hebraic alphabet and the Latin alphabet | |||
||the Hebrew, Arabic and Syriac abjads | |||
'''Syrunian''' is a [[Wikipedia:Romance languages|Romance]] conlang, or ''romlang'' | '''Syrunian''' is a [[Wikipedia:Romance languages|Romance]] conlang, or ''romlang'', designed to be a plausible descendant of Latin which sounds (and, at time, acts) like a [[Wikipedia:Semitic languages|Semitic]] language. It is derived from a fictional [[Wikipedia:Latin language|Vulgar Latin]] spoken in Roman Syria. Its primary influence is [[Wikipedia:Aramaic of Jesus|Aramaic]], but there are later borrowings from Arabic and modern loans French and English, like ''h-aurdinatur'' from the French “l’ordinateur” (computer). | ||
It is derived from a | |||
==Etymology== | ==Etymology of Name == | ||
''h-Lez sirunyya'' is derived from the Syrian-Latin phrase '''hic lahez Siria Romane''' | הלעז סירוניא (Romanised ''h-Lez sirunyya'', IPA / həlaʕz sirʊˈniːja /) is derived from the Syrian-Latin phrase '''hic lahez Siria Romane''' (the language of Roman Syria, i.e. the Latin of Syria). | ||
* '''H''' : definite article, “the.” [> L ''hic'' (cf: | * '''H''' : definite article, “the.” [> L. ''hic'' (cf: Hebrew def. article ‘h, ה’)] | ||
* ''' | * '''Lez''' : language [> SrL ''lahez'' > Amc ''laʕaz'' (לעז) a foreign, non-Hebrew/Aramaic language] | ||
*''' | *'''Sirunyya''' [> L ''Siria+Romane'' → sirya rumanya → sir' runanya → sirunyya] Syrian Roman/Latin, a type of Vulgar Latin spoken in Roman Syria. | ||
== | ==Alternate history== | ||
[elements of history that are different from reality are given in ''italics'']<br /> | [elements of history that are different from reality are given in ''italics'']<br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
[[Wikipedia:Aramaic language|Aramaic]] had served as a language of administration in Mesopotamia and was the day-to-day language in Judea from about 539 BCE to 70 CE. | [[Wikipedia:Aramaic language|Aramaic]] had served as a language of administration in Mesopotamia and was the day-to-day language in Judea from about 539 BCE to 70 CE. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
During the Roman period, the great city of Antioch was the capital of the Province of Syria. It was one of the largest cities in the ancient world and an important centre of trade. Although Greek was the lingua franca in the eastern Roman Empire, ''Latin remained the language of administration in many Syrian cities, facilitating trade with the western Empire, and was widely understood by those in the urban sphere of influence.'' Latin was also spoken by the Roman army. The Empire's major cities in Syria eventually adopted Greek, ''however, in small villages (especially between Antioch and Damascus) administrators and merchants continued to use Latin on a daily basis.'' | |||
''Their Latin was greatly influenced by Aramaic, the vernacular of the broader region, especially in terms of pronunciation. Aramaic geographic, and Hebrew religious terminology was absorbed into their language, commonly referred to as Syrian Latin.''<br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Syria remained | Syria remained under Roman/Byzantine control until 638 CE, when it was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate and the Levant as a whole was brought under Arab-Islamic rule. ''Nevertheless, Early Syrunian survived as a vernacular in small villages.'' By the late 11th century, Syria was conquered first by the Seljuk Turks and then carved between Turkmen tribes and participants of the first Crusade. Sections of the coastline of Syria were briefly Frankish crusader states, ''which reintroduced Latin (via Old French) to the region. Although Arabic was not displaced as the dominant language, this reinforced the status of Syrunian in the areas where it was still spoken.'' The region was part of the Ottoman Empire from the 16th through 20th centuries ''and the Syrunian language was already in steady decline.'' After World War I, the Ottoman Empire was dissolved. In 1922 the League of Nations ceded to France the territories of modern-day Syria and Lebanon. ''This gave rise to numerous French loans in the Syrunian idiom.'' Syrian independence was acquired in April 1946. | ||
By the late 11th century, Syria was conquered first by the Seljuk Turks and then carved between Turkmen tribes and participants of the first Crusade. Sections of the coastline of Syria were briefly Frankish crusader states, ''which reintroduced Latin (via Old French) to | |||
After World War I, the Ottoman Empire was dissolved | |||
Syrian independence was acquired in April 1946. | |||
===Syrunian in Modern times=== | ===Syrunian in Modern times=== | ||
Syrunian is a minority language, spoken in a few villages in South-western Syria, | Syrunian is a minority language, spoken in a few remote villages in South-western Syria, bordering Lebanon. The distance from other major cities and isolating geological features have aided the survival of Syrunian. However, modern roads and transportation, as well as accessibility to Arabic-language television and print media, are eroding the Syrunian language. | ||
==Phonology== | ==Phonology== | ||
{| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0; margin-right:10px;" | |||
!colspan=17 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| Consonants | |||
|- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: x-small; height: 2em" | |||
! | |||
! colspan="2" | Labial | |||
! colspan="3" | Dental~Alv. | |||
! colspan="3" | Alveolar | |||
! Post-Alv. | |||
! Palatal | |||
! colspan="2" | Velar | |||
! Uvular | |||
! colspan="2" | Pharyngeal | |||
! Glottal | |||
|- | |||
! Nasal | |||
| m || | |||
| || || | |||
| n || || | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| (ŋ) | |||
|- | |||
! Plosive | |||
| b || p | |||
| d || t || tˤ | |||
| || || | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| g || k | |||
| q | |||
| || | |||
| ʔ | |||
|- | |||
! Fricative | |||
| v~β || f | |||
| ð || θ || | |||
| z || s || sˤ | |||
| ʃ | |||
| | |||
| ɣ || x || | |||
| ʕ || ħ | |||
| h | |||
|- | |||
! Approx. | |||
| w | |||
| || || | |||
| l || || | |||
| || | |||
| j | |||
| || | |||
| ʁ̞~r | |||
|} | |||
{| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0; margin-right:10px;" | |||
|+Vowels | |||
|- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: x-small; height: 2em" | |||
! !! Front !! Central !! Back | |||
|- | |||
! High | |||
| i || || ʊ~u | |||
|- | |||
! MId | |||
| e~ɛ / ē|| || | |||
|- | |||
! Low | |||
| || ä~a / ā || | |||
|} | |||
===Writing systems=== | ===Writing systems=== | ||
Syrunian is written with | Syrunian is written with the Hebrew alphabet, although there is an official Syrunian-Latin alphabet. Historically, the [[Wikipedia:Syriac alphabet|Syriac script]] was used too, along with other writing systems of the majority culture round about them. | ||
[[File:Syrunian alifbeth.jpg]] <br /> | [[File:Syrunian alifbeth.jpg]] <br /> | ||
Note that the Syrunian dagesh functions differently | Note that the Syrunian dagesh functions differently than the Hebrew and Aramaic dagesh. It is used with Ssadi and Zayn for /tʃ/ and /ʒ/. | ||
==General linguistic characteristics== | ==General linguistic characteristics== | ||
===Syntax=== | ===Syntax=== | ||
The predominant word order in Syrunian is VSO (Verb – Subject – Objects). VSO is the word order of Literary Syriac, as well as Biblical Hebrew | The predominant word order in Syrunian is VSO (Verb – Subject – Objects). VSO is the word order of Literary Syriac, as well as Biblical Hebrew and Classical Arabic. Within the noun phrase, both adjectives and possessors follow nouns. Possessors precede adjectives when modifying the same noun. Syrunian uses prepositions, some of which are proclitic. | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
===Morphology=== | ===Morphology=== | ||
Syrunian is more inflecting than most Romance languages and is comparable to Romanian. Nouns resemble Syriac/ Aramaic nouns, but their forms derive from Latin. | Syrunian is more inflecting than most Romance languages and is comparable to Romanian. Nouns resemble Syriac/Aramaic nouns, but their forms derive from Latin. The Syrunian definite article «h-, ה» is derived from the Latin word ''hic'' (this) and resembles the Hebrew definite article ''hə, ה''. It is used in all numbers, states and genders. <br /> Syrunian marks direct objects with «la-, לא», which is derived from the same root as the definite article in modern Western Romance languages, like French and Italian. This developed under the influence of the Aramaic prefix «l-, ל» which marks the direct object. | ||
====Pronouns==== | ====Pronouns==== | ||
| Line 87: | Line 133: | ||
|| || '''Subject''' forms || '''Object''' forms || | || || '''Subject''' forms || '''Object''' forms || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''1 Sing. Common''' || eħ<br /> | || '''1 Sing. Common''' || eħ<br />עח || miħ<br />מיח || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''2 Sing. Masc''' || tu<br /> | || '''2 Sing. Masc''' || tu<br />תו || tiv<br />תיב || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''2 Sing. Fem''' || ta<br /> | || '''2 Sing. Fem''' || ta<br />תא || tavā<br />תבא || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''3 Sing. Masc''' || lu<br />לו || ei<br />עי || | || '''3 Sing. Masc''' || lu<br />לו || ei<br />עי || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''3 Sing. Fem''' || | || '''3 Sing. Fem''' || liā<br />ליא || eā<br />עא || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''1 Pl. Common''' || nu<br />נו || nuṡ<br /> | || '''1 Pl. Common''' || nu<br />נו || nuṡ<br />נוש || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''2 Pl. Common''' || vu<br />בו || vuṡ<br /> | || '''2 Pl. Common''' || vu<br />בו || vuṡ<br />בוש || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''3 Pl. Common''' || alu<br />אלו || aus<br />אוס || | || '''3 Pl. Common''' || alu<br />אלו || aus<br />אוס || | ||
| Line 105: | Line 151: | ||
====Nouns==== | ====Nouns==== | ||
Syrunian only has a definite article «h-, ה» which is a contraction of the Latin word ''hic'' (this). It is also the | Syrunian only has a definite article «h-, ה» which is a contraction of the Latin word ''hic'' (this). It is also related to the Hebrew definite article ''hə, ה''. It is used in all numbers, states and genders. <br /> | ||
Syrunian has two grammatical genders, masculine and feminine. The feminine absolute singular is usually marked by the ending | Syrunian has two grammatical genders, masculine and feminine. The feminine absolute singular is usually marked by the ending –ā א or –at את . Nouns can be either singular or plural, but an additional 'dual' number exists for nouns that usually come in pairs. <br /> | ||
Syrunian nouns and adjectives can exist in one of three states; these states correspond in part to the role of cases in other languages.<br /> | Syrunian nouns and adjectives can exist in one of three states; these states correspond in part to the role of cases in other languages.<br /> | ||
* The '''emphatic or determined state''' <br /> | * The '''emphatic or determined state''' <br /> | ||
is the basic form of the noun and is used to mark the topic and subject of a sentence. If an emphatic noun is preceded by the preposition '''la, לא''' it is the direct object of a sentence.<br /> | is the basic form of the noun and is used to mark the topic and subject of a sentence. If an emphatic noun is preceded by the preposition '''la, לא''' it is the direct object of a sentence.<br /> | ||
The emphatic also governs the prepositions: '''in, ין''' (in, at) and '''pur, | The emphatic also governs the prepositions: '''in, ין''' (in, at) and '''pur, פור''' (for, to). | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
* The '''absolute state''' <br /> | * The '''absolute state''' <br /> | ||
is a prepositional state. In the | is a prepositional state. In the plural, it is often marked with the suffix –im.<br /> | ||
The absolute governs the prepositions: '''a, א''' (towards); '''ṡe, | The absolute governs the prepositions: '''a, א''' (towards); '''ṡe, שע''' (out of, from); '''di, די''' (from, concerning); '''cum, כום''' (with); '''ṡem, שעם''' (without); '''suv, סוב''' (below); '''sifr, סיפר''' (above).<br /> | ||
* The '''construct state'''<br /> | * The '''construct state'''<br /> | ||
is a form of the noun used to make possessive phrases. Unlike a genitive case, which marks the possessor, the construct state is marked on the possessed. This is mainly due to | is a form of the noun used to make possessive phrases. Unlike a genitive case, which marks the possessor, the construct state is marked on the possessed. This is mainly due to Semitic word order: ''possessed[const.] possessor[abs./emph.]'' They are treated as a speech unit, with the first unit (possessed) employing the construct state to link it to the following word. Together, the make a ''construct chain'''.<br /> | ||
Possessive phrases in Syrunian are | Possessive phrases in Syrunian are often made with the preposition di-, rather than the construct case. <br /> | ||
For example, the various forms of possessive phrases (for 'the book of the queen') are: | For example, the various forms of possessive phrases (for 'the book of the queen') are: | ||
# | # הליברע המלכא (''h-livre h-malaca'') — the possessed object (''h-liver,'' 'the book') is in the construct state (i.e. ''livre'') ; the possessor (''h-malaca,'' 'the queen') is in the emphatic state. | ||
# | # הליבר דמלכא (''h-liver d-malaca'') — both words are in the emphatic state and the relative particle ''d-'' is used to mark the relationship | ||
# | # הליברע דמלכא (''h-livre d-malaca'') — the possessed object is in the construct state and the preposition ''d-'' is used to reaffirm the relationship. <br /> | ||
In Modern Syrunian, the last form is by far the most common. | In Modern Syrunian, the last form is by far the most common. | ||
<br /><br /> | <br /><br /> | ||
{| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | |||
!colspan=6 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| Inflection of "malac" (regular noun) | |||
|- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | |||
|- | |||
|| ||colspan=2 | KING <br />Masculine || ||colspan=2 | QUEEN <br />Feminine || | |||
|- | |||
|| || '''singular''' || '''plural''' || || | '''singular''' || '''plural''' || | |||
|- | |||
|| '''Emphatic''' ||width="50"| mal'''a'''c<br />מל'''א'''ך ||width="50"| mal'''i'''c'''i'''<br />'''מל'''י'''כ'''י || || width="50"| malac'''a'''<br />מל'''א'''כא ||width="50"| mal'''a'''c'''ay'''<br />'''מל'''א'''כ'''אי || | |||
|- | |||
|| '''Absolute''' || malc'''im''' <br />'''מלכ'''ם || malc'''is'''<br />'''מלכ'''ס || || | malc'''ut''' <br />'''מלכ'''ות || malc'''as'''<br />'''מלכ'''אס || | |||
|- | |||
|| '''Construct''' || malc'''e'''<br /> '''מלכ'''ע || malc'''es'''<br />'''מלכ'''עס || || | malc'''ut'''e<br /> '''מלכ'''ותע || malc'''ese'''<br />'''מלכ'''עסע || | |||
|} | |||
<br /> | |||
{| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | {| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | ||
!colspan= | !colspan=5 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| Inflection of "ucul" (eye, regular with dual) | ||
|- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | |- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| || '''singular''' || '''plural''' || | || || '''singular''' || '''dual''' ||'''plural''' || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''Emphatic''' || | || '''Emphatic''' || uc'''u'''l <br /> וכול || uc'''u'''l'''in'''<br />וכולין || uc'''i'''l'''i'''<br />וכילי || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''Absolute''' || | || '''Absolute''' || ucl'''im''' <br />וכלים || ucl'''ayym'''<br />וכלאיים|| ucl'''is'''<br />וכלס || | ||
|- | |- | ||
|| '''Construct''' || | || '''Construct''' || ucl'''e'''<br />וכלע || ucl'''eyn'''<br />וכלעין || ucl'''es'''<br />וכלעס || | ||
|} | |} | ||
'''Superficially''', Syrio-Aramaic and Latin nouns had similar inflection forms. Thus, they survived in Syrunian. | '''Superficially''', Syrio-Aramaic and Latin nouns had similar inflection forms. Thus, they survived in Syrunian. | ||
{| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | {| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | ||
!colspan=4 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| Comparative inflection of regular nouns | !colspan=4 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| Comparative inflection of '''regular''' nouns | ||
|- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | |- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 172: | Line 236: | ||
====Verbs==== | ====Verbs==== | ||
Verbs conjugate for number; and in the singular for gender too. Singular verbs do not require the pronoun to be stated explicitly in the sentence, however, pronouns must always be used with plural verbs. | Verbs conjugate for number; and in the singular for gender too. Singular verbs do not require the pronoun to be stated explicitly in the sentence, however, pronouns must always be used with plural verbs. Verbs exist in two base forms: the perfect and imperfect. Time is expressed by using these forms in compound tenses. | ||
{| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | {| style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | ||
!colspan=4 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| The regular verb AMAR (to love) | !colspan=4 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| The regular verb AMAR (to love)<br /> ROOTS | ||
|- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | |- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 197: | Line 261: | ||
|} <br /> | |} <br /> | ||
Passive/ adjectival form: a[perfect form] (ie: the perfect from, with an Alif prefix) | {|style="text-align: center; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1pt solid #c0c0c0;" | ||
!colspan=7 style="text-align:center; background: #efefef;"| The construction of tenses and moods | |||
|- style="vertical-align: center; font-size: small; height: 2em" | |||
|- | |||
|| ||'''Past perfect'''|| '''Imperfect''' ||'''Present''' || '''Future''' || '''Future perfect''' ||'''Passive''' || | |||
|- | |||
|| Eng. example|| I have loved || I loved || I love || I will love|| I will have loved ||I am loved || | |||
|- | |||
|| '''Syrunian'''|| to have [IMP]<br /> + PERF || PERF|| IMP || to go [IMP] <br /> + INFINITIVE || to go[IMP] <br /> + PERF ||{alif (he)}PERF || | |||
|- | |||
|}<br /> | |||
Passive= adjectival form: a[perfect form] (ie: the perfect from, with an Alif prefix) | |||
==Texts== | ==Texts== | ||
''See:'' [[Syrunian texts]] | ''See:'' [[Syrunian texts]] <br /> | ||
Also consult the [[Syrunian word-list]] | |||
===Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights=== | ===Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights=== | ||
Anasħuttuvin h-culs h-ħuni libris e eqlis cum h-cuvdim e h-yuris. Adunavin h-culs la-raṡin e la-cussett, e devin alu aus sis agir in h-ruħe d-fratiryya. <br /> | |||
אנאסחוטובין הכולס החוני ליבבריס ע עקליס כם הכובדם ע היורס. אדונאבין הכולס לא-ראשין ע לא-כוצעט, ע דעבין אלו אוס סס אגיר ין הרוחע דפראתירייא<br /> | |||
Read by David Salo: [[Media:Syrunian_UDHR1.ogg]]. <br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
סונט נאסחוטאתס אונעס חוני ליבערס ,עחואלס עט סאם אל-דיהנטע אל-זּיהורסכע. סונט דונאטי לויר דאל-ראשנים דאל-קוסחעצימסכע עט עסט-צּי אוּולעט כ אגישינט ילאר סיףראל-אוטרעס סאם אל-סףירטע ףראתרעס. | compared to this version, in my earliest draft of "Levantine Romance":<br /> | ||
Sunt nasħuntaθs aunes ħuni libers, eħuals et sam al-dihnte al-żihursqe. Sunt dunati luir dal raσnim dal cusħentsimsqe et est-ċi avulet q’ agiσint ilar sifral-autres sam al-sfirte fraθres.<br /> | |||
סונט נאסחוטאתס אונעס חוני ליבערס ,עחואלס עט סאם אל-דיהנטע אל-זּיהורסכע. סונט דונאטי לויר דאל-ראשנים דאל-קוסחעצימסכע עט עסט-צּי אוּולעט כ אגישינט ילאר סיףראל-אוטרעס סאם אל-סףירטע ףראתרעס. <br /> | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
'''More texts available on the [[Syrunian texts]] page''' | |||
[[Category:Conlangs]] [[Category:Romance conlangs]] | [[Category:Conlangs]] [[Category:Romance conlangs]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:13, 25 January 2024
| Syrunian h-lez sirunyya : הלעז סירוניא | |
| Spoken in: | Syria (formerly, Roman Province of Syria) |
| Conworld: | Alternate |
| Total speakers: | ca. 6,000 |
| Genealogical classification: | Indo-European
|
| Basic word order: | VSO |
| Morphological type: | inflecting |
| Morphosyntactic alignment: | Nominative-Accusative |
| Writing system: | a Hebrew-derived alphabet, historically also the Aramaic/Syriac abjads |
| Created by: | |
| Culmær | December 2010 |
Syrunian is a Romance conlang, or romlang, designed to be a plausible descendant of Latin which sounds (and, at time, acts) like a Semitic language. It is derived from a fictional Vulgar Latin spoken in Roman Syria. Its primary influence is Aramaic, but there are later borrowings from Arabic and modern loans French and English, like h-aurdinatur from the French “l’ordinateur” (computer).
Etymology of Name
הלעז סירוניא (Romanised h-Lez sirunyya, IPA / həlaʕz sirʊˈniːja /) is derived from the Syrian-Latin phrase hic lahez Siria Romane (the language of Roman Syria, i.e. the Latin of Syria).
- H : definite article, “the.” [> L. hic (cf: Hebrew def. article ‘h, ה’)]
- Lez : language [> SrL lahez > Amc laʕaz (לעז) a foreign, non-Hebrew/Aramaic language]
- Sirunyya [> L Siria+Romane → sirya rumanya → sir' runanya → sirunyya] Syrian Roman/Latin, a type of Vulgar Latin spoken in Roman Syria.
Alternate history
[elements of history that are different from reality are given in italics]
Aramaic had served as a language of administration in Mesopotamia and was the day-to-day language in Judea from about 539 BCE to 70 CE.
During the Roman period, the great city of Antioch was the capital of the Province of Syria. It was one of the largest cities in the ancient world and an important centre of trade. Although Greek was the lingua franca in the eastern Roman Empire, Latin remained the language of administration in many Syrian cities, facilitating trade with the western Empire, and was widely understood by those in the urban sphere of influence. Latin was also spoken by the Roman army. The Empire's major cities in Syria eventually adopted Greek, however, in small villages (especially between Antioch and Damascus) administrators and merchants continued to use Latin on a daily basis.
Their Latin was greatly influenced by Aramaic, the vernacular of the broader region, especially in terms of pronunciation. Aramaic geographic, and Hebrew religious terminology was absorbed into their language, commonly referred to as Syrian Latin.
Syria remained under Roman/Byzantine control until 638 CE, when it was conquered by the Rashidun Caliphate and the Levant as a whole was brought under Arab-Islamic rule. Nevertheless, Early Syrunian survived as a vernacular in small villages. By the late 11th century, Syria was conquered first by the Seljuk Turks and then carved between Turkmen tribes and participants of the first Crusade. Sections of the coastline of Syria were briefly Frankish crusader states, which reintroduced Latin (via Old French) to the region. Although Arabic was not displaced as the dominant language, this reinforced the status of Syrunian in the areas where it was still spoken. The region was part of the Ottoman Empire from the 16th through 20th centuries and the Syrunian language was already in steady decline. After World War I, the Ottoman Empire was dissolved. In 1922 the League of Nations ceded to France the territories of modern-day Syria and Lebanon. This gave rise to numerous French loans in the Syrunian idiom. Syrian independence was acquired in April 1946.
Syrunian in Modern times
Syrunian is a minority language, spoken in a few remote villages in South-western Syria, bordering Lebanon. The distance from other major cities and isolating geological features have aided the survival of Syrunian. However, modern roads and transportation, as well as accessibility to Arabic-language television and print media, are eroding the Syrunian language.
Phonology
| Consonants | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labial | Dental~Alv. | Alveolar | Post-Alv. | Palatal | Velar | Uvular | Pharyngeal | Glottal | ||||||||
| Nasal | m | n | (ŋ) | |||||||||||||
| Plosive | b | p | d | t | tˤ | g | k | q | ʔ | |||||||
| Fricative | v~β | f | ð | θ | z | s | sˤ | ʃ | ɣ | x | ʕ | ħ | h | |||
| Approx. | w | l | j | ʁ̞~r | ||||||||||||
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| High | i | ʊ~u | |
| MId | e~ɛ / ē | ||
| Low | ä~a / ā |
Writing systems
Syrunian is written with the Hebrew alphabet, although there is an official Syrunian-Latin alphabet. Historically, the Syriac script was used too, along with other writing systems of the majority culture round about them.
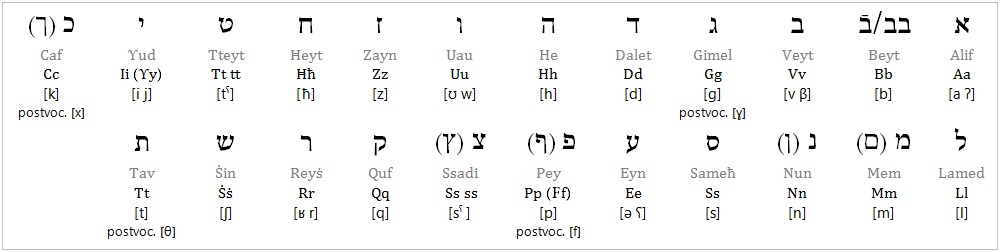
Note that the Syrunian dagesh functions differently than the Hebrew and Aramaic dagesh. It is used with Ssadi and Zayn for /tʃ/ and /ʒ/.
General linguistic characteristics
Syntax
The predominant word order in Syrunian is VSO (Verb – Subject – Objects). VSO is the word order of Literary Syriac, as well as Biblical Hebrew and Classical Arabic. Within the noun phrase, both adjectives and possessors follow nouns. Possessors precede adjectives when modifying the same noun. Syrunian uses prepositions, some of which are proclitic.
Morphology
Syrunian is more inflecting than most Romance languages and is comparable to Romanian. Nouns resemble Syriac/Aramaic nouns, but their forms derive from Latin. The Syrunian definite article «h-, ה» is derived from the Latin word hic (this) and resembles the Hebrew definite article hə, ה. It is used in all numbers, states and genders.
Syrunian marks direct objects with «la-, לא», which is derived from the same root as the definite article in modern Western Romance languages, like French and Italian. This developed under the influence of the Aramaic prefix «l-, ל» which marks the direct object.
Pronouns
| Pronouns | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject forms | Object forms | ||
| 1 Sing. Common | eħ עח |
miħ מיח |
|
| 2 Sing. Masc | tu תו |
tiv תיב |
|
| 2 Sing. Fem | ta תא |
tavā תבא |
|
| 3 Sing. Masc | lu לו |
ei עי |
|
| 3 Sing. Fem | liā ליא |
eā עא |
|
| 1 Pl. Common | nu נו |
nuṡ נוש |
|
| 2 Pl. Common | vu בו |
vuṡ בוש |
|
| 3 Pl. Common | alu אלו |
aus אוס |
|
Nouns
Syrunian only has a definite article «h-, ה» which is a contraction of the Latin word hic (this). It is also related to the Hebrew definite article hə, ה. It is used in all numbers, states and genders.
Syrunian has two grammatical genders, masculine and feminine. The feminine absolute singular is usually marked by the ending –ā א or –at את . Nouns can be either singular or plural, but an additional 'dual' number exists for nouns that usually come in pairs.
Syrunian nouns and adjectives can exist in one of three states; these states correspond in part to the role of cases in other languages.
- The emphatic or determined state
is the basic form of the noun and is used to mark the topic and subject of a sentence. If an emphatic noun is preceded by the preposition la, לא it is the direct object of a sentence.
The emphatic also governs the prepositions: in, ין (in, at) and pur, פור (for, to).
- The absolute state
is a prepositional state. In the plural, it is often marked with the suffix –im.
The absolute governs the prepositions: a, א (towards); ṡe, שע (out of, from); di, די (from, concerning); cum, כום (with); ṡem, שעם (without); suv, סוב (below); sifr, סיפר (above).
- The construct state
is a form of the noun used to make possessive phrases. Unlike a genitive case, which marks the possessor, the construct state is marked on the possessed. This is mainly due to Semitic word order: possessed[const.] possessor[abs./emph.] They are treated as a speech unit, with the first unit (possessed) employing the construct state to link it to the following word. Together, the make a construct chain'.
Possessive phrases in Syrunian are often made with the preposition di-, rather than the construct case.
For example, the various forms of possessive phrases (for 'the book of the queen') are:
- הליברע המלכא (h-livre h-malaca) — the possessed object (h-liver, 'the book') is in the construct state (i.e. livre) ; the possessor (h-malaca, 'the queen') is in the emphatic state.
- הליבר דמלכא (h-liver d-malaca) — both words are in the emphatic state and the relative particle d- is used to mark the relationship
- הליברע דמלכא (h-livre d-malaca) — the possessed object is in the construct state and the preposition d- is used to reaffirm the relationship.
In Modern Syrunian, the last form is by far the most common.
| Inflection of "malac" (regular noun) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KING Masculine |
QUEEN Feminine |
|||||
| singular | plural | singular | plural | |||
| Emphatic | malac מלאך |
malici מליכי |
malaca מלאכא |
malacay מלאכאי |
||
| Absolute | malcim מלכם |
malcis מלכס |
malcut מלכות |
malcas מלכאס |
||
| Construct | malce מלכע |
malces מלכעס |
malcute מלכותע |
malcese מלכעסע |
||
| Inflection of "ucul" (eye, regular with dual) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| singular | dual | plural | ||
| Emphatic | ucul וכול |
uculin וכולין |
ucili וכילי |
|
| Absolute | uclim וכלים |
uclayym וכלאיים |
uclis וכלס |
|
| Construct | ucle וכלע |
ucleyn וכלעין |
ucles וכלעס |
|
Superficially, Syrio-Aramaic and Latin nouns had similar inflection forms. Thus, they survived in Syrunian.
| Comparative inflection of regular nouns | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LATIN | SYRIAC (Aramaic) |
SYRUNIAN | ||
| Nominative/ Emphatic |
Vita | šeqle | liver | |
| Accusative/ Absloute |
Vit-am | šeql-în | livr-im | |
| Genitive/ Construct |
Vit-æ | šeql-ay | livr-e | |
| translation | "life" | "tax" | "book" | |
Adjectives
Adjectives agree with their nouns in number and state, but only attributive. Predicative adjectives are in the construct state regardless of the state of their noun (a copula can, but need not be written). Thus, an attributive adjective to an emphatic noun, as in the phrase 'the good king', is written also in the emphatic state : h-malac h-ben — the king[emph.] good[emph.]. In comparison, the predicative adjective, as in the phrase 'the king is good', is written in the construct state: h-malac beni — the king[emph.] good[cons.] An alternative is : es beni h-malac – is good[cons.] the king[emph.].
Note that Dual numbers take plural adjectives. Adjectives never inflect for the dual.
| Inflection of "ben" (good) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masculine | Feminine | ||||
| singular | plural | Singular | Plural | ||
| Emphatic | ben בן |
bens בנס |
bena בנא |
benat בנאת |
|
| Absolute | benim בנם |
bens בנס |
benam בנם |
benat בנאת |
|
| Construct | beni בני |
benis בניס |
beni בני |
benis בניס |
|
Verbs
Verbs conjugate for number; and in the singular for gender too. Singular verbs do not require the pronoun to be stated explicitly in the sentence, however, pronouns must always be used with plural verbs. Verbs exist in two base forms: the perfect and imperfect. Time is expressed by using these forms in compound tenses.
| The regular verb AMAR (to love) ROOTS | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Imperfect forms | Perfect forms | ||
| 1 Sing. Common (I) | amaħ אמאח |
amav אמאב |
|
| 2 Sing. Masc (you) | amut אמות |
amavis אמאביס |
|
| 2 Sing. Fem | amat אמאת |
amavit אמאבית |
|
| 3 Sing. Masc (he/it) | amu אמו |
amavis אמאביס |
|
| 3 Sing. Fem (she) | amya אמיא |
amavit אמאבית |
|
| 1 Pl. Common (we) | amamus אמאמוס |
amavam אמאבאם |
|
| 2 Pl. Common (you) | amass אמאץ |
amavatiss אמאבאתיץ |
|
| 3 Pl. Common (they) | amayn אמאין |
amavin אמאבין |
|
| The construction of tenses and moods | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Past perfect | Imperfect | Present | Future | Future perfect | Passive | ||
| Eng. example | I have loved | I loved | I love | I will love | I will have loved | I am loved | |
| Syrunian | to have [IMP] + PERF |
PERF | IMP | to go [IMP] + INFINITIVE |
to go[IMP] + PERF |
{alif (he)}PERF | |
Passive= adjectival form: a[perfect form] (ie: the perfect from, with an Alif prefix)
Texts
See: Syrunian texts
Also consult the Syrunian word-list
Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights
Anasħuttuvin h-culs h-ħuni libris e eqlis cum h-cuvdim e h-yuris. Adunavin h-culs la-raṡin e la-cussett, e devin alu aus sis agir in h-ruħe d-fratiryya.
אנאסחוטובין הכולס החוני ליבבריס ע עקליס כם הכובדם ע היורס. אדונאבין הכולס לא-ראשין ע לא-כוצעט, ע דעבין אלו אוס סס אגיר ין הרוחע דפראתירייא
Read by David Salo: Media:Syrunian_UDHR1.ogg.
compared to this version, in my earliest draft of "Levantine Romance":
Sunt nasħuntaθs aunes ħuni libers, eħuals et sam al-dihnte al-żihursqe. Sunt dunati luir dal raσnim dal cusħentsimsqe et est-ċi avulet q’ agiσint ilar sifral-autres sam al-sfirte fraθres.
סונט נאסחוטאתס אונעס חוני ליבערס ,עחואלס עט סאם אל-דיהנטע אל-זּיהורסכע. סונט דונאטי לויר דאל-ראשנים דאל-קוסחעצימסכע עט עסט-צּי אוּולעט כ אגישינט ילאר סיףראל-אוטרעס סאם אל-סףירטע ףראתרעס.
More texts available on the Syrunian texts page