Kelanian
| Kelanian Kélanìanē | |
| Timeline/Universe: | (not yet named) |
| Total speakers: | none |
| Genealogical Classification: | Kelanian |
| Basic word order: | OSV |
| Morphological type: | fusional |
| Morphosyntactic alignment: | fluid-S |
| Created by: | |
| Andrew | 2007 |
Kelanian (native name Kélanìanē) was the original language spoken by all people. It was how the first men interpreted the speech of the Kélanui (sg. Kélanu), or "holy ones," who shaped the earth, govern its existance, and guided men in their earliest days. In truth, the actual speech of the Kelanui is more complex than Kelanian, with each Kelanu having his or her own slightly different version, but the two were close enough to be mutually intelligible.
Phonology
Consonants
Kelanian contains 21 consonantal phonemes. The majority, 13, of these are stops. It has labial, dental and velar aspirated and unaspirated stops, both voiced and unvoiced, as well as the glottal stop q /?/, as in "uh-oh". There is only 1 fricative, s /s/. The remaining 7 are sonorants. It has three nasals, m /m/, n /n/, and ñ /N/. Each nasal is inherently linked to a certain group of stops- m with the labials, n with the dentals, and ñ with the velars. There are two liquids, l /l/ and r /r/, and two semivowels w /w/ and y /j/.
| Labial | Dental | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | |
| Stops, unaspirated | p b | t d | k g | q | |
| Stops, aspirated | ph bh | th dh | kh gh | ||
| Fricatives | s | ||||
| Nasals | m | n | ñ | ||
| Liquids | l r | ||||
| Semivowels | w | y |
Allophony
r is realized as [4] (an alveolar flap) when not initial or geminated.
Before or after voiced stops, s is realized as [z].
Vowels
There are 5 vowels, a, e, i, o, and u, which can all be short or long. Long vowels are written with a macron, ā, ē, ī, ō, ū. The two mid vowels, e and o, are tense when they are long, /e: o:/ and lax when they are short /ɛ ɔ/.
| Front | Central | Back | |
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | o | |
| Open | a |
There are also 8 diphthongs, essentially treated as long vowels. They are formed when i follows a, e, o, or u and when u follows a, e, o, or i. The first element becomes long (the macron isn't written), and the second becomes a semivowel, ai ei oi ui au eu ou iu are /a:j e:j o:j u:j a:w e:w o:w i:w/.
Phonotactics
Consonants and consonant clusters are always viewed as syllable onsets. There may only be a coda on a final syllable. Word initial or medial syllables are of the form (C)(C)(w,y)V, though there are very strict rules for what clusters can be formed (see below). Final syllables are of the form (C)(C)(w,y)V(sonorant, fricative). Only a vowel or diphthong is required to form a syllable.
Consonant Clusters
There are rules for what consonant combinations form permissable clusters. All of the clusters formed by the following rules may be medial, but not all may be initial. The ones that can are marked so.
Note: 3 is a stop, but cannot be used to make clusters. All of the rules that refer to "stops" do not apply to 3.
Liquids can precede nasals and stops.
Anything but stops can be geminated.
s can precede or follow stops. (can be initial)
Stops can follow their matching nasals. (can be initial)
The semivowels w and y can follow a consonant or cluster. (allowed initial clusters followed by w and y are also allowed initially)
Accent
In Kelanian, the accent is always found on the word's root vowel. For words that have two or more syllables after the root vowel, every second vowel from the root vowel gets a secondary accent.
Words that don't have analysable roots, e.g. pronouns, prepositions, &c., are always three or less syllables, and are accented on the first. The addition of derivational prefixes and suffixes, like the comparative or superlative, do not move the stress to earlier or later in the word; it is completely fixed.
A long accented vowel is written with a circumflex, a short accented vowel with an acute. A secondary accent is written with a grave.
Elision
If one word ends with a vowel and the next begins with one, the first vowel is dropped in speech if it is short. If it is long and the second vowel is short, that one is dropped. If both are long, neither is dropped.
There is one notable instance when elision doesn't occur—the formation of verbs. This lack of elision is emphasized in writing by using a hyphen, e.g. tséraye-éni.
Morphology
Word Derivation
Primitive Root Structure
The roots of Kelanian are of the structure (C)(C)(w,y)VCV. The initial cluster may only be one of the clusters outlined above as permissible initially. Other than this, there is only one rule concerning the consonants in a root: there must be one between the vowels.
There are two vowels in every root. The second is called the "determining vowel" of the root, because it determines what the first vowel, the "root vowel," will be. (It is not very common for two roots to differ only by the determining vowel.) If the determining vowel is e or i, the root vowel is e. If it is o or u, the root vowel is o, and if the determining vowel is a, in the majority of cases the root vowel will be e, though it may be o if the initial consonant cluster contains a w. The root vowel, as mentioned above, is the vowel that is accented in all words derived from a certain root.
Lexeme Formation
Lexeme derivation from primitive roots is accomplished through the addition of suffixes, though sometimes the root vowel is also lengthened. The suffixes are of the form CV. For example, by using the suffix -nū, the root ETA gives étanū man/person.
When nouns are derived, the form produced is the absolutive singular. When modifiers are derived, the form produced is the imperfective active.
Word Formation
Lexemes themselves are words, though there are a variety of words that can be derived from them, as well as many inflections that can be added. To derive totally new words from lexemes, the final vowel is dropped and suffixes are added. These suffixes are of the form (V)VC or (V)VCV. For example, étanū gives étanothē, a host of men by dropping the final vowel and adding the suffix -othē.
The various inflections that can be added onto a lexeme or a new derived word include suffixes and prefixes of many different forms. They are clearly marked throughout the rest of this article.
Nouns
Nouns are split into 5 declensions and are marked for 3 numbers and 8 cases.
Declensions
Nouns fall into three main categories: animate nouns, a small group of abstract nouns, and inanimate nouns.
Animate nouns include people, animals, and anything else that was seen as having a will of its own. This includes some things that, to us, are inanimate, but were perceived as being conscious, such as the sun and the moon. The reason for this is mythological.
The abstract class of nouns is not found in anything but the singular, since they are intangible concepts and cannot logically be pluralized.
The class of inanimate nouns consists of anything non-living (besides abstract nouns). Since they are not seen as having a will of their own, the inanimate nouns are not found in the nominative case, which shows intent and thoughtful purpose. Some inanimate nouns, the so-called "mass nouns," (e.g. water, knowledge, information, &c.) can also not be pluralized.
Based on these distinctions, nouns are split into 5 declensions, each with its own characteristic vowel. The 1st (u declension) and 2nd (o declension) include the animates, the 3rd (a declension) and 4th (e declension) the inanimates, and the 5th (i declension) is for the abstracts. For proper nouns, these distinctions are not maintained-names may fall into any declension.
Number
Kelanian nouns are marked for three numbers: singular, paucal and plural. Singular refers to a single object. Paucal refers to a small, usually countable, number of something. For certain nouns (e.g. ears, eyes, hands, &c.) it refers to exactly two of something (dual). The paucal is formed by adding the prefix e- to the singular form of the noun. Plural refers to a large, usually uncountable, number of something. It is formed by adding the suffix -i after the stem, before the case ending. When a specific number of something is referenced, the adjectival number is applied to the singular form.
Cases
Kelanian nouns are marked for 8 cases: nominative (agentive), absolutive (patientive), dative, genitive, instrumental, comitative, locative/temporal, and essive. Cases mark the semantic function of a noun only. Syntactic functions are indicated by other means. (see Syntax)
The nominative marks the agent of an active verb or the willing experiencer of an eventive verb. Inanimate nouns cannot have a will and, therefore, cannot be in the nominative.
The absolutive marks the patient of an active verb or the unwilling experiencer of an eventive verb.
The dative marks the indirect object of verbs of giving or transferring. It also marks alienable possessions or qualities, purpose, or something/someone with a vested interest in the action (benefactive). It can also have an allative meaning.
The genitive marks the literal or figurative source of something, and inalienable possessions or qualities (as opposed to the dative). It can also have an ablative meaning.
The instrumental marks the tool or instrument, be it a physical object or figurative concept, used to perform an action or instigate a state. It is also used to introduce an inanimate agent or to make an animate agent non-volitional.
The comitative marks the company an action or event is done with.
The locative/temporal marks the location or time at which an action was done or a state was experienced. With prepositions it marks a referential location or time.
The essive marks a temporary state or being, usually the same as the English "like/as a...".
The genitive, instrumental, comitative, locative/temportal, essive and, in some usages, the dative all change nouns into modifiers.
Paradigms
Singular
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | |
| Nom | déranul | rémadhol | léranal | sénesel | mbênalìle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abs | déranū | rémadhō | léranā | sénesē | mbênalī |
| Dat | déranur | rémadhor | léranar | séneser | mbênalìre |
| Gen | déranòbhō | rémadhòbhō | léranèbhō | sénesèbhō | mbênalìbhō |
| Instr | déranòtye | rémadhòtye | léranètye | sénesètye | mbênalìtye |
| Com | déranum | rémadhom | léranam | sénesem | mbênalim |
| Loc | déranu | rémadho | léranan | sénesen | mbênali |
| Ess | déranuis | rémadhois | léranais | séneseis | mbênalīs |
Paucal
The paucal is not included, as it is identical to the singular except for a prefixed e-.
Plural
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | 5th | |
| Nom | déranuil | rémadhoil | léranail | séneseil | no plural |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abs | déranui | rémadhoi | léranai | sénesei | no plural |
| Dat | déranùire | rémadhòire | léranàire | sénesèire | no plural |
| Gen | déranòibhō | rémadhòibhō | léranèibhō | sénesèibhō | no plural |
| Instr | déranòitye | rémadhòitye | léranèitye | sénesèitye | no plural |
| Com | déranuim | rémadhoim | léranaim | séneseim | no plural |
| Loc | déranui | rémadhoi | léranain | sénesein | no plural |
| Ess | déranīs | rémadhīs | léranīs | sénesīs | no plural |
Even though inanimate nouns cannot be in the nominative, a nominative form is given anyway for the 3rd and 4th declension, for the case of proper nouns.
Pronouns
Pronouns are stand-ins for nouns. Like nouns, they are also marked for case and number. Because of how they’re formed, all pronouns except for the 1st and 2nd person personals, come in pairs—one animate, used for nouns that can be in the nominative, and one inanimate, used for nouns that cannot be in the nominative. There are three types of pronouns: personal, demonstrative, and interrogative.
Personal
Personal pronouns substitute directly for a noun or a name. They come in all three persons. The first and second persons do not differentiate animacy, but the third person pronoun does. There are also both inclusive and exclusive first person plural pronouns, indicating whether or not the person being spoken to is included.
1st Person
| Singular | Plural-Inclusive | Plural-Exclusive | |
| Nom | bhál | bháril | bhálil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Abs | bhâ | bhárī | bhálī |
| Dat | bháre | bhárire | bhálire |
| Gen | bhábhō | bhárbhō | bhálbhō |
| Instr | bhátye | bháritye | bhálitye |
| Com | bhám | bhárim | bhálim |
| Loc | bhá | bhárei | bhálei |
| Ess | bhâis | bhárīs | bhálīs |
2nd Person
| Singular | Plural | |
| Nom | lénal | lénil |
|---|---|---|
| Abs | lénā | lénī |
| Dat | lénare | lénire |
| Gen | lénabhō | lénibhō |
| Instr | lénatye | lénitye |
| Com | lénam | lénim |
| Loc | léna | léni |
| Ess | lénâis | lénīs |
3rd Person
| Animate | Inanimate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singular | Plural | Singular | Plural | |
| Nom | ñgwól | ñgwíl | ||
| Abs | ñgwô | ñgwî | dyê | dyî |
| Dat | ñgwóre | ñgwíre | dyére | dyíre |
| Gen | ñgwóbhō | ñgwíbhō | dyébhō | dyíbhō |
| Instr | ñgwótye | ñgwítye | dyétye | dyítye |
| Com | ñgwóm | ñgwím | dyém | dyím |
| Loc | ñgwó | ñgwí | dyén | dyín |
| Ess | ñgwôis | ñgwīs | dyêis | dyīs |
Demonstrative
Demonstrative pronouns substitute for a specific noun with reference to its proximity to the speaker, be it physical or abstract. They should not be confused with demonstrative modifiers (see below):
Pronoun: I like this.
Modifier: I like this car.
The demonstrative pronouns are the substantive (see Modifiers:Substantives) forms of the demonstrative modifiers dhê, this and dhâ, that. These modifiers are unanalyzable, and inflections described under Modifiers below cannot be applied, with the exceptions of the comparative and superlative. The comparative and superlative are used to emphasize exactly how close or far something is. For instance, the superlative-distal modifier ksēdhâ would mean "that thing, way over there."
Interrogative
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. Similar to the demonstrative pronouns, they are the substantive forms of the interrogative modifier ûtse, which. When used with a noun, the interrogative modifier asks for indication of a specific example of that noun. When used with a verb, it forms a yes or no question, with word order indicating with constituent is being questioned. Like the demonstrative modifiers, the interrogative modifier is also unanalyzable, and cannot be inflected except for the comparative and superlative. Many of the various question words found in most languages are the declined forms of the two pronouns "who" and "which."
| "Who?" | "Which?" | |
|---|---|---|
| Nom | Who? | |
| Abs | Whom? | Which?, What? |
| Dat | For whom? | For what?, Why? |
| Gen | Whose? | Of what? |
| Instr | By whom? | With what?, How? |
| Com | With whom? | (Along) with what? |
| Loc | At whose location? | At what?, Where?, When? |
| Ess | Like whom? | Like what? |
Prepositions
Prepositions are used just about as frequently as in English, with some exceptions. The use of “from” or its temporal equivalent “after” is taken over by the genitive, “to” or “towards” or its temporal equivalent “until” by the dative and “at,” “in,” or “on” by the locative.
Modifiers
Kelanian modifiers include everything in English that would be classified as an adjective, adverb or participle, as well as derived modifiers formed by applying oblique cases to nouns and pronouns.
Adjectives vs. Adverbs
There is no morphological difference between the use of modifiers as adjectives, participles, or adverbs, implying that meaning is entirely dependent on context: when used with a noun it is an adjective or participle, and when used with a verb it is an adverb. In both cases, modifiers precede what they modify. Because modifiers can be used as adjectives, participles or adverbs, they are not marked for case and number to agree with the nouns they modify like in other languages.
Stative and Eventive Modifiers
There originally were two types of modifiers that could be derived from each root, based on some object's or some person's relation to a state of being and whether the state is fixed or changing. Stative modifiers were used to show fixed states, and eventive modifiers were used to show changing states. Furthermore, there were transitive and intransitive versions of each of these categories, indicating whether the state or change of state was being felt by or being caused by the noun being modified.
Stative to Perfect
The stative-eventive and transitive-intransitive distinctions split modifiers into four categories (stative-intransitive, stative-transitive, eventive-intransitive and eventive-transitive) though this four-way split was not maintained for long. By the time of the form of Kelanian being described here, the stative modifiers became viewed simply as the perfect aspect of eventive modifiers. (This has some weird implications. What would normally be considered plain adjectives, such as red or big, are now the perfect form of verbs such as to become red and to become big.)
Voice
The collapse of the stative-eventive distinction, described above, simplified the modifier system to a simple two-way split (ignoring aspect) based on transitivity-the source of Kelanian's two voices: the eventive and the active. The eventive voice is 'intransitive' and, naturally, marks events, i.e. the change in state being described is being felt by the modified noun. The active voice is 'transitive' and, in a similarly obvious fashion, marks actions, i.e. the change in state being described is being caused by the modified noun.
Aspect
The original eventive-intransitive and eventive-transitive modifiers (see above) could have been marked for three aspects: the imperfective, the habitual and the aorist. With the collapse of the stative-intransitive and stative-transitive modifiers, another aspect, the perfect, was created.
The imperfective is used for events or actions that are happening at the time specified. It conveys the meanings of the progressive and simple participles.
The habitual is used for events or actions that happen on a regular basis at the time specified. It conveys the meaning of the relative clause "who/what routinely [verbs]."
The perfect is used for events or actions that are completed, resulting in a state.
The aorist isn't really an aspect, as much as a combination of the perfective aspect and past tense. It conveys the meaning of the relative clause "who/what once [verbed]".
Paradigm
| Eventive | Active | |
| Imperfective | moitséraye | tséraye |
| Habitual | moitséraya | tséraya |
| Perfect¹ | tsêrawe | tatsêrawe |
| Aorist² | mòiatsér- | atsér- |
¹ As can be seen, the perfect is formed quite differently from the other modifiers. There are different markers for the two voices, the root vowel is lengthened, and there is the suffix -we.
² The aorist forms given are the eventive and active stems instead of modifiers. See Verb:Morphology:The Aorist below for more information.
Modifiers from Oblique Nominal Cases
It was said above that applying oblique nominal cases form modifiers from nouns and pronouns. The form given by such derivations does not correspond perfectly to any form described above, and ordinary inflectional affixes cannot be added.
Comparison
Modifiers can be marked for both the comparative and the superlative. (The unmarked form is called the positive.) In the perfect aspect, the comparative and superlative have their normal "more-most" meanings. But in other aspects, the comparative and superlative show increasing degrees of intensity for the action or event, not usually comparable to any construction in English.
The comparative is formed by adding the prefix rā-, and the superlative by adding ksē-.
Substantives
When a modifier is used with one of the third person personal pronouns, it becomes a noun meaning an animate being (with ñgwô) or inanimate object (with dyê) having that trait.
The Copula
The copula is a heavily inflected word used to relate nouns to other nouns or to modifiers. Its most common use is to relate a noun to a modifier to create a verbal phrase. It is inflected for mood and tense.
Mood
There are 6 moods: the indicative, subjunctive, potential, hortative, imperative, and optative. The indicative marks statements that the speaker intends to be understood as true. The subjunctive marks statements that are logically possible and have some probability of being true. The potential marks that the subject has some capability. The hortative marks an insistance that the statement come to be true. It is a "polite imperative" in the second person. The imperative marks an order or command. It is only found in the second person. The optative marks a wish or desire for the statement come to be true.
Tense
There are three tenses: past, present and future. The only one of any real value discussing is the future, since the past and present speak for themselves. The future is used only for things that are certain to be true, and therefore is found only in the indicative.
Paradigm
| Indicative | Subjunctive | Potential | Hortative | Imperative | Optative | |
| Past | énai | éntai | éndai | énau | élnai | |
| Present | éni | énti | éndi | énu | énō | élni |
| Future | énoi |
Verbs
The term "verb" refers to a verbal phrase created with the copula and a predicate modifier. Active verbs are formed with modifiers in the active voice, and eventive verbs from modifiers in the eventive voice. Since a verb is formed from a modifier and the copula, it is marked for voice, aspect, tense and mood. For a full description of each of these, see the so-named sections under Modifiers and The Copula, above. There is also an optional set of pronominal suffixes that agree with the syntactic subject.
Alignment and Core Arguments
Eventive verbs are all perfectly fluid-S, meaning that their subject can be marked as either an agent or a patient (nominative or absolutive) based on its percieved level of control over the change in state. Inanimate objects cannot have this control, so they cannot be put into the nominative in this situation, or ever.
The agent of active verbs are also marked to show volitionality. When the agent is volitonal, it is in the nominative, and the patient is in the absolutive. If the agent isn't volitional, however, it is put into the instrumental. If just one argument is expressed with a transitive verb, then an ambiguous argument can be supplied in translation to fill the spot of the other (i.e. "something" or "someone").
Aspect-Mood Interaction
Aspect and mood have some unpredictable interaction. They are shown here with the active verb "to lift [something]" with a first person agent (if possible).
| Indicative | Subjunctive | Potential | Hortative | Imperative³ | Optative | |
| Imperfective | I am lifting. | I might be lifting. | I can be lifting. | I should be lifting. | Lift! | Would that I be lifting. |
| Habitual | I do lift. | I might lift.¹ | I can lift. | I should lift. | Lift! | Would that I lift. |
| Perfect² | I've lifted. | I might've lifted. | I could've lifted. | I should've lifted. | Be lifted! | Would that I had lifted. |
| Aorist | I lifted. | Maybe I lifted. | I could lift. | I had to lift. | (does not exist) | (does not exist) |
¹ A more accurate translation is "I might be the one who lifts," since the way it is written here implies a future possibility, which is the meaning of the imperfective subjunctive.
² "Have" has been contracted to "'ve" to save space.
³ The two forms of the imperative have different meanings that aren't clear here. The imperfective is an order to do something immediately, while the habitual is an order to acquire a future behavior. The imperative also is only found in the second person.
It might not be clear here, but the potential, hortative and optative are all contrafactual in the perfect. In the aorist, the potential and hortative give no indication of whether they are factual or not, which explains why the optative is not found in the aorist-it is inherently contrafactual.
The Aorist
As mentioned under Modifiers:Aspects, the aorist is a combination of the perfective (not perfect) aspect and past tense. It refers to a past action viewed as a single whole. In English the equivalent form is the simple past, the preterate in Spanish and in ancient Greek a tense of the same name. Unlike the perfect, there are no implied effects on the present when using the aorist.
The aorist is not formed with a modifier and the copula like the other verb forms, meaning that voice and mood are marked differently——aspect and tense are, by nature, fixed. Even though the aorist isn’t formed with aorist modifiers, aorist participles can still be derived, hence its inclusion on the modifier charts. The copula, however, is not used at all in constructing the aorist.
There is more than one way to form it, so the aorist form generally must be learned along with each modifier. To form all the aorist's inflections, including its verbal moods and its modifier, various affixes are added into the aorist stem.
There are 2 ways to form the aorist stem:
The first method, called the strong aorist, was usually, but not exclusively, used for words with an initial cluster. From an imperfective-active modifier, the final -ye is dropped and the characteristic vowel is prefixed and dropped. E.g. tséraye → atsér-
The second method is called the weak aorist. The imperfective-active modifier is taken, the final -ye is dropped, and -ts is added after. E.g. déraye → dérats-
While which method used to form the aorist stem isn’t completely predicatable, the formation of the indicative, subjunctive, potential, hortative and modifier from this stem is highly regular.
| Indicative | Subjunctive | Potential | Hortative | Modifier |
| atsérī | atséron(e) | atsérom(e) | atsérau | atsére |
Verbal Nouns
Each modifier can form two verbal nouns: one from the active voice and another from the eventive voice. They roughly correspond to active and passive infinitives. For the modifier "sending," the active verbal nouns would mean "the act of sending [something]" while the eventive would mean "being sent."
The verbal nouns are formed by taking the perfect form of an active or eventive modifier, dropping the final -we, and adding rī. Verbal nouns belong to the fifth declension.
Gerundive
From each verbal noun, a gerundive may also be formed. The gerundive is a modifier showing that the modified noun is supposed to either perform an action or undergo an event. For the modifier sending," the active gerundive would mean "supposed to send [something]" while the eventive would mean "supposed to be sent" or "for sending."
The gerundive is formed by contracting the dative form of the verbal noun so that the word ends in -rre instead of -rire.
Syntax
Phrase Structure
Phrases are groups of words that funtion as a single constituent. Every phrase has a head, a central word which determines what type of phrase it is. For example, a nouns in core cases are the heads of a nominal phrases and verbs comprised of a modifier and copula are the heads of a verbal phrases. Nouns in oblique cases are the heads of adjectival phrases. The only exception to this rather simple rule is prepositional phrases, which require a noun in the locative as well as a preposition. Prepositional phrases are bounded by the preposition at the beginning and the locative noun at the end.
The rest of the phrase is made of modifiers added onto the head and each other. Phrases are left-branching, meaning that all modifiers, including nouns in oblique cases, are put before the head in order of descriptiveness, with the most descriptive modifier coming directly before the head.
Clause Structure
Word Order
Since the head of each phrase in the language is marked, the order of these phrases could be rather flexibile. But because word order is important in determining syntactic roles, there is a standard word order for the core arguments of verbal phrases—OSV. For intransitive verbs, the one constituent is the subject. For transitive sentences, the subject of transitive verbs is not necessarily shown morphologically (see Subject-Verb Agreement below for the exception). Determining whether the agent or the patient is the subject is the subject is mostly done through syntax. The constituent that is nearer to the verb is the subject, the other is the object.
These rules are almost always followed in prose and speech, with some special exceptions. To topicalize or especially emphasise a word, it may be positioned at the beginning of the sentence. This isn’t very common with verbs. Word order conventions are not followed very strictly in poetry.
Independent Clauses
Active, Passive and Weather Constructions
For intransitive verbs, the single nominal constituent is always the subject, but if it is omitted, the verb becomes a "weather" verb.
For transitive verbs, if the patient is the subject, the verb is the equivalent of a passive. If the agent is the subject, the verb is the equivalent of an active. If either constituent is omitted, then the remaining one is the subject and a general noun like "someone" or "something" is understood to be the second constituent. These are the standard order of all types of sentences, including simple statements, questions, exclamations, etc, as well as sub-clauses.
Copulaic Clauses
The copula can be used to show that a noun belongs to a class defined by another noun, e.g. "He is a king." In these situations, since they are always simple statements of fact, no indication of voice or aspect is needed. The argument referring to class is put into the absolutive, and the other's case is determined the same was as it would be for an eventive verb. In the above example, a king would be in the absolutive, and he could be either nominative or absolutive, depending on whether "he" wants to be a king or not.
To form a sentence with a noun and a predicate adjective, then the perfect-eventive modifier is used with the copula to construct an eventive verb.
Dependent Clauses
Relative Clauses
Since there are no relative pronouns, there are no relative clauses like there are in many languages. The equivalent is formed by treating a would-be relative clause like a long string of adjectives or by using a coordinated clause (see Coordinated Propositions below). The first method is usually used for short relative clauses, where the verb is indicative. If the verb is supposed to be in other moods, the second method must be used.
For example, the sentence "The man, who we saw on TV, is over there," could be formed as something along the lines of "The seen-by-us-on-TV man is over there," or by adding another whole proposition. This second way is roughly equivalent to saying, "The man is over there, seen by us on TV," with "seen" agreeing with "the man," or "The man we saw, over there," with "to be over there" agreeing with "the man".
But in the sentence "The guy, who you might have met before, is coming today" the verb of the relative clause "might have met" has to be in the subjunctive, so it can't be formed by modifiers alone. The correct way to form this would be along the lines of "You might have met the guy before, coming today," with "coming" agreeing with "the guy."
Declarative Clauses
The term "declarative clause", aka indirect statement, refers to an independent clause becoming lowered to a dependent clause, and being used as one of the consituents of a higher clause. In the sentence "you said that he fell," "that he fell" is an example of an indirect statement. It would be formed by saying something along the lines of "you spoke of his falling," using the verbal noun of the verb in the indirect statement as the object of the main clauses' verb. The agent in the indirect statement is put into the genitive if it has will and into the dative if it doesn't have will, the same way the nominative or absolutive can be used for eventive verbs.
Subject-Verb Agreement
As was mentioned above under Verbs, an optional pronominal suffix may be added onto a verb that agrees with the syntactic subject in person, number and case (either nominative or absolutive). So, while word order is the main method used to identify the subject, the agreement of the pronominal suffix with the subject may also be used. This is most common when the OSV word order is broken to topicalize a constituent by moving it to the beginning of the sentence, or when forming coordinated propositions.
Coordinated Propositions
Explicitly marking the subject of a verb is necessary when forming coordinated propositions, where the constituent of the first verb acting as the subject of the second isn't repeated and therefore can't be determined by word order. For example, in the sentence "Étanui déranul déraya-éni, qêñiwe-éni," the agent "déranul" happens to be the subject of the first verb "déraya-eni" because of word order, so the first part of the sentence means The king leads the people. But the subject of the second verb "qêñiwe-eni," to be happy is undeterminable since no suffix is given, so it is unclear whether the king or the people are happy. If there were a nominative, third person, singular suffix, the subject would be the king, and if there were an absolutive, third person, plural suffix, the subject would be the people. If the suffix were something else, it would either not make sense or be referring to another constituent from a previous sentence, perhaps the topic of the conversation.
Scripts
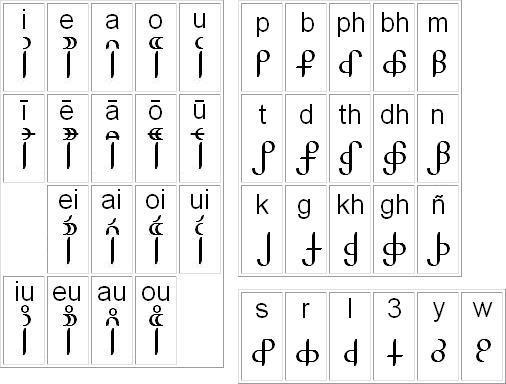
Kelanian can be written with two scripts. The first to develop was a logographic script called Tsêrilī, but it was complex, like the Ancient Egyptian writing system. When the demand for a simpler writing system grew large enough, a phonemic script was developed to be easier to write by hand, called the Êlewe Tsêrilī, or "fast writing". The older script became used mainly for monuments, stone inscriptions, and some holy texts, while the 'fast writing' was used to write just about everything else.
The Êlewe Tsêrilī