Piscean language
Piscean (Piscean: pisceesum) is the official language of the New Piscean Workers' Nation, founded on the manmade island New Pisces - off the coast of western France - that was created in 2028. Despite being the constructed language of Representative S.C. Anderson, Piscean is linguistically derived from Old English and Modern German; however, it is written not with the Latin or runic alphabets, but with the 'pro-Phoenician' Andersonic writing system devised in 2007. (For the purpose of this article, examples of Piscean will be transliterated into the Latin alphabet.)
Articles
The Piscean language includes three 'logical' grammatical genders. While in many languages, the genders do not often relate to physical properties of nouns, they do in Piscean; therefore, most nouns are neuter, while creatures of the male sex are masculine and creatures of female sex are feminine. If one refers to a creature, but does not wish to distinguish sex, the neuter gender can be used as a substitute. Observe the following examples:
- teet Sunne - the sun (no sex, so neuter)
- teet Mann - the person (no sex specified, so neuter)
- se Mann - the man (male, so masculine)
- seo Mann - the woman (female, so feminine)
The above example shows the importance the article plays in Piscean of distinguishing between sexes in a language where one noun fits all.
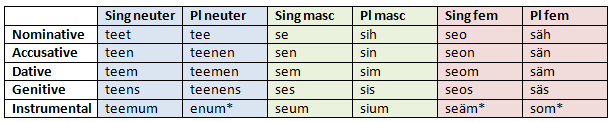
Definite article
The definite article is inflected in various ways, firstly split into three depending on grammatical gender, then into six depending also on quantity - whether singular or plural - and finally into a further thirty depending on grammatical case - whether nominative, accusative, dative, genitive or instrumental.
Those words highlighted with an asterisk follow irregular patterns. 'Enum' is a contraction arising from a rather complex - and now incorrect - 'teemenum'. 'Seäm' is a result of 'seoum', which is difficult for a Piscean speaker to pronounce. The O and U thus collapse into Ä. Similarly, 'som' is contrived, as 'säum' is awkward in speech, giving way instead to a collapse of Ä and U into O.
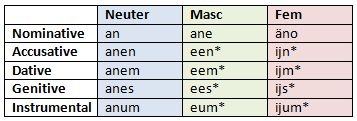
Indefinite article
The indefinite article (in English, 'a/an') is inflected in much the same way as the definite article, but lacking plural forms (which are shown not with an article, merely by inflecting the noun itself).
Those words highlighted with an asterisk follow irregular patterns. 'Een', 'eem', 'ees' and 'eum' are contracted forms of 'aneen', 'aneem', 'anees' and 'aneum', respectively. Regarding the feminine irregularities, 'änoen', 'änoem', 'änoes' and 'änoum' first contracted to 'oen', 'oem', 'oes' and 'oum', but - for even easier pronunciation - the O (and E, where applicable) finally collapsed into the dipthong IJ, which sounds like the English word 'eye'.
Cases and prepositions
Piscean implements five cases: nominative, accusative, dative, genitive and instrumental. Anderson affirms that these have greatly important and stylistic purposes.
Nominative
This case is used for the subject of the sentence (i.e. the noun doing the verb) and as a complement after: 'bean' ('to be'), 'weortan' ('to become') and 'hatan' ('to be called').
Accusative
This case is used for the direct object (i.e. the noun having the verb done to it/them) and after certain prepositions:
- to (for)
- ijmbe (around)
- geond (through)
- ot (until)
- butan (without)
- wider (contrary to)
- on (against)
The accusative case allows for flexible sentence structure that can place emphasis on a certain word by changing its location, yet retaining original meaning. For example:
- Se Hund bit sen Mann - The dog bites the man
- Sen Mann bit se Hund - The dog bites the man
Both of the above Piscean sentences have the same translation into English. On first glance, an English speaker might confuse the second example as 'the man bites the dog', although this is because the object comes before the subject. Because the word 'Mann' is preceded by the accusative article and 'Hund', by the nominative, those skilled in Piscean can easily deduce the sentence's meaning. Meanwhile, the first example places emphasis on the subject, while the second places greater emphasis on the object.
Dative
This case is used for the indirect object (i.e. the noun receiving or being given/sent/lent something); note that in this usage, there is no requirement to translate the word 'to' from English to Piscean:
- Icc geef hit sem Leerere - I give it (to) the teacher
The 'to' is not translated because it is suggested by the dative case ('sem').
When one goes to a place, that place is technically 'receiving' one, so the dative case is used when referring to travel. For example:
- Icc far teem Larenhus - I go to the school; I go to school
Note that proper nouns (that don't take an article) can also be inflected to reflect case:
- Lundenburg - London (nominative)
- Lundenburgen - London (accusative)
- Lundenburgem - London (dative)
- Lundenburges - London (genitive)
- Lundenburgum - London (instrumental)
The action of going to London would involve the dative case:
- Icc far Lundenburgem - I go to London
It is also used after certain prepositions:
- eet (at)
- ut (outside)
- fram (from)
- ofer (about)
- eefter (after/according to)
- ongean (opposite)
- sittan (since)
- butan (except)
- mid (with)
Genitive
This case is used to denote possession or ownership. 'The man's car' translates literally as 'the car of the man', but without any word for 'of'.
- Teet Wagen ses Mann - the man's car (the car of the man)
To put proper nouns into the genitive case: if the noun ends in a consonant, add 'es'; if the nound ends in a vowel or Y, add 's'. For example:
- Teet Rum Seanes - Sean's room (the room of Sean)
- Teet Deejweorc Gaynores - Gaynor's job (the job of Gaynor)
Instrumental
The first use of the instrumental case is to replace words such as 'with' and 'by' in English in the context that they mean 'by means of' - in other words, to indicate that the noun in question is an 'instrument'. Usually, the instrumental case is not used with an article, unless for emphasis; therefore, the noun itself must be inflected. Despite the rule in Piscean that all nouns begin with a capital letter, when in the instrumental case, this capital is dropped. If a noun ends in a consonant, one must add 'um' to make it instrumental; if a noun ends in a vowel, one must add 'num'.
- Teet Bän - the train
- Icc far bänum - I go (by) train
- Teet Culi - the pen
- Icc writ culinum - I write (with a) pen
The second use of the instrumental case is to denote belonging, belief or status. When the noun is inflected, it can become similar to an adjective:
- Englaland - England
- Icc bee englalandum - I am English
- Icc sprec englalandum - I speak English
- Commjunizmäs - communism
- Icc bee commjunizmäsum - I am communist