Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
..... Seven generic nouns
..
There are seven generic nouns in béu. Actually there meaning is so general that they don't have that much meaning content. For example if you hear nèn "thing" ... you know what is being referred to doesn't belong to one of the other six generic categories, but that is about all that nèn tells you.
Note that the first two have an irregular ergative ... nòs and mìs.
..
| nèn, nòs | thing |
| mìn, mìs | person |
| làu | amount |
| kài | kind, type |
| dà | place |
| kyù | time, occasion |
| sài | reason |
..
Because the above are so lacking in information content that they are frequently used for unknowns. For example ... you have a situation (a clause) but one component of that situation is either unknown* or is awkward to express for some reason. When used in this fashion, the generic noun is always fronted.
SOME EXAMPLES
Now there are two interesting particles in béu ... ?ó and kò. The latter is used for requesting a material thing, the former for requesting information. So ...
?ó = "tell me"
kò = "give me"
Only used for first person singular and the here and now. For anything other than the first person singular and the here and now, the suppletion forms XXXX and YYYY are used.
It can be seen that ?ó plus one of the "algebraic" clauses I talked about above, are questions.
EXAMPLE, EXAMPLE, EXAMPLE
In fact there is an altenative set of question forms.
..
| ?ó nèn, ?ó nòs | what | nén, nós |
| ?ó mìn, ?ó mìs | who | mín, mís |
| ?ó làu | how much | láu |
| ?ó kài | what kind of | kái |
| ?ó dà | where | dá |
| ?ó kyù | when | kyú |
| ?ó sài | why | sái |
..
The two forms are in complementary distribution. The longer form tends to be used if the question is a new topic of conversation. The shorter version tends to be used when the question is part of an established conversation. But if you mix this up, nobody feels you are murdering the language. The longer form is also used anytime you want to give the question more emphasis.
..
Mention YES/NO questions !!!
These 7 particles do not take nài to form a relative clause. That is why I classify them as particles as opposed to normal nouns.
EXAMPLE
..
* A bit like in Algebra. Maybe you first come across "x" in an equation such as "2(x+3)=10". I posit this equation is an analogy of the situation (clause) I referred to above. Where one component is unknown. Initially it is necessary to refer to the unknown by using the other elements in the clause. ( Perhaps) later the unknown can be identified uniquely.
..
..... Questions questions
..
English is quite typical of languages in general and has 8 question words ... "which", "what", "who", "whose", "where", "when", "how" and "why". *
..
..
If you hear any of these words you know you are being solicited for some information. These words have no other function apart from asking questions.
..
Notice that there is no word for "how" or "why" in the above table. These are expressed by wé nái and nenji** respectively.
On the other hand, béu has single words where English has "how much" and "what kind of".
..
The first two have dual forms ... nén and mín are the absolutive forms and nós and mís are the ergative forms.
..
Now ʔai? always comes utterance final ... ʔala always comes between two NP's. This leaves 7 QW's. Of these nén mín dá and kyú are fronted***. láu is sometimes fronted.
And láu kái dá and nái **** are found in their respective slots within a NP ... 
Note that when questioning who owns something yó mín occurs within the NP ... this is a sort of secondary usuage of mín and is not considered here.
Also note that dá can be either fronted or within a NP. When fronted it asked where the action takes place. When within a NP it asks about the NP's location. For example ...
..
| jene-s | halma | dá | hump-o-r-u |
|---|---|---|---|
| Jane- ERG | apple | where | eat-3SG-IND-FUT |
=> where is the apple that Jane will eat
A suitable answer to the above is pazbala "on the table"
| dá | jene-s | halma | hump-o-r-u |
|---|---|---|---|
| where | Jane- ERG | apple | eat-3SG-IND-FUT |
=> where will Jane eat the apple
A suitable answer to the above is pazba?e "at the table"
láu is an interesting QW. When you expect an integer answer between 1 and 1727 ... "láu senko" are fronted. Otherwise "senko láu", "olus láu" or "saidau láu" are in situ.
[Note to self : I need some examples of the above]
..
Statement .... bàus glán nori alha = the man gave the woman flowers
Question 1 .... mís glán nori alha = who gave the woman flowers ?
Question 2 .... minin bàus nori alha = the man gave flowers to who ?
Question 3 .... nén bàus glán nori = what did the man give the woman ?
Question 4 ... bàus glán nori láu alha = How many flowers did the man gave the woman ?
Question 5 ... bàus glán nori alha kái = What kind of flowers did the man give the woman ?
Question 6 ... dá bàus glán nori alha = Where did the man give the woman flowers ?
Question 7 ... kyú bàus glán nori alha = When did the man give the woman flowers ?
Question 8 ... í glá nái bàus nori alha = to which woman did the man gave the flowers ?
Question 9 .... há bàu nái glán nori alha = which man gave the woman flowers ?
Question 10 .... bàus glán nori alha ʔala cokolate = Did the man gave the woman flowers or chocolate ?
Question 11 ... ʔír doika ʔala jaŋka = Do you want to walk or run
Question 12 .... bàus glán nori alha ʔai? = Did the man gave the woman flowers ?
Question 13 ... minji bàus glán nori alha = Why did the man give the woman flowers ?
..
*Note ... there was also a "whom" until quite recently. Also some people count "whose" as a separate QW ... however it shouldn't be ... it is just "who" + "z" (the genitive clitic).
**Well nenji is the normal traslation of "why". In certain situations you might hear minji ... when it is knows that an action/state is for somebody's benefit and no other reason is applicable.
***Around one third of the world's languages front a question word. English is one of them. [ see http://wals.info/feature/93A#2/25.5/151.2 ]
****Actually these 4 words often stand alone. But when they do, they are still considered within a NP ... only that the rest of the NP has been dropped.
..
In the table of question words above I have marked the top two and the bottom two off. The top two because they are the QW's par excellence ... they are used more than the other QW's. The bottem two because their answers are restricted to two items. ?a is restricted to "yes" or "no" ... ?ala to one of the NP's that sandwich it.
láu kái dá kyú and nái each have low tone equivalents. These particles are important grammatical words in their own right and they each are related to their high tone equivalent in subtle ways. Basically làu introduces the "partitive construction" , kài means "like" or "similar", dà introduces an adverbial phrase of location, kyù introduces an adverbial phrase of time, and, nài is a "relativizor".
..
..... Why oh why
..
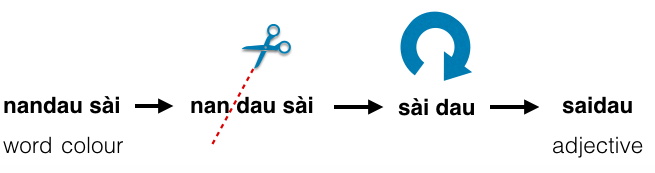
"Why" is nenji in béu. Obviously derived from nén and the jì (the pilamo). "Why" is asking for what reason an event/state came about. The answer to nenji can by said to comform to one of the four scenario's shown below.
..
..
gərfi and ngò are followed by a clause. là cì and jì are followed by a noun (usually a persons name).
..
gərfi is used when the questioned event/state was caused by an event/state in the past. That is the questioned event/state is a consequence of an event/state in the past.
ngò is used when the questioned event/state exists to facility some event/state that is envisaged in the future.
là cì is used when the person following là cì (or at least a some supporter/collaborator of hs/her) has requested the questioned event/state at a previous time. cì = matter/affair
jì is used when the subject of the questioned event decided to do something for the benefit of the person following jì. The subject is the initiator of the action in this case. The benefits of the action are likely to materialize at a future time.
..
..
..... The conditional sentence
..
Conditional sentences are for making plans, for considering contingencies.
In English ... "if you go, they will kill you" ... two clauses ... the first introduced by "if" .... "if (A), (B)".
Sometimes "then" can introduce the second clause [ "if (A), then (B)"] but this is not considered essential in English. However some natlangs require a particle in front of the second clause. In Chinese the particle 就 jiù is needed.
..
kyù jiru / gì dainuru => "when you go, they will kill you"
| kyù | j-i-r-u | / | gì | dain-u-r-u |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| when | go-2SG-IND-FUT | "pause" | you | kill-3PL-IND-FUT |
..
tà jiryu / gì dainuryu => "if you go, they will kill you"
| tà | j-i-ry-u | / | gì | dain-u-ry-u |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| if | go-2SG-CON-FUT | "pause" | you | kill-3PL-IND-CON-FUT |
..
dà jiryu / gì dainuryu => "if you would go, they would kill you"
| dà | j-i-ry-u | / | gì | dain-u-ry-u |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| if | go-2SG-CON-FUT | "pause" | you | kill-3PL-CON-FUT |
Note ... dà jiru is a place ... "where you will go"
..
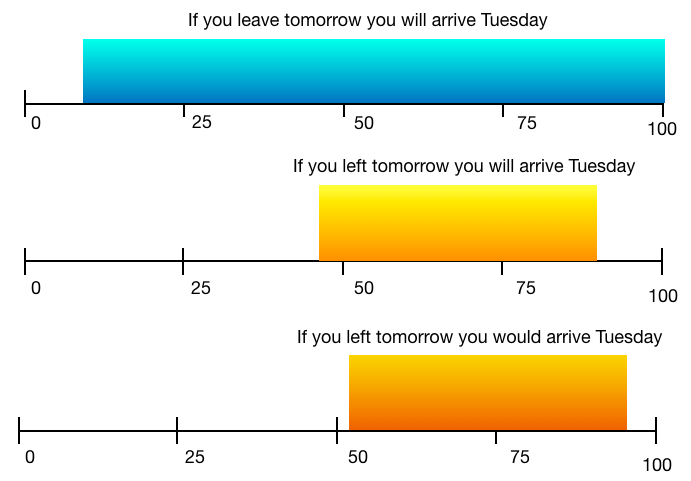
You will see that béu has a nice symmetrical system when it comes to counterfactuality.
This is different from English, which has quite a lopsided system ...
The blue reflects a plain "if" conditional. The 15% to the left would be expressed with "when" rather than "if".
Now the plain "if" conditional can be used in situations with wildly different truth values.
However if you want to be more specific as to truth value, you would use one of the orange constructions above. These constructions are a bit messy ... past tense => counterfactual : pluperfect => past tense + counterfactual. Plus none of the above represent 100% counterfactuality. If one of the orange constructions above represented 100% counterfactuality, then a tag such as "but you won't leave tomorrow" would be ungrmmatical. So the English system is a mess (although naturalistic).
..
Note ... In béu the sequence yi is not allowed. And while the sequence ye is allowed it never occurs in the conditional marker. So how does béu express a conditional sentence in which one or both clauses is set in the past. Well you must use ryo plus an adverb. An adverb such as "this morning", "yesterday", "in the past", etc. etc.
Oh ... and one final thing. In béu (as in English) the consequent can precede the antecedent. This is a bit unusual. Joseph Greenberg’s Universal 14 says … “In conditional statements, the conditional clause precedes the conclusion as the normal order in all languages.” (Greenberg 1966: 84; Greenberg 1990: 49) Greenberg states that “the antecedent almost invariably precedes the consequent in the unmarked, or only permissible case …. " I believe the following languages are strictly antecedent first … Turkish, Mongolian, Tamil, Korean, Chinese, Japanese
EXTRA ... Because of the distribution of "if" + "past tense" (its range quite far towards the LHS), it is possible to cancel* "if" + "past tense" conditional sentence. For example "If you had enough money, you could visit Australia", could be cancelled by adding "... well you have enough money, you can visit Australia". This sort of cancellation can not be used with "da" [the LHS of "da" would have to spread a lot further to the RHS to make it cancelable].
..
..... Six important particles
..
Namely làu jía kài "wé nài" ?ài and ?aibis
..
wé and nài are particles in their own right but the combination "wé nài" is more than the sum of its parts (or perhaps "is more than the product of its parts" is more appropriate). Hence "wé nài" should be considered a separate particle made up of two words.
..
... làu
..
There are 3 main uses for làu
..
1] The first use is when we are using the extended number set. làu stands between the noun (senko or olus) and the extended number ...
..
3,05112 elephants => sadu làu uba wú odaija
| sadu | làu | uba | wú | odaija |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| elephant | "partitive particle" | 3 | 123 | 51 |
..
Note ... the singular form of senko always used when quantity is given by this method.
We have already touched on this in the previous chapter [ see the section Numbers ... (the extended set) ].
I call làu a partitive particle when it is doing this function.
To the left of làu, the noun always has a generic meaning hence in this position it would never take the kai prefix. [ cf. sadu = elephant : kaizadu = elephant-kind, "the elephant as a species" ]
So *kaisadu làu uba wú odaija is illegal.
This construction is often seen with "magnifier" duplication ...
sadu làu wú wú = thousands of elephants : sadu làu nàin nàin = millions of elephants : sadu làu hungu hungu = billions of elephants
When specifying an amount of an olus, làu is use with any number, not just an extended number ...
..
Two cups of hot milk => ʔazwo pona làu hói hoŋko
| ?azwo | pona | làu | hói | hoŋko |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| milk | hot | "partitive particle" | 2 | cup |
..
Two baskets of peaches => pice làu hói kapu
| pice | làu | hói | kapu |
|---|---|---|---|
| peaches | "partitive particle" | 2 | basket |
..
pice is in fact olus. A single peach would be picai. By the way, if the basket was more pertinent than the peaches you could say ... kapu picia <= kapu pic-ia <= "basket peaches-having"
..
2] I also call làu a partitive particle when it is doing its second function ...
..
Three of these doctors => moltai.a dí làu léu
| moltai.a | dí | làu | léu |
|---|---|---|---|
| doctors | this | "partitive particle" | 3 |
..
Note ... the plural form of senko is always used for this construction.
..
Two cups of this hot milk => ʔazwo pona dí làu hói hoŋko
| ?azwo | pona | dí | làu | hói | hoŋko |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| milk | hot | this | "partitive particle" | 2 | cup |
..
Of course, for an olus there is no plural form.
This second function of làu is when we are taking a portion from a larger amount. The first function of làu is when we are taking a portion of X out of the sum total of all the X in the universe.
For the olus, there is not so much difference between function 1) and function 2).
..
3] I call làu a quantitative particle when it is doing this function. Here is a typical example of làu functioning as a quantitative particle ...
..
tomo r jutu làu jono => "Thomas is as big as John"
..
The construction is ... "copula adjective làu noun" as opposed to English "AS adjective AS noun"
In the negative it is ... "bù copula adjective làu noun" as opposed to English "not SO adjective AS noun" ... (By the way ..." not AS adjective AS noun" is also valid in English)
..
In béu the final noun can be replaced by a clause introduced by gò. For example ...
Thomas is so clever that he doesn't have to go to school => tomo r jini làu gò bù byór jò banhain
| tomo | r | jini | làu | gò | bù | by-ó-r | jò | banhai-n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| thomas | is | clever | "equalitative particle" | that | not | have-3SG-IND | go | school-DAT |
..
Now as copula + adjective is more or less equivalent to "verb" so the following is included here ...
Thomas thinks as fast as John => tomo wòr saco làu jono
as the same construction type.
..
We have talked about what I call the quantitative particle above. This is used when two nouns, verb to the same degree. But how you describe a situation when we have "more" or "less" degree ?
I think this is a suitable time to go into this.
Taking the last example, we get ...
Thomas thinks faster than John => tomo wòr yú sacois jonowo
with more degree.
Notice the lack of làu, the adverbial suffix -is and the suffix -wo on the noun.
For less degree we have ...
Thomas thinks not so fast than John => tomo wòr wì sacois jonowo
..
And for the copula adjective constructions with "more" or "less" degree. This paradigm is shown below ...
..
Question ... tomo r jutu láu => "how big is Thomas ?"
Answer[A] .... tomo r jutu làu jono => "Thomas is as big as John"
Answer[B] .... tomo r wì jutu jonowo => "Thomas is less big than John"
Answer[C] .... tomo r yú jutu jonowo => "Thomas is bigger than John"
Answer[D] .... tomo bù r jutu làu jono => "Thomas is not as big as John"
Notice that D, invariably in English, makes Thomas smaller than John. Not so in béu. A B and C tend to be used a lot more than D.
[Note to self : get rid of -ge ? .... use it only in NP ? an alternative to C ? ]
Two more examples ... just for fun.
| jono-s | huz-o-r | làu | kulno |
|---|---|---|---|
| john-ERG | smoke-3SG-IND | like | chimney |
=> John smokes like a chimney
..
| taud-o-r-a | làu | hunwu | huakod-ia |
|---|---|---|---|
| to be annoyed-3SG-IND-PRES | like/as | bear | headache-having |
=> he/she is annoyed like a bear with a sore head
..
... jía
..
jía has two functions.
..
Also it has two shorthand forms ... the only word in the language to be so honoured. The leftmost word is never used. The => character used for the second function. The remaining character used for the first function.
..
1) In most languages you can drop certain components if they are obvious from context. And when you do the remaining utterance stays unchanged. However béu does not work like that*. We saw in the previous section that the particles used to show cause/reason are different, depending upon whether they are followed by a simple noun or by a clause. The same happens when we are making a statement by way of comparison. For example ...
..
Thomas thinks as fast as John => tomo wòr saco làu jono
Now obviously "John thinks" is underlying here. However if you want to make "John thinks" overt you must change làu to jía ...
Thomas thinks as fast as John thinks => tomo wòr saco jía jono wòr
Notice that English patterns the same way for both the above examples.
..
2) In English we have the verb "to equal" ... it bit of a strange verb. Almost exclusively found in a mathematical setting. (The adjective "equal" has the same form as the verb "to equal" .. but anyway ... )
The béu particle jía is used in most situations where we find the English verb "to equal". In a setting such as 2+3=5 ... well there are no need for tense or aspect ... we are talking about a timeless truth. Also no need for person affixes ... the elements (arguments) involved are always stated the the left and the right of jía. Also no need for evidential markers ... the world of béu considers evidentials as appropriate for the human world ... but the world of mathematics is so far beyond the human world ... to have evidentials on a mathematical expression would be to drag the matheverse down into the dirt. Hence jía is an invarient particle. By the way jiagan = "equation".
..
* Now why have I set things up like this ... well in béu it is quite easy to define a clause. A clause is a chunk that contains one active verb (active verb = a verb having an "r" ). I guess I have set things up like this, so as to firmly draw a line between one clause constructions and two clause construction.
[ Note to self : why DO you want it like this ?]
..
... kài and wé nài
..
There are 6 main uses for kài.
..
1] In this first function it is equivalent to "like" or "similar to" in English.
..
| jono | r | kài | dada | ò |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| john | is | like | older brother | his |
=> John is like his older brother
..
2] Sometimes kài can best be translated as "made of" ...
a/the wooden house => tìa kài wuda
the house is made of wood => tìa r kài wuda
..
3] Sometimes kài can best be translated as "for" ...
water for drinking => moze kài solbe
water for washing clothes => moze kài laudo
this water is for washing clothing => moze dí r kài laudo
(in the above three examples, kài and what follows it can be considerd an adjective)
..
4) In the fifth function kài actually merges with a following senko ...
elephant = sadu
elephant-kind = kaizadu
this is actually a noun, the idea being something like "that which is like an elephant"
[ Note ... it is interesting that the béu word for "species" is kaija. Probably from " kài aja ", aja being an obsolete word for "one". ]
..
5) In its sixth function kài actually merges with a following saidau ...
red = hìa
reddish = kaihia
..
6) And the sixth function ...
..
| gì | r | gombuʒi | kài | jono |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| you | are | argumentative | like | John |
=> you are argumentative like John .............................. i.e. in the same manner ... for example ... shouting over other people when they try and put forward their arguments
..
This only is applicable to "complicated "adjectives ... adjectives that like have internal structure. I find it difficult to imagine a situation where this construction would be suitable for an adjective like "short".
I see "short" as a one dimensional adjective while I see gombuʒi as a multifaceted adjective.
You are treating gombuʒi ss one dimensional when you say ...
..
| gì | r | gombuʒi | làu | jono |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| you | are | argumentative | like | John |
=> you are as argumentative like John ...........................i.e. to the same degree
..
In the above to examples, I would call kài a "qualitative particle", and I would call làu a "quantitative particle".
..
Now as "copula + adjective" is more or less equivalent to "verb" so the following is included here ...
..
| jono-s | klud-o-r | kài | tomo |
|---|---|---|---|
| john-ERG | writes-3SG-IND | like/as | thomas |
=> John writes like Thomas writes
..
In most languages you can drop certain components if they are obvious from context. And when you do the remaining utterance stays unchanged. However béu does not work like that. We saw in the previous section that the particles used to show amount by way of comparison are different, depending upon whether they are followed by a simple noun or by a clause. The same happens when we are making a statement about manner by way of comparison. For example ...
..
Now in the above example, it is obvious that "thomas writes" but "writes" has been dropped. If we want to make this "writes" covert we must change the particle.
..
| jono-s | klud-o-r | wé nài | tomo-s | klud-o-r |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| john-ERG | writes-3SG-IND | "in the manner that" | thomas | writes-3SG-IND |
=> John writes like Thomas writes
Note ... when the final verb is dropped, the ergative marking on tomo is also dropped.
..
làu and kài sometimes gets mixed up. For example in the following example kài might actually get used more often than làu. While làu might be correct "logically", kài is more felicitous for savouring the rich imagery of "a fish out of water".
Perhaps if béu was a spoken language kài might take over from làu in many situations.
..
| bù | ?oim-o-r-a | làu | sainyi | moz-ua |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| not | to be happy-3SG-IND-PRES | like/as | fish | water-lacking |
=> he/she is unhappy like a fish out of water
..
This chart below might be of interest ...
..
..
It shows how three question words correspond to three low tone particles.
..
..
One more example ... just for fun.
| tomo-s | futuba | lent-o-r | kài | yuzebi.o |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| thomas-ERG | football | play-3SG-IND | like | Eusabio |
=> Thomas plays football like Eusabio ............................................................ i.e. attacking the goal directly, strong on the ball with a powerful shot
..
... ?ài and aibis
..
These are mention here because they overlap with the first function of kài
These particles plus the noun (or NP) they qualifies are equivalent to adjectives.
?ài is derived from ?à "one". There are quite a number of adjectives derived from nouns by the suffixing of -i ... (the meanings of these derived adjectives are often on the quirky side).
[ Note ... the English word "same" < P.I.E. "sem" meaning "one" ]
?aibis is formed from ?ài plus the suffix -bis meaning "tending to".
?ài and ?aibis overlap in meaning with kài when in the first of its six functions.
We can say ... kài = "like"/"similar to" : ?ài = "identical to"/"the same as" : ?aibis = "a bit like"/"similar to"
You use ?ài or ?aibis if you want to specify the amout of similarity, use kài if you want to leave this vague.
Other related words/expressions are ... ?aiko = to equalize : sàu ?ài = to be equal : mwe?ai = to equate, to consider equal : bù ʔài = "different" : sàu bù ?ài = "to differ"/"to be different" ?aiti = similarity (one feature) : kuwai ?ài = similarity (in general) : u?aiti = difference (one feature) : kuwai u?ai = difference (in general)
..
Examples of ?ài usage ...
..
1) jono lé jene sùr ʔài (bèn) = "John and Jane are the same" ... logically the bèn is unnecessary, but it is often included for euphony .... (bèn is used about 97% of the time in this construction)
2) jono r ʔài jene = "John is the same as Jane"
The above two examples are ambiguous as to whether John and Jane are the same w.r.t. one characteristic or the same w.r.t. all characteristic. It should be known from context. If not you can disambiguate by ...
A) jono r ʔài jene jutuwo = "John is the same size as Jane"
B) jono r ʔài jene uwe = "John is the same as Jane in every way"
C) jono lé jene sùr ʔài (bèn) jutuwo = "John and Jane are the same size" .... (bèn is used about 50% of the time in this construction)
D) jono lé jene sùr ʔài (bèn) uwe = "John and Jane are the same in every way" .... (bèn is used about 50% of the time in this construction)
..
Note that (A) can also be expressed as jono r jutu làu jene ... see the third fuction of làu.
For comparison of ability to do something ...
jono r bòi làu jene kludauwo = "John is as good at writing as Jane"
[Note to self : sort out ... how to say "a similarity" ? ... "a difference" ? ]
[Note to self : sort out ... ʔài dù = exactly the same ? ... ʔaimai = similarity ... lomai = difference ]
..
... Stuff to sort
..
Usually for particles that can either be followed by a NP or a clause, I add gò after the particle when a clause follows. This is to prevent errors in comprehention. For example jì means "for" and is followed by a NP (usually a person). I have jì gò meaning "in order that" ... jì gò being followed by a clause. In béu the first word of a clause is often a noun. If I had jì meaning "in order that" there might be misunderstanding (albeit temporary). English does this also in many constructions [ I should go into this more fully ??? ]. Of course I could have a totally different particle for "in order that" but I wanted to emphasis the semantic overlap between these to constructions.
There are 4 nouns that are associated with 4 of these above question word / indefinite pairs. làus = amount, quantity : kàin = kind, sort, type : dàs = place : kyùs accasion, time.
These 4 nouns are never followed by nài. The table below is interesting. It shows the logical equivalence of a hypothetical expession (on the LHS) and the logical equivalent actually used (on the RHS).
..
*làus nài => làu
*kàin nài => kài
*dàs nài => dà
*kyùs nài => kyù
..
There are two adjectives associated with these question word / particle pairs. laubo meaning "enough" and kaibo meaning "suitable".
Also there are two nouns associated with these question word / particle pairs. lauja meaning "level" and kaija meaning "species/model".
..
nù r jutu làu sadu = "they're as big as an elephant" (talking about elephants in general) : nù r jutu làu sadu dí = "they're as big as the elephant"
..
Good, Better, Best
..
| >>> | boimo | best |
| > | boige | better |
| = | làu bòi | as good |
| < | boizo | less good |
| <<< | boizmo | least good |
..
The top and the bottom items are the superlative degree and so have no "standard of comparison".
The fourth one down is used less frequently than the second one down. This is because its sentiment is sometimes expressed by negating the third one down. For example ...
gì bù r làu bòi pawo = "you're not as good as me" can be used instead of gì r boizo pawo "you are less good than me"
[ actually gì r boizo pawo would be the normal way to express this sentiment. But gì bù r làu bòi pawo would be used, for example, as a retort to "I'm as good as you" ]
The superlative forms are found as nouns more often than as adjectives. That is boimo and boizmo are rarer than boimos and boizmos. (see table below)
..
boimos = the best : bàu boimo = the best man
boizmos = the least good : bàu boizmo = the least good man
..
..... Three important particles
..
... dà
..
dà = where
pà twahu dà yildos twaire = meet me where we met in the morning ........................ dà yildos twaire can be considered an adverb of place.
..
... kyù
..
kyù = when
toili gìn naru kyù twairu = I will give you the book when we meet ............................ kyù twairu can be considered an adverb of time.
..
... nài
..
In English "who", "that" and "which" are relativizors ... a particle that introduced a relative clause. For example ...
"The man who ate the chicken"
"The chicken that was eaten"
"The knife and fork which were used to eat the chicken"
..
In béu there is only one relativizer, which is nài. For example ...
glá nài bàu timpori = "The woman who the man hit"
Now ... in the above ... glá is being modified by nài bàu timpori. nài bàu timpori implies a clause bàu timpori glà.
To construct a relative clause for glá, nài is inserted between the noun and clause, and the noun is dropped from the clause.
Now in the above example ... the roll of glá in the clause is absolutive (i.e. glá is unmarked). However if the roll of the noun ... in the clause ... is one defined by one of the 17 pilamo, this pilamo must be suffixed to nài. For example ...
..
pi ... the basket naipi the cat shat was cleaned by John.
la ... the chair naila you are sitting was built by my grandfather.
... mau / goi / ce / dua / bene / komo ...
tu ... báu naitu ò is going to market is her husband = the man with which she is going to town is her husband ... kli.o naitu he severed the branch is rusty
ji ... The old woman naiji I deliver the newspaper, has died.
-s ... báu nàis timpori glá_rò jutu sowe = The man that hit the woman is very big.
wo ... The boy naiwo they are all talking, has gone to New Zealand.
-n ... the woman nàin I told the secret, took it to her grave.
fi ... the town naifi she has come is the biggest south of the mountain.
?e ... tìa naiʔe she lives is the biggest in town = the house in which she lives is the biggest in town
-lya ... the boat nailya she has just entered is unsound
-lfe ... the lilly pad nailfe the frog jumped was the biggest in the pond ... (note to self : improve this, work out translation for all these concepts)
..
If the roll of the noun (in the clause) is one not specificated by the 17 pilamo then the noun can not be dropped entirely, it must be represented by a pronoun. For example ...
| gwài | nài | polg-u-r-a | ala | ʃì |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| the islands | REL | sail-1PL-IND-PRES | between | them |
Literally "the islands that we are sailing between them" ... or ... in good English ... "the islands that we are sailing between"
[Note to self : or maybe bain should mean "between"]
| gawa | nài | toti-s | lent-o-r-e | tài | nù |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| the women | REL | children-ERG | play-3SG-IND-PAST | in front of | them |
Literally "the women that the children played in front of them" ... or ... in good English ... "the women that the children played in front of"
..
| há | gawa | nài | toto-s | lent-o-r-e | tài | nù | waudo | dainuru |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERG | the women | REL | children-ERG | play-3SG-IND-PAST | in front of | them | dog | kill-3PL-IND-FUT |
Literally "the women that the children played in front of them, will kill the dog" ... or ... in good English ... "the women that the children played in front of will kill the dog"
..
In English we have what is called a headless relative clause. béu has this also ...
nài mwair rò nài mair = "what you see is what you get"
nàis mwor rò nàis mair = "that which sees is that which gets"
ò nàis mwor rò ò nàis mor = 'he that sees is he that gets" ... [this one not headless of course ... a pronoun has been added to narrow down what exactly we are talking about]
..
..
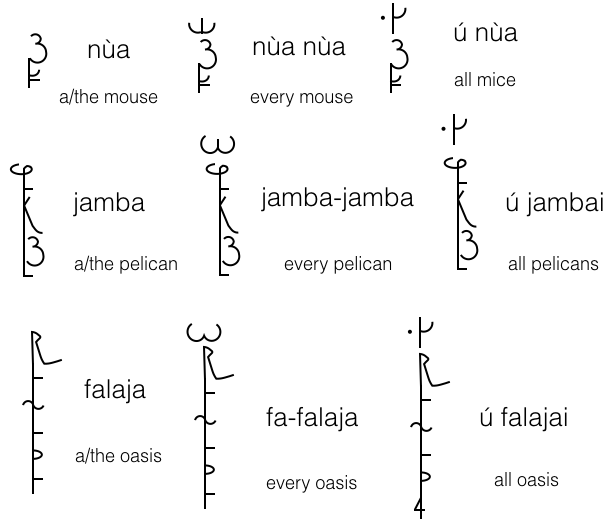
..... Totality ... collectively or individually
..
Sometimes we want to talk about all members of the category "noun" acting (or being acted upon) COLLECTIVELY.
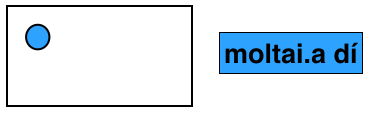
For this we use the particle ú before the plural of the noun. For example ...
moltai = a/the doctor
moltai.a = doctors
ú moltai = all doctors
Note ... the same word, when appended to a noun, means "the whole" or "entire". For example ...
goize ú = all morning
..
The opposite of the above is when all members of the category "noun" is acting (or is being acted upon) INDIVIDUALLY.
By doubling the noun (or the first part of a noun) you give what can be called a distributive meaning.
Some examples ...
nùa = a/the mouse
nùa nùa = every mouse
jamba = a/the pelican
jamba jamba = each pelican
falaja = oasis
fa-falaja = every oasis
Notice that for words over two syllables, only the initial consonant and following vowel/diphthong is prefixed.
..
..
The "word-hood" of these duplications is murky. When the word in its entirety is dublicated, they are written as to seperate words. When a word is only partially duplicated I write it as a hyphenated word. In the béu script a special symbol is used to indicate duplication.
Single syllable words retain their tone when duplicated ... which indicates two separate words. However you also get phonological processes that are usually only word internal. That is to say, these structures show some "sandhi".
For example ...
yildos yildos (every storehouse) would be pronounced / yildoʃ yildos /. If this was two seperate words it would be pronounced / yildos yildos /. If this was one word it would be pronounced / yildoʒyildos /
bàu bàu can be pronounced bàu vàu ... [ If you remember ( Chapter 1.1) b and v are in free variation ]
là bàu bàu = "on every man" .... indicates that bàu bàu is multi-word as the pilamo is in its stand alone form.
fa-falaja?e = "at every oasis" .... indicates that fa-falaja is a single word as the pilamo is appended.
Anyway ... these constructions are never written out in full. Instead a special symbol is placed above the simple noun. This symbol can vary a bit, depending on the font being used : it can vary from a lower half circle bisected by a vertical stroke to a shape that looks a bit like the Arabic shaddah.
For example ...
..
It some contexts, semantically, it does not matter whether the individual or the collective form is used. When this is the case, the default choice is "individual" structure. ú tends to be used with tangible nouns more, it is hardly ever used with nouns denoting periods of time.
Note (as in English) the plural verb form is used for the collective structure, the singular verb form for the individual structure. For example ...
ú bàu súr = all men are
bàu bàu sór = every man is
NOTE TO MYSELF
Every language has a word corresponding to "every" (or "each", same same) and a word corresponding to "all". "all" emphasises the unity of the action (especially when the NP is S or A) while "every" emphasises the separateness of the actions. Now it is not always necessary to make this distinction (perhaps in most cases). It seems to me, that in that case, English uses "every" as the default case (the Scandinavian languages use "all" as the default ??? ). In béu the default is "all" ù.
The meaning of this word (in English anyway) seems particularly prone to picking up other elements (for the sake of emphasis) with a corresponding lost of power for the basic word when it occurs alone. (From Etymonline EVERY = early 13c., contraction of Old English æfre ælc "each of a group," literally "ever each" (Chaucer's everich), from each with ever added for emphasis. The word still is felt to want emphasis; as in Modern English every last ..., every single ..., etc.)----
TO THINK ABOUT
?à ?à bàu hù ?ís = any man that you want ( ?ís ... "you would want" ???? )
?ài ?ài bàu hù ?ís = any men that you want
?ài bàu = some men
..
..... And for a verb ... many many iterations
..
As duplication has (a very iconic) function with nouns, it has also a function with verbs (and very iconic too ... if I may say so)
..
| jò | to go | jojo | to scatter, emit |
| té | to come | tete | to gather, collect |
| pyá | to stop off | pyapya | to stutter (person or engine) |
| dàu | to die | daudau | to fade away |
| nda | to put | ndanda | to dump |
| mài | get, receive | maimai | to rely on |
| náu | give | naunau | to support |
| pila | to put | pipila | to arrange |
| timpa | to hit | titimpa | to beat |
| yáu | to have | yauyau | to have in abundance |
| ?ái | to want | ?ai?ai | to be greedy |
| lí | to press | lili | to crowd, to throng |
| tí | to touch | titi | to fondle, to caress |
| jwòi | to undergo | jwoijwoi | to be taken advantage of, to be a victim |
| ?áu | to take | ?au?au | to strip something bare |
..
pila "to place something correctly and orientate correctly" : pipila "to arrange", "to tidy up", "put in order" .... jenes pazba pipilaru = Jane will arrange the table ... a room, a house, [any place], an institution
Also ... look.look = inspect : listen.listen = to sound out (a group of people) : talk.talk = to try and sell an idea (to an individual, but more commonly, to a group of people)
..
..... lé .... lú .... ló
..
Earlier we have seen that when 2 nouns come together the second one qualifies the first.
However this is only true when the words have no pilana affixed to them. If you have two contiguous nouns suffixed by the same pilana then they are both considered to contribute equally to the sentence roll specified. For example ...
jonos jenes solbur moze = "John and Jane drink water"
In the absence of an affixed pilana, to show that two nouns contribute equally to a sentence (instead of the second one qualifying the first) the particle lé should be placed between them. For example ...
jenes solbori moʒi lé ʔazwo = "Jane drank water and milk"
jonos jenes mwuri hói sadu lé léu ʔusfa = John and Jane saw two elephants and three giraffes.
[ Compare the above two examples to á jono jene solbori moze = Jane's John drank water ... i.e. The John that is in a relationship with Jane, drank water ]
This word is that is never written out in full but has its own symbol. See below ...
..
Note ... in the béu script, the "o" before "r" is always dropped. This is just a sort of short hand thing.
..
The following construction is also found.
lé moze lé ʔazwo = "both water and milk"
The above construction emphasizes the "linking" word lé
Another linking word is lú meaning "or".
jenes blor solbe moze lú ʔazwo = "Jane can drink water or milk"
The following construction is also found.
lú moze lú ʔazwo = "either water or milk"
The above construction emphasizes the "linking" word lú
There is another word that corresponds to the English "or". This is ʔala and it is a question word. For example ...
ʔís moze ʔala ʔazwo = "would you want water or milk"
And the answer expected of would be either "water" or "milk"
Say you were asking somebody if they were thirsty and you had only water or milk to give them. Then you would say ... ʔís moze lú ʔazwo ʔai@
The expected answer to the above question would be either "yes" or "no" (as is always the case when you have @ ( @ is pronouced a bit like ʔai but has contour tone instead of a normal high tone, it has a special symbol and I am using "@" to represent this symbol in my transliteration)).
Now if the question was "would you want water or milk, or both" you should say ...
ʔís mose ʔala ʔazwo ʔala leume
But sometimes (either because of the laziness of the speaker or because the likelyhood was not considered) ... ʔís moze ʔala ʔazwo ʔala leume comes out as ʔís moʒi ʔala ʔazwo.
So ʔís leume (I would like both) is an acceptable answer to the question ʔís moze ʔala ʔazwo
If the questioner would like to rule out the answer ʔís leume he would use the construction .
ʔís ʔala moze ʔala ʔazwo
So ʔala before the first item does exactly the same as lé or lú before the first item : it emphasizes the linking word.
..
... "no"
..
In béu, jù corresponds to "no".
"neither water nor milk" would be translated as jù moʒi jù ʔazwo
..
... lists
..
So far we have restricted ourselves to two items. We can summarize the system for two items as below ...
..
| lé | giving | 2 | items | |||||
| lú | giving | 1 | item | ..... | ʔala | asking for | 1 | item |
| jù | giving | 0 | items |
..
However we can join up more than two items. When more than two items are joined by the above 4 linking words, it is considered good style to have the linking word before the first item and the last item, before each item (except the first and the last) should be a slight pause (I call it a gap ... see "punctuation and page layout" earlier on this page).
For example ...
jenes mwori lé ifa sadu _ uba ʔusfa _ ega moŋgo lé oda gaifai falaja dí = Jane saw two elephants, three giraffes, four gibbons and five flamengos this morning.
..
... other
..
ló = other
lói = others
kyulo = again
welo = otherwise
..
... Making it flow
..
Grammar provides ways to make the stream of words coming out a speaker's mouth nice and smooth ... no lumpy bits.
Getting rid of the lumps entails dropping the elements that are already known ... these elements that are already uppermost in the mind. (De-lumping also involves inserting words that efficiently link to these elements that are already uppermost in the mind ... this will be covered in the section called "Linking Back")
This section omits anaphora and is about dropping known elements ... both arguments and person-tense markers. (However anaphora and all types of dropping involve a similar mental process)
A sentence [utterance = ???] is made up of one or more clauses [r-blocks]. Two r-blocks are separated by è or another particle. é is the most common particle for joining clauses and means "and then".
In béu the particle for joining nouns and adjectives is lé
In English "he eats cheese and nuts" could be analyzed as "he eats cheese and (he eats) nuts" with the bracketed part dropped. In béu this analysis is not available. The particle between the two nouns would be lé (ar perhaps if the speaker had added "nuts" on as an afterthought ... uwe "also" would come after "nuts" (a pause before) ). The particlle è would not be used. It only separated two clauses that have dissimilar verbs.
Now in English allows the dropping of an S or A argument in a sentence when this argument has already been established as the topic. béu is pretty much the same. When two clauses are joined certain arguments are dropped from the second clause. The béu rules for dropping arguments are not atypical of the worlds languages*. The rules are given below.
..
..
In the above "C1" stands for "the first clause" and "C2" stands for "the second clause". And also in béu it is possible to integrate the two clauses further ... if the two claues share a subject and all the tense/aspect/evidential of the two verbs match, then the second verb can take its i-form (and as the definition of a béu clause is "one r-block" ... the result should be considered ONE clause. The dropping of the subject in the second clause is more or less mandatory, it would sound quite strange to retain it. As for conflating the two verbs ... well it depends how tightly bound logically the two verbs are ...
..
..
Two examples are given above. The choice between conflated and not conflated depends upon the larger body of text that these examples are embedded in. But the relative likelyhood of conflation (over all situations) is given above. It can be seen that the more predictable second verb has a greater chance of being converted into its i-form. This makes sense as more unpredictable => more information. And we do not like to put to much information in one clause.
Examples are given below ...
1) The man hit the woman and then [the man] smashed her glasses. [ there are different objects ..... can be two clauses ]
2) The man awoke and then [the man] ate his breakfast. [ this would usually be conflated ]
3) The man drank all the beer and then [the man] slept. [ this would usually be conflated ]
4) The man coughed and then [the man] went to sleep. [ maybe two clauses ... no real logical tie between the two verbs ]
5) The man hit the woman and then [the man] was spat on. ... the C2 O argument can only be dropped if the C2 A argument is irrelevant ??? [ can not be conflated ... different subject ] .... to undergo ??
6) The man woke up and then [the man] was spat on. ... the C2 O argument can only be dropped if the C2 A argument is irrelevant ??? [ can not be conflated ... different subject ] .... to undergo ??
7) The man hit the woman. Then the woman shot the man.
8) The man hit the woman. Then the woman cried.
9) The thief robbed the girl. Then the pirate raped her.
Note ... For examples 5 & 6, the dropped arguments are counted as S arguments. In béu they are considered O arguments.
Note ... For examples 5 & 6, the A argument can be supplied in a hí phrase (similarly, in English the agent can be supplied by a "by" phrase)
Dropping arguments is appropriate when the to clauses are bound together in meaning (and when bound together in meaning, by iconicity, usually on the same tone contour).
The last three cases which could not drop any arguments, are felt to be, not so tightly bound together. It is no co-incidence, that these clause pairs are often given separate tone contours ... that is ... they are separate sentences.
..
... Agents
..
kludau = to write (a verb) : kludala = writing (an adjective ... actually a participle)
Two nouns can be formed by simply adding pú in front ...
pú kludau = author, writer, novelist, playwrite, essayist : pú kludala = somebody that is writing right NOW
This is quite non-surprising. Take Thai .... เขียน khiian "to write". If you add ผู้ , คน or นัก in front, you have an agent.
[Note to self : I need a term that implies, one makes ones living from ACT]
..
daumo = pen : daumo <= kludaumo
dauno = a keyboard/typewriter : dauno <= kludauno
..
... Telling the time
..
To ask what time of day it is you say jondi kí nái or kí nái
To ask what day it is you say hoite dinda nái or simply kòi nái
To ask what season it is you say jondi sabata nái or simply sabata nái
To ask what year it is you say jondi toze nái or simply toze nái
To ask which cycle it is you say omba nái
..
Actually omba is more precisely called ombatoze'. However in a situation where time is being discussed ... omba by itself will do.
The word for time in general kyugan.
The word tozegan can be translated as "age" or "generation" or "century". Actually it is a period of 128 years.
The word ombakas means epoch or eon (also "calendar", "time reckoning system"). However unlike the English terms ombakas has a specific length (about 400,000 years).
kyù translates as the noun "occasion" as well as the particle "when/while/during". I guess kyù is not a senko as it is not tangible.
Below I have given one value of the ombakas. The total set of possible values can specify a time from around 200,000 years ago to 200,000 year in the future down to the nearest 50 seconds.
omba bene odaudai dimaku ?oli sunaba ajau
..
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| omba | (komo/bene) | odaudai | dimaku | ?oli | sunaba | ajau |
..
1) ring/cycle/circle ... Every value of the ombakas starts with omba
2) (negative/positive) ... these can be dropped if it is known from context or from a tense affix, whether we are talking about the past or the future. By the way ... negative corresponds to the past.
3) "the number of the 128 year long cycle". odaudai = 55012 = 78010. As time zero in the béu calendar is 22 Dec 2083, we are talking roughly about a hundred thousand years in the future here.
4) "the particular year of the 128 cycle". dimaku means python and is the 100th year of the 128 year cycle.
5) "the particular sabata of the year" ... there are 5 sabata a (73 day long period) in one year ... ?oli pwè gú gamazu and yika
6) sunaba is the sixteenth day of the 73 day sabata ... [ In chewa, sabata means "week" ... and Yes, I know this is very unlikely to have Bantu provenance ]
7) "the particular fraction of the day that has past" ... ajau => 10012: 24 hours = 100012 : hence ajau = a twelfth of a day or 2 hours. As the day starts at 06:00, ajau corresponds to eight in the morning.
[ By the way ... if you put pluralize ajau you get ajau.a. This word corresponds to the time period between 08:00 and 10:00 ... ifau.a = 10:00 => 12:00 ... ibau.a = 12:00 => ... (well you get the idea)
..
Now a ombakas can be put at the periphery of a clause to identify when an action is happening. This is what they are nearly always used for. However ombakas are hardly ever given in full. For example it might be deemed sufficient just to give the time of the day. When time of the day occurs by itself it MUST be preceded by the particle jé.
To show "where" an action takes place, béu places ?é before the "where".
In a similar manner, to show when an action takes place, béu places jé before the "when". For example ...
..
| jene-s | d-o-r-e | jé | ajau | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jane-ERG | arrive-2SG-IND-PST | at | 08:00 |
=> Jane arrived at eight in the morning
..
Only in the situations above do you get jé introducing a truncated jekas.
At this point I should stress something before moving on. A full jekas defines a point in time (50 sec) apart. A jekas with ajau at its RHS spefifies a point at exactly 08:00. Similarly ajaujai specifies a point at exactly 08:10. And similarly ajaujaija specifies a point at exactly 08:10:50 (that is 50 seconds past ten minutes past eight).
The above represents points in time. As mentioned before, a range of times can be given by pluralizing the point ... that is ajau.a = 08:00 to 10:00 and ajaujai.a = 08:10 to 08:20. (ten minutes is the smallest range that can be specified in this way ... by the way 08:00 to 08:10 = ajaujua)
If a jekas is truncated by deleting the "time if day" then it actually specifies a time range (24 hours). If it is further truncated by deleting the day of the sabata then it actually specifies a time range (73 days). So to say something will be done on Tuesday ... no need for the "on". To say something will be done in January ... no need for the "on". For example ...
..
| g-a-r-u | geufa | |
|---|---|---|
| do-1SG-IND-FUT | on the seventh day of the month |
=> I will do it on the seventh
..
| tomo-s | d-o-r-i | geufa | ajau | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thomas-ERG | arrived-2SG-IND-PST | on the seventh day of the month | at 08:00 |
=> Thomas arrived on the seventh day of the month at eight in the morning
..
| tomo-s | c-o-r-u | ?oli | geufa | ajaujai | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thomas-ERG | leave-2SG-IND-FUT | in the first month | on the seventh day | at ten past eight |
=> Thomas will depart in the first month on the seventh day at ten past eight
..
This time system is sufficient for all of human history. Of course to talk about cosmology, or even geology, some sort of extended system is needed.
..
Relative time words and their provenance
..
So far we have learnt how to give the time in an absolute manner. Time is sometimes also given in a relative manner ...
..
jana = yesterday
heute = today
kuzaza = tomorrow
bezaza = the day after tomorrow (<= be + kuzaza)
kojana = the day before yesterday (<= ko + jana)
Three of the above have natlang provenance jana from Swahili, kuzaza from Zulu and heute from German ... and Yes, (I am aware that the german word is not pronounced heute these days ... maybe it once was.
..
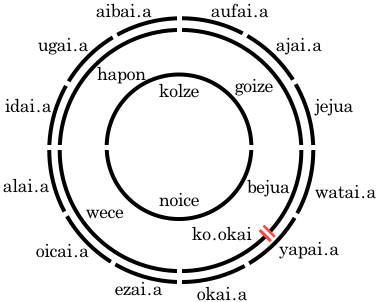
..
The above two wheels represent 24 hours in the béu time reckoning. A 24 hour period is called dinda and dinda is the unit of time [in the Western tradition the second is the unit of time].
The LHS wheel represents periods of time. Actually each 2 hour time period can be further subdivided into 12 periods of 10 minutes. For example aibai.a can be divided up into aibaijua aibaijau.a aibaifau.a aibaibau.a aibaigau.a aibaidau.a aibailau.a aibaicau.a aibaizau.a aibaikau.a aibaipau.a aibaitau.a . This scheme is seldom used though. By the way ... jejua => jejujua jejujau.a jejufau.a etc.
the first 10 minutes after midday is called abaijau.a.
The RHS wheel represents points of time ... jé aibai = midday : jé okai = midnight : jé jù = 6 o'clock in the morning (the start of the béu day). Only twelve points are shown, however there are actually 1728.
When ko.okai becomes bejua is unclear. A period of time that varies through-out the year is the jondia "dawn. It starts when the sun is first seen above the horizon and continues until it is clear of the horizon. This period will also vary according to position ... if you live in a deep valley jondia will come later than if you stay on the coast or on a plain. jindia is the jondia midpoint. This is a point of time.
The small wheel shows Sundown koikau and Sunrise jondia. koikau is important for spiritual observancies. These obviously vary through-out the year.
jindia is a technical term and not used a lot. It specifies when the middle of the sun clears the horizon at your particular locality. If you live in a valley this time would be of course delayed compared to your neighbours outside the valley. Trees or other man made obstructions are not taken into consideration when calculating this number.
Here are some examples of the system in use ...
| g-a-r-u | kolze |
|---|---|
| do-1SG-IND-FUT | day |
==> "I will do it during daylight hours"
| gì | tw-a-r-u | jé | ugai |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2SG | meet-1S-IND-FUT | at | 14:00 |
==>"I'll meet you at 2 in the afternoon"
..
| garu kolze | I'll do it during the day |
| garu noice | I'll do it at night |
| garu goize | I'll do it in the morning |
.... and so on
| garu jejua | I'll do it between 6 and 8 in the morning |
| garu ajai.a | I'll do it between 8 and 10 in the morning |
.... and so on
| gì twaru jé jù | I'll meet you at 6 o'clock in the morning |
| gì twaru jé ezai | I'll meet you at 10 o'clock at night |
| gì twaru jé ajaujaija | I'll meet you at exactly 08:10:50 (that is 50 seconds past ten minutes past eight). |
.... and so on
..
| g-o-r-∅ | dinda-s |
|---|---|
| do-3SG-IND-HAB | "24 hours period"-ADV |
==> "He/she does it daily"
..
| gor kolzes | He usually does it during daylight hours |
| gor noices | She usually does it at night |
| gor aibai.as | He usually does it in the early afternoon |
.... and so on
Four of the terms in the LHS wheel have natlang provenance ...
goize (basque) : hapon (cebuano) : wece (bosnian) : noice (portuguese)
..
Also the meaning of two terms on the RHS wheel have expanded ...
aibai = noon => high point, zenith
okai = midnight => low point, nadir
..
When the 5 relative time words combine with others the relative comes first. For example ... kuzaza jejua = early morning tomorrow
..
There are also two undefined periods of time. jin and jon. jon is an order of magnitude greater than jin (but both are not rigorously defined).
jondi = now
jindi = exactly now
"longtime" súa / short-time gìa the latter giving rise to the adverb uzuas "soon"
kí = a time interval of 50 seconds ... I suppose it should be included when talking about daily time but it is invariably dropped. For example 8 o'clock is jé ajau not jé kí ajau.
[Note to self : talk about "the first century" = "century zero" : "the first kilometer" = "kilometer zero"]
..
... Ways to join clauses timewise
..
In the previous sections we have seen how to give time information. However there is another way to give the time ... with respect to an evert or action.
We will cover six particles in this section which allow us to give time information with respect to an event ... jón koca beda kogan began jindu and jonde.
..
jón = "while" or "when"
koca = before
beda = after
kogan = until
began = since
jindu = as soon as
In a similar manner to English, they can either introduce a clause, a noun (that designates a time) or an infinitive phrase (by the way ... I disapprove of the term "infinitive clause")
“After I ate breakfast”
“After the gold rush”
“After the eating of my breakfast”
The above are all time adverb phrases. A time adverb phrase is a dependent clause* (called an under clause in béu) ... shown in red below. The main clause is shown in yellow.
..
Tha arrow is the arrow of time** ... with the past to the left (komo), and the future to the right (bene).
I have given events wavey borders to represent "not so well defined". So, for example, on the top diagram ... the main clause action could start before the under clause action ... it could also outlast the under clause action ... the important thing is that for a substantial amount of time, the two actions were going on at the same time.
In the bottom four examples I have made the under clause actions very short. This is for illustration purposes only. The under clause actions can actually have any length ... depend on the verb/situation.
Now these five examples show how two clauses can be joined in a timewise fashion. The béu rules are quite similar to English. That is ...
A) the under clause must be introduced with one of these 6 particles.
B) we can have main clause and then the under clause ... or the other way around.
Here are examples to illustrate the 5 examples above ...
..
1) jón = while, as, when, during
pás pintu saikaru jón gís pazba saikiru = "I will paint the door, while you paint the table"
jón gís pazba saikiru_pás pintu saikaru = "while you paint the table, I will paint the door"
jón saiko pazba_gís huʒiri = "while painting the table, you smoked"
..
2) koca = before
pazba saikaru koca pintu (saikaru) = "I will paint the table before (I will paint) the door"
koca pintu saikaru_pazba saikaru = "before I paint the door, I will paint the table"
koca saiko pintu_pás pazba saikaru = "before painting the door, I will paint the table"
..
3) beda = after
pintu saikaru beda pazba (saikaru) = "I will paint the door after (I will paint) the table"
beda pazba saikaru_pintu saikaru = "before I paint the door, I will paint the table"
beda saiko pazba_pás pintu saikaru = "after painting the table, I will paint the door"
..
If you wanted to emphasize that the first action will continue until the second action you would use ...
4) kogan = until
gís huʒiri kogan dare saiko pazba = "you smoked until I started to paint the table"
kogan dare saiko pazba_gís huʒiri = "until I started to paint the table, you smoked"
kogan día saiko pazba_gís huʒiri = "until starting to paint the table, you smoked"
..
If you wanted to emphasize that the first action has been continuing all the time since the second action you would use ...
5) began = since
gís ʔès huʒira began care saiko pazba = "you have smoked since I stopped painting the table"
| gí-s | ʔès | huʒ-i-r-a | began | c-a-r-e | saiko | pazba |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| you-ERG | already | smoke-2S-IND-PRES | since | stop-1S-IND-PAST | painting | table |
==> "you have smoked since I stopped painting the table"
began care saiko pazba_gís huʒira = "since I stopped painting the table you have smoked"
began cùa saiko pazba_gís ʔès huʒira = "since stopping painting the table, you have smoked" ... [By the way ... began ìa saiko pazba_gís ʔès huʒira = "since finishing painting the table, you have smoked" ]
..
There is one added complication in the above scheme ... if the intersect time of the two actions is in the future, then jindu (<jín "a moment" + dù "exact") can be used instead of began.
..
..
* I guess I should say what is the difference between a main clause and an under clause. (I should read about what other linguists say about this some day). Take the sentences ...
(1) I will finish this drink before I go home. ......... (2) I will go home after I finish this drink.
In terms of pure logic these both mean exactly the same. Also the choice of whether a verb is in the main or the under clause says nothing about the speakers attidude towards that verb ... i.e. relish, disgust, foreboding, sadness etc. But is seems that the verb in the main clause is the target of the speakers determination/willpower/resolve whereas the verb in the underclause is the target of nothing. I guess you can say it is background material..
** The organization of the Chinese writting system seems to have affected the language itself. The primary writing direction was top_to_bottom so of course the calendar was written top_to_bottom as well. From that "above" got associated with "the past" and "below got associated with "the future".
午 wǔ "noon" : 上 shàng "above" : 下 xià "under" => 上午 shàngwǔ "morning" : 下午 xiàwǔ "afternoon"
A similar thing happened in béu. The practitioners of béu are above all engineers and the algebraic convention of having time along the horizontal axis has affected the language somewhat.
..
jón used to mean an interval of time. It still does but nowadays you see it most often as the particle meaning "when"/"while". The conjunction jonde "and then" is derived from it.
jín means an interval of time an order of magnitude shorter than jón. The particle jindu is derived from it.
The adverbs jondi and jindi are derived from the above. They both mean "now". jondi is the one usually used. jindi is used for emphasis (for example in a swiftly changing situation).
..
... Linking Back
..
Now the section above shows how two clauses can be joined in a timewise manner. To do this takes a bit of working out in the mind of the speaker [of course for written language this is not a constaint. The writer has more than enough time to work out complicated patterns].
However in conversation, often things are not laid out so neatly. Consider the case where one clause has been spoken. The speaker considers himself done and gives the "finished speaking" intonation to the end of his utterance. Then ... after a split second it comes into his head that another event (clause) is also of interest to the hearer. In this case, one of the below constructions must introduce the "afterthought".
..
The s (is) suffix is the adverbial marker. And the adverbials jonis, bedais*, kocais make a connection back to the clause just spoken** ... back to the information which is still uppermost in everybody's mind [this phenomena is often called "anaphora" from the Greek "carry back"]. All the elements of the clause last enunciated are still whirring around the brain : they are easily accessible. And the words jonis, bedais and kocais connect to the "just spoken clause" [kind of like a time portal :-) ].
Now these are adverbs which must come at the periphery of the clause. Hence above I have shown the adverbs occurring clause final as well. However clause initial is the preferred location.
The dí is the proximal determiner (i.e. "this"). In béu dí is also used a lot for linking back*** to clauses just spoken. In fact dí represents the just spoken clause in its entirety.
Note that the dí constructions can only occur initially.
Now how to explain the pattern in the diagram above ? Well some believe that for an adverbial to exits, it must be quite common. That is kogan and began as afterthough introducers are quite uncommon, hence the phrases kogan dí and and began dí are used as opposed to *koganas or *beganas. Notice that koca can exist as an afterthought indroducer in the form kocais or koca dí. It is not known why the terms *jón dí and *beda dí are not allowed.
..
Now the most common way to join clauses is to use the particle è "and then". When è is used both clauses that circumscribe it are main clauses.
By the way ... when people are narrating a sequence of events (or when they are just thinking to themselves), they go through the events in the order in which they happened 9 times out of 10. It is for this reason that this section is all about "and then" and not "before that".
..
..
The above diagram shows two clauses A and B. In the normal course of events and when the speaker has the time to plan ahead, (1) would be used. If the speaker had not had time to plan ahead, one of the resumptive stategies (2), (3) or (4) can be used. dùs = "and then immediately" : diadilaIs = "eventually"" and bedais = "afterwards" as we have covered before. Now because these three adverbs can come either clause initial or clause final ... a pause "_" is mandatory. Well you would expect a pause before bedais because this is a resumptive stategy ... this is the sentence you end up with if you don't think ahead and hence fail to produce the sentence with the è "and then" particle. But dùs and diadilaIs are not resumptive strategies (at least not primarily), but a pause is insisted upon.
..
Another word that is commonly used to refer back to a recently utterance is wedi [examples 5 & 6]. It translates as "in that way".
And wede [example 7] is the cataphoric equivalent of wedi. It translates as "thus" or "like this".
wedi and wede can appear at either end of a clause, but it is more common to find them in the end of the clause nearest to the clause they refer back/forward to.
..
And yet another word that is commonly used to refer back to a recently utterance is iwe [examples 8] "anyway".
There is a word uwe that sort of counterbalances iwe. However uwe is not used for anaphora, instead it appears clause final and is a particle meaning "completely".
..
*Translating bedais unto English gives "afterwards" or "after this" or just plain "after" ... a good example of the messiness of natural languages I think.
..
**Actually a "first clause" can be absent ... these adverbs can appear after a long period of silence. In this case "the after what" refers to some action that is uppermost in everybody's mind although not recently spoken about. For example ... say you are a painter and decorator working with your helper on some sight. Now you both know that the next task will take around 15 minutes and will be a two man job. Your helper hints that he is desperate for a cigarette. To put him off for a bit, you can simply say bedais. So in this case not linking back to anything spoken ... but linking to what is uppermost in everybodies mind.
..
***Notice that English does something similar with "that". Also then ... but "then" does not represents the just spoken clause in its entirety, it only represents the time of the action.
Also in béu dè the distal determiner (i.e. "that") is used to create a link to the clause ABOUT to be spoken. For example ...
| unya | gì-n | fy-a-r-u | dè | _ | bla bla bla bla |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| and | 2SG-DAT | tell-1SG-IND-FUT | distal determiner | pause | "unspecified following clause" |
=> And I will tell you this, bla bla bla bla bla
Note that the béu system is the opposite of the English system.
Also note ... instances such as the above (i.e. cataphora) are a hundred times rarer than anaphora. Really insignificant.
..
... Other ways to join clauses
..
unya = "and" (some logical connection ... well if no logical connection, the two clauses would not be appearing side by side)
tè "but"
imwa = "but"
tè ?ài kyù = "but"
??? "but" can sometimes come before nouns in English. For example ... "all but me" .... in béu' we use u?u ???
There are also some phrases with more "sound.weight" that have the exact same meaning as tè.
?? Well this is the more neutral particle (the particle plí can also be used ??
??? sé kyude/è kyude : these mean that action B follows action A but not necessarily immediate. Sometimes sé è are dropped.
??? kyugo : this means that action A and B happen at the same time. Usually we have different actors in the two clauses, but not always.
jì dè = in order to
ji?is = because
ji?is wo = because of
huzu = to smoke
koʔia = to cough
?atsi = to sneeze ... (Butanese)
solbe = to drink
caume = medicine
Notes on grammar .... If you have two clauses, the particle must come between them : the element containing only infinitives (for example ... figo ìa saiko pazba) is not a clause. I call it a "clause adjunct" or "adverbial phrase" [I should pick one term] : for the examples above containing a clause adjunct, note that only the main clause has a subject : notice that what is marked by the perfect in English is marked by ʔès "already" in béu. In English the perfect has 3 functions ... the resultative, the experiential and the so called universal which indicates that activity has been going on for sometime and still is. In béu the perfect marker was derived from a verb meaning "finish" ... a marker derived from this source can scarcely be expected to have this "universal" function.
Also note ... cùa jì gò saiko pazba = "to leave in order to paint the table" ... In English you can drop "in order" to get "to leave to paint the table". In béu this would result in "to stop painting the table" ... never leave out jì gò.
Usually this type of clause adjunct does not express a subject ... but sometimes it can ... the subject is places after the word sàin "reason, cause, origin" and sàin comes after the object (if there is one) and the object comes after maŋga. The only element allowed to the left of maŋga is the negative jù. For example ....
timpa jene sàin jono r kéu = John's hitting of Jane was bad .... [maybe hí is better than sàin ???]
There are five particles used to introduce these time adverb phrases. Each of these particles defines a different time relationship between the main action and the under action.
Note ... Both the main action and the under action can vary considerably in length. In the above diagrams I give what I consider typical time lengths.
Note ... In English "since" can only be used for an under clause that occurs in the past. For example ...
beda jono joru_ufan rù bòi = After John goes, everything will be fine
The literal translation of the above is "since John will go, everything will be good" ... In English "since" has taken on a second meaning*. In béu, jefi has no such secondary meaning and it is perfectly to use jefi with a clause set in the future. [In the chart I specify a NOW ... this is really to signify the situation for typical usuage of the English word. The NOW is not relevant to the béu usuage]
..
*GIVE THAT EXAMPLE FROM DEUTSCHER'S BOOK.
..
The usuage of these five particles is quite straightforward. However there is one little quirk that should be pointed out. For example ...
jono liga ko?ori kogan ós solbori moze = John was coughing until he drank some water ..... ko?ia = to cough
Now the above can be recast ...
John was coughing until the drinking of water by him => jono liga ko?ori kogan solbe moze hí ò
This can be futher cut ...
John was coughing until the drinking of water => jono liga ko?ori kogan solbe moze
And further cut ...
John was coughing until drinking => jono liga ko?ori solben .... Not *jono liga ko?ori kogan solbe
When the verb-noun is only one word it will take the suffix -n instead of the particle kogan
In a similar way, when the verb-noun is only one word it will take the suffix -fi instead of the particle jefi. For example ...
John has been coughing since he smoked a cigarette => jono ko?ora jefi ós huzore ʃigita ... huzu = to smoke, to suck
John has been coughing since smoking => jono ko?ora huzufi .... Not *jono ko?ora jefi huzu
..
For beda and koca, when the time between the two events are stated ... it comes immediately after bade or koca. For example ...
beda odai yanfa jene fori = After five minutes Jane left (is féu Ø or H ?) .... [ yanfa = 5 seconds, odai = 5012 = 6010 ... so the translation is 100% accurate ]
..
..
7) jì gò = "in order that" "so" "so that"
It shows that the first action was done in order to bring about the second action/state. The particle is always between the clauses.
jonos jenen toili nori jì gò ós ò klór = John gave Jane a book in order that she would like him.
The second clause is the <purpose> of the first clause .... jonos jenen toili nori is a clause : ós ò klór is a clause : jì gò ós ò klór is an adverbial adjunct
The second clause always has the aortist tense form in this construction ... actually the gò jì makes the second verb sort of irrealis.
..
Notice that if the second clause was replaced by a NP ... jì "for" or "for the benefit of" would be the particle used.
If both clauses have the same subject, then the second one usually becomes an "infinitive adverbial adjunct, and the particle jì is used.
toili mapari jì kludau ʃila = I opened the book in order to write in it
tarye dían jì twá gì = I came here (in order) to meet you
Occasionally you can have this construction where the object of the first clause is the subject of the second clause ...
pà babas gaidoryə dían twá gì = My father brought me here to meet you
From the underlying semantics of the above, it is pretty obvious that "the father" was not intent in "meeting you"
[ Note to self ..... In English "in order to" is only used with same subject constructions .... interesting ]
..
8) plùa = "therefore" "so" "hence"
It shows that a second clause follows on logically from the first clause. The particle is always between the clauses.
ò klár plùa òn nari toili = I like her so I gave her a book
The second clause is the <result> of the first clause .... No adverbial adjuncts in this construction
..
9) sài gò = "because" "as" "since"
It shows that the second state/action is a consequence of the first action/state. The particle is always between the clauses.
jenes jono klór sài gò òn nori toili = Jane likes John because he gave her a book
The second clause is the <reason> for the first clause .... jenes jono klór is a clause : òn nori toili is a clause : sài gò òn nori toili is a adverbial adjunct
..
Notice that if the second clause was replaced by a NP ... sài "because of" would be the particle used.
..
10) dà = where
pà twá dà twaire yildos = meet me where we met in the morning
pà twá is a clause ... twaire yildos is a clause ... dà twaire yildos is an adverbial adjuct .... "adjunct" is something that can be added to a clause
..
11) kyù = when
kyù twaru jene òn fyaru = When I see Jane I will tell her.
12) tà = if (hypothetical)
13) ʔáu gò = if (counterfactual) ... maybe equivalent to "suppose, imagine, assume".
Actually the above 3 form a sort of continuum as regard to the likelihood of the matrix verb actually occurring. We could say ...
kyù covers the likelihood range of 100 % => 90 % : tà from 90 % => 10 % : ʔáu gò 10 % => zilch
All three are used with pretty much the same frequency in béu.
Actually the context determines to a large extent likelihood of the matrix verb actually occurring in English (and in most languages). For example ... "when pigs can fly"
..
Note on English .... English uses "if" for both hypothetical and counterfactual. Things are a bit twisted in the English usuage.
"If it rained tomorrow, people would dance in the street." .... notice that the conditional clause has a past tense verb, but is actually talking about the weather
"If it had rained yesterday, people would have dance in the street." .... and to get a counterfactual "past tense meaning", we actually have to use the past perfect form.
..
14) tè gò = unless .... [the above 5 conjunctions .... should they use gò to separate the clauses : should they use plùa to separate the clauses ???) ..
15) dó = "although" "though" "even if"
This conjunction introducing a clause denoting a circumstance that might be expected to preclude the action of the main clause, but does not. It has a more emphatic variation .... ?emodo
Notice that dó and plàu are related. Any pair of clauses joined by plàu can be transformed into a pair of clauses joined by dó ...
a) negating the first clause
b) swapping the clause positions
c) get rid of plùa and insert dó between the clauses.
He is tall so he is good at baskerball
He is good at basket ball although he is short
..
16) kài = "as", "like", "the way"
kài is sufficient for joining clause (kài gò is never seen). If you look back on the chart at Ch2.11.1 you see that kài is an introductory particle indicating "manner". Manner means some action and action means a clause.
"I was never allowed to do things as I wanted to do them"
..
... Extending a NP using the partitive ..."làu"
..
In section 2.7 we analyzed the the different components that can go into seŋko kaza or the noun phrase if you will. Here we will go into it in a bit more detail. It will be seen that there is a bit of "internal structure" ... a bit of complexity that is not obvious upon first blush.
..
.. Sets and subsets
..
Nearly every seŋko occurs in multitudes. OK, there are a few counter examples, such as kòi "sun" but for the most part they occur in multitudes. When we talk about any plurality of these nouns it is possible to change the scope of the set under discussion ... it as if we can zoom in and zoom out and this ability to "zoom" is defined by grammar (what else).
Let as take the noun moltai "doctor" to demonstrate this. Below ... represented by the orange area is all the doctors in the world (and also presumable the Universe*).
*This "zooming" idea is not fully air-tight, there is a bit of fuzzyness about it ... hence the inclusion of "presumably".
..
The above is as far as we can zoom out. Call the total orange area the "u* set". This scope is appropriate for generic pronouncements. Such as ...
moltai.a súr jini = "doctors are clever"
* u for universal.
..
OK ... now lets zoom in a bit. To zoom in we need to take in or give out some narrative. So now we hear the following ....
Next week British junior doctors will withhold many services in protest against the long hour expected of them
OK ... after hearing that ... and if the NP "these doctors" moltai.a dí is mentioned and commented on it becomes fixed in the mind of all the interlocators.
moltai.a dí is represented by the orange area in the Venn diagram below.
OK ... lets hear another bit of narrative and change the "set" of doctors under consideration again. The narrative is ...
Much to the disgruntlement of the senior doctors who will have a hard week ahead of them making up for the short fall.
OK ... after hearing that ... and if the NP "those doctors*" moltai.a dè is mentioned and commented on it becomes fixed in the mind of all the interlocators.
moltai.a dè is represented by the orange area in the Venn diagram below.
OK ... after hearing that, the NP "those doctors*" moltai.a dè is represented by the orange area in the Venn diagram below.
* This is presuming that the NP moltai.a dí was actually talked about after the first narrative. If not ... then the NP moltai.a dí would be used to refer to the senior doctors. So it is like the particles dí and dè are letting us keep track of two "sets" of doctors at the same time. That is ... the NP's moltai.a dí and moltai.a dè have been set up in the minds of all interlocators to refer to two different sets. The second NP ( moltai.a dè ) only exists as a sort of contradistinction to the initial NP moltai.a dí .
OK ... this is as far as we can go with this example. I believe if you add the set "senior" doctors to the set "junior" doctors you have a set identical to the "set" doctors (However I could be wrong about this)
..
Lets change the example to take this idea further. Let us take bawa "men" for our noun. OK assume some narrative was given, and then bawa dí was mentioned to cement it into everybody's mind.
Then more narrative was given (defining a further subset) and bawa dé was mentioned to cement it into everybody's mind. A further NP can be used to refer to all bawa outside the first two sets. This NP is bawa lò "other men"
Actually bawa lò is usually used just one ... the set referred to as bawa lò are hardly ever kept in anybody's mind for more than a few seconds. In actual fact the first two terms don't usually persist long in a discourse either. We are continually zooming in ... zooming out ... changing our perspective.
..
.. The extended NP
..
When we were talking about how the NP was built up ( chapter 2.7 ) we mentioned the "numerative slot" that comes just before the head. We said that in this slot we can have either a "numerative" or a "selective". In this section we will discuss how these two classes of words interact with the singularity/plurality of the head noun. Also we will introduce a construction called "the extended NP" which gives a "partitive" meaning.
..
| 1 | jù moltai dí... | no doctor here | moltai.a dí làu jù... | none of these doctors |
| 2 | ʔà moltai dí... | one doctor here | moltai.a dí làu ʔà... | one of these doctors |
| 3 | hói moltai dí... | two doctors here | moltai.a dí làu hói... | two of these doctors |
| 4 | léu moltai dí... | three doctors here | moltai.a dí làu léu... | three of these doctors |
| 5 | iyo moltai dí... | a few doctors here | moltai.a dí làu iyo... | few of these doctors |
| 6 ... | euca moltai dí... | seven doctors here | moltai.a dí làu euca... | seven of these doctors |
| 7 | hài moltai dí... | many doctors here | moltai.a dí làu hài... | many of these doctors |
| 8 | ú moltai dí... | all the doctors here | moltai.a dí làu ú... | "all of the doctors here" or "every one of the doctors here" |
..
In the table above the RHS has a "partitive" meaning. For example ... euca moltai dí means that we are talking about "seven doctors" and they are "here". But moltai.a dí làu euca means, we are talking about "seven out of a (significantly) larger number of doctors here". The RHS expressions I call an "extended NP's" ... [ NP + làu + numerative = extended NP ]
làu has been mention before in Chapter 2.12.1 ... it is a particle and it serves a number of functions*
* These different functions are not totally unrelated to each other ... they "impinge" on each other ... just as particles in natural language do.
To use an extended NP is to "zoom in". It is to narrow the scope of the items we are focusing on (as discussed in the previous section).
..
..
TWO RULES ...
A) For non-extended NP ... in any numerative before the head, then the head is SINGULAR.
B) For extended NP ... the head is PLURAL.
..
But what about the "selectives". What about ín and èn ? Listing the four possibilities below ...
..
9 ) ín moltai dí = any doctor here
10) ín moltai.a dí = any doctors here
11) èn moltai dí = some doctor here
12) èn moltai.a dí = some doctors here
..
It can be seen that following a "selective" ... the head can can be either SINGULAR or PLURAL
Now how can we interpret a sentence ... such as ... "any two doctors here" ?
Well the rules state that only one word is allowed in the numerative slot ... so ... *ín hói moltai dí or *hói ín moltai dí are not allowed.
However we can use extended NP's. For example ...
..
| 9 | ín moltai dí | any doctor here | => | [ empty due to Rule B ] | |
| 10 | ín moltai.a dí * | any doctors here | => | ín moltai.a dí làu hói | any two doctors here |
| 11 | èn moltai dí | some doctor here | => | [ empty due to Rule B ] | |
| 12 | èn moltai.a dí | some doctors here | => | èn moltai.a dí làu hói | two doctors here ** |
..
* ... ín moltai.a dí exists, however it is a very rare beast. By far the most common use of ín is with a singular head. But in certain situations you have a situation where it is known that a PLURALITY is needed. For example "to lift up a long narrow table". So in this situation ín moltai.a dí could be used ( "any doctors here can lift the table" ... just an example). However in most situations where it is known that a plurality is needed ... it is know exactly HOW MANY are needed. In the above example TWO ... hence you would hear ín moltai.a dí làu hói more often than hearing ín moltai.a dí
COMMON .... ín moltai dí >>> ín moltai.a dí làu X (where X is any numerative) >>> ín moltai.a dí ... UNCOMMON
..
** You don't know which two ... bit we are defining them now ... henceforth we shall refer to them as nù.
..
The particle nò can also occur in the tail of an extended NP. For example ...
moltai.a dí làu nò = "several of these doctors"
In this case ... nò can be looked on as indicating plurality neutrally ... without any connotations of HIGH MAGNITUDE as hài ... or LOW MAGNITUDE as iyo.
Note that nò now has 3 uses ... it is a noun "number" ... it is a plural marker for most monosyllable nouns ... and now this use. Note that it is not a numerative (or a selective either for that matter).
..
moltai.a dí làu ʔà lú more = "one or more of these doctors" ??????????????
..
Note ... ʔà moltai dí means pretty much the same as èn moltai dí ... one a selective, one a numerative.
In béu, èn is preferred over ʔà to code indefinite [ ??? go into indefiniteness after this section ??? ]
ʔà moltai dí could mean "the one man here" but ʔà/"one" is superfluous in both béu and English (unless you were to appand a relative clause)
..
Two other numeratives that we haven't mentioned yet are tontu "the majority"/"most" and tonji "the minority".
ton = bit/part/section ... tontu <= ton jutu ... tonji <= ton tiji ... toŋko = to seperate ???
..
The distributive can occur in the tail of an extended NP. For example ...
moltai.a dí làu ò ò ... = You see the doctors here ... well everyone of them ...
[ Of course if "the doctors here" was on the top of every ones mind ... then only ò ò would be expressed ]
OK ... I have explain all the above using the determiner dí. But it is exactly the same pattern with a different determiner or no determiner at all.
I have explain all the above using a multi-syllable head. But the same pattern holds for mono-syllable heads ... regular and irregular. For example you could change wèu "vehicle" or "car" for moltai and nò wèu for moltai.a in the above explanation and everything would hold. Or bàu for moltai and bawa for moltai.a.
Also pronouns follow the above pattern. But note ... "those two*" in English is hói nù "two us" in béu ... "you three" is léu jè ... "us four" (including you) is ega magi ... "us five" (excluding you) is oda manu ... and so on.
"five of them" being nù làu oda of couse, following the exact same pattern that a normal noun takes for partitiveness.
á hói manu doikuarua í london = "the two of us will walk to london" OR "us two will walk to london" ... [ I guess there would be a tendency to drop manu??? ]
á manu làu hói doikuarua í london = two of us will walk to london ... [tendency to drop manu??? ]
* I guess English is a bit irregular with the 3rd person plural pronoun. This would be "they two" if it patterned the same as the other pronouns.
( write about partitive in Finnish ) ... ( write about the other uses of làu ) ... ( revisit the DISTRIBUTIVE )
WHAT ABOUT .... enough of the men .... too many of the men ... above 100 of the men ... more of the men
all others => ú lòs
some others => nò lòs
any doctor => ín moltai
any doctor here = any of these doctors => ín moltai dí
any of the doctors here => ín moltai.a dí
..
ʔà ʃì = it ... nò ʃì = them (inanimate)
..
| 1 | ʔà ʃì nái | which one |
| 2 | nò ʃì nái | which ones |
| 3 | léu ʃì nái | which two |
| 4 | léus nái | which two |
..
... Compound words
..
Many words in béu are constructed from amalgamating two basic words. The constructed word is non-basic semantically ... maybe one of the concepts needed for a particular field of study.
Compound-words are found in most languages A typical example is “lighthouse”. The meaning of "lighthouse" can't be determined from the meaning of the constituent-words (though it can be guessed at).
In English (and presumably other languages) many normal words started life as compound-words … for example “husband”, “hustings” and “hussy” (originally “hūsbōnde”, “hūsthing” and “hūswīf”). With these above three examples, the journey from free expression* to indivisible word took time and it is hard to say exactly when the change happened. In béu it is obvious when the transformation from free expression* to indivisible word took place. Also this change can be considered a deliberate act. béu speakers (in a similar way to Australians) have a limited tolerance for long words turning up frequently. In béu there was a “fuck this” moment when somebody decided that toili nandau was too long and started using nandali … similar to when some Australian decided “registration” was too much of a mouthful and started using “rego”. Or when some Australian decided “afternoon” was too long and started using “arvo”.
..
In béu when 2 nouns are come together the second noun acts as an attribute of the first**. For example ...
toili nandau (literally "book word" ... "book" is the head and "word" is the attribute).
Now the person who first thought of the idea of compiling a list of words along with their meaning would have called this thing he created toili nandau.
However over the years as the concept toili nandau became more and more common, toili nandau would have morphed into nandali.
Often when this process happens the resulting construction has a narrower meaning than the original two word phrase.
The process for generating the new word is shown above.
First you trim the original expression. (A) The first syllable is dropped (provided the head has at least two syllables). (B) If the expression ends in a consonant, n or s is deleted (provided the attribute has at least two syllables). (C) If the expression ends in a diphthong, u or i or a is deleted (again provided the attribute has at least two syllables).
Then the position of the two components are swapped. Finally the components are merged into one word.
Below is another example ....
megau means "a body of knowledge" or "a subject". peugagau means the sum total of knowledge that a civilization has achieved.
And another example ...
It can be seen in this example that the assembled words has a much more restricted meaning than the product of the component words. (there are about a thousand saidau compared to 12 nandau sài.
wé means "way", "method" or "manner" and deuta means "soldier". deutawe is an adverb meaning "in the manner of a soldier".
wèu means "vehicle" or "wagon". sò means "row" or "series". soweu means "train".
..
Many locations and humans holding rank are two word expressions. These can be classified as intermediary with respect to free expressions and a formula (in Jesperson's terminology). They are fixed expressions but never collapse into a compound-word. Examples are Lake Geneva, Mountain Green, Loch Lomond, Desert Sahara, River Thames, Town London, Captain Turner or Doctor Johnson. (Note ... English is inconsistent and sometimes has the specific before the general, cf London town and Sahara desert)
[ Note to self : Béu has 5 other words "public company(big, medium, small) and "private company"(big small) that behave similar to Captain, Mountain etc ]
[ Note to self : what about Mr, Mrs etc etc ? ]
..
In future, when a non-basic (nb) word is introduced it will be marked as such along with its provenance. For example ...
gozofai = fruterer : (nb : <kanfai gozo)
kwofan = bicycle : (nb : <ifan kwò)
..
There are thousands of assembled words. Assembled words are listed in Ch 9.
[note to self : decide about the following forms]
sword.spear => weaponry ... shield.helmet => armour, protection ... knife.fork => cuttlery ... table.chair => furniture
..
* See Jespersen (1924) _Philosophy of grammar_, free from <https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.282299> discussion about free expression is about page 24.
..
** Actually there are three words that can be used to bind the two words together ... perhaps if you want to make the relationship between the two more concrete. These words are yó "property, gù "master"/"lord" and kài "kind"/"type"
waudo yó bàu = "the man's dog", bàu gù waudo = "the man who owns a/the dog", loweu kài banhai = "a/the school bus"
But as I said before, usually speakers are happy to drop these linking words.
By the way "whose" can be translated into béu using the gù construction ... "the man whose dog bit me" => bàu gù waudo nài pà ilkori
"the man who owns a dog bit me" would be rendered bàus gù waudo_ós pà ilkore (a single clause ... bàus gù waudo and ós being in apposition)
..
... Bicycle + +
..
Above I explained the word for bicycle ...
There are a few more words that follow the same pattern. Remember fron the last chapter that ifan = a duo, uban = a threesome, egan = a foursome, odan = a fivesome, etc.
..
kwafan = bicycle
kwoban = tricycle
..
pomafan = a biped ..................................... poma "leg"
pomagan = a quadruped
pomalan = an insect
pomazan = an spider (béu is one of the few languages in the world to give the octopus a name without "eight" as an elemeent)
..
kandaban = a threeway intersection ......... kanda "intersection"
kandagan = a fourway intersection
kandadan = a fiveway intersection
Etc. etc.
..
dalnoban = a triangle ................................ dalno "edge", "boundary", "border", "margin"
dalnogan = a quadrilateral
dalnodan = a pentagon
dalnolan = a hexagon (this word is further eroded to nolan and takes on the meaning "townhall")
dalnocan = a heptagon
Etc. etc.
..
daizlodan = tetrahedron ............................ daizlo "face", "facet", "side"
daizlolan = cube (this word is further eroded to lolan and takes on the meaning "dice" or "die")
daizlozan = octahedron
daizlojain = dodecahedron
daizlojaizan = icosahedron
..
dauzodan = a 5-cell ................................... dauzo "cube", "block"
dauzozan = an 8-cell
dauzogan = a 16-cell
dauzofain = a 24-cell
dauzopain = 120-cell
dauzogaufain = 600-cell
..
I am a bit unhappy with the lack of phonetic distinctness of the above. However I guess we can live with this indistinctness, after all English works OK with "can" and "can't", with "fifty" and "fifteen".
Another part of the language which suffers from phonetic indistinctness is the verb train. In particular the impersonal verb form versus the various personal verb forms ... ostar toilia "I sell books" : ost+r toilia "books are sold" ... hala nyalera "you(pl) are wearing away the rock" : hala nyal+ra "the rock is being worn away". However nothing is perfect.
..
... Set Phrase and idioms
..
If you meet somebody who you have not met for sometime you say gò yír fales "may you have peace".
If you meet some people who you have not met for sometime you say gò yér fales "may you have peace"
On taking your leave of somebody who you have not met for sometime you say gò nela r gimau "may the blue sky be above you"
On taking your leave of somebody who you have not met for sometime you say gò nela r jemau "may the blue sky be above you"
If you pass somebody in the street or you meet your workmates for the first time in the morning fales is sufficient. If you say gò yír fales it typically means that you are going to have a ten minute (at least) chat.
..
There are some set phrases ... these are not a million miles from interjections
Also there two phrases { "j" and "k" } which could be considered interjections. They have the intonation pattern of a single word.
(A) yuajiswe.iʃʃ which expresses consternation and/or grief. In about 30% of cases it is shortened to swe.iʃʃ only.
It means ... (say "iʃʃ" for us)
(B) hambətunmazore which expresses great joy. In about 70% of cases it is shortened to hambətun only.
It means ... (the gates to heaven have opened)
(C) And finally when somebody is telling a story or giving detailed instructions, you might say plirai at suitable intervals. This is simply a contraction of plìr ʔai? ... "do you follow ?"
(D) ... OK, we are scrapping the bottom of the barrel here. Not an exclamation in béu but maybe an exclamation in another language ... hù nén.
It expresses sudden consternation/dismay, equivalent to ... WHAT !!
(E) kè kè = "sorry" or "excuse me" ... Related to the word kelpa meaning "to apologize".
(F) sè sè = "thank you" ... Related to the word senda meaning "to thank".
(G) mwehu dè = "voila", "look at this" ... I guess an idiom because if the object to be looked at is senko, the phrase should be mwehu nende [ However if the thing to be looked at is an event ... then mwehu dè is grammatical.
(H) jonjau.e = wait a moment ..
... How béu codes definiteness
..
In English if the definite article "the" comes before a noun it means that the noun is specific to both the speaker and the spoken to ... that is [S 1 1]
Also in English if the indefinite article "a" comes before a noun, it means that the noun is non-specific to the spoken to ... that is [S 0 0]
[S 1 0] is coded the same way as [S 0 0]. Most modern Western European languages do things in a similar way. However it is possible to code [S 1 1] and [S 1 0] together. For example ...
..
..
béu follows Futuna-Aniwa and Samoan in codeing [S 1 1] and [S 1 0] the same way. For [S 1 1] and [S 1 0] the noun comes before the verb, for [S 0 0] (which includes both [S 0 0 1] and [S 0 0 0]) the noun comes after the verb. So we have ...
bàu doikori = The man walked / A man walked ..... [S 1]
doikori bàu = A man walked .................................. [S 0]
The first example encompassing both [S 1 1], [S 1 X] and [S 1 0]. Actually in béu ... for [S 1 0] if the speaker intends to talk about this object for a bit (if he intends to make it "known" to the listener) then the first time it is mentioned this object will have ʔà "one" in front of it. If it is a plural object it will have nò in front of it and the object itself will appear in its base form. For example ...
ʔà bàu doikori ... = This/a man walked ... (I know who but you do not)
nò bàu doikuri ... = These men walked ...
..
béu can also code indefiniteness by the particles ín and èn. These two particles are nearly used in the same way as "any" and "some" (see Haspelmath's Implicational Mapin the previous section). See below ...
..
..
(??? what about using glu.ia "known" ... glu.ua "to be known" ... uglu.ia "unknown" ... uzwia "unsaid" ??? )
..
Addendum
..
*Futuna-Aniwa (Dougherty 1983: 135, 23)
a) na-n tukia ta fatu
pst-1sg hit spec rock
‘I hit against a rock.’
b)
a roroveka kaseroitia ma sa ika aratu
art Roroveka catch neg nonspec fish tomorrow
‘Roroveka won’t get any fish tomorrow.’
..
Samoan ...
o sa fafine = a woman
o le fafine = a woman
..
... 16 common words in a neat 4x4 matrix
..
Sixteen very common and useful little words are given in the table below ...
They obviously were erosions of what were two word expressions. For example *ú pú "all people" => upu. For the indefinite particles èn and ín it appears that an inversion of normal words order has also happened. These 16 words are mandatory ... for example ... if you heard *ú pú instead of upu you would think it very very strange.
..
| uda | everywhere | uku | always | upu | everybody | ufan | everything |
| juda | nowhere | juku | never | jupu | nobody | jufan | nothing |
| ida | anywhere | iku | anytime | ipu | anybody | ifan | anything |
| eda | somewhere | eku | sometime | epu | somebody | efan | something |
Eight of sixteen have plural forms. Six of these eight give you a choice ... use a special correlative form or use a generic noun with the relevant indefinite particle. For example ...
| ida | anywhere | iku | anytime | ipu | anybody | ifan | anything |
| nda ín or inda | any places | nkyu ín or inku | any times | mpu ín or impu | any people | fanyoi ín | any things |
| eda | somewhere | eku | sometime | epu | somebody | efan | something |
| nda èn or enda | some places | nkyu èn or enku | some times | mpu èn or empu | some people | fanyoi èn | some things |
..
(Note to self : resolve the stuff below)
The columns are related to the words ... dàn = place ... kyùs = time/occasion ... fanyo = thing
upu can mean "each person" and "all the people". If they act together uwe can be added. If they act individually bajawe can be added.
..
... The non-alphabet symbols
..
Below are a list of shorthand symbols which are commonly used. Punctualtion symbols are also shown (on the RHS).
..
..
... Animal noises
..
The name and animal noise for cat and pig are identical. That is pigs go sú sú and cats go méu. Also dogs go wáu wáu (probably some connection to their name waudo). They also howl háu háu as do wolves.
Sheep and goats go mé and cows go mù. Actually the last three cries tend to break the phonological rules. Maybe a more faithful rendering would be háuuu, mé?é?é and mùu, but they are always written as háu, mé and mù.
Notice that animals smaller than humans have high tone cries, while animals bigger than humans have low tone cries.
..
By the way, wáu also means a pair of eyes and háu also means ???.
..
... Index
- Introduction to Béu
- Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds
- Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
- Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
- Béu : Chapter 4 : Adjective
- Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
- Béu : Chapter 6 : Derivations
- Béu : Chapter 7 : Way of Life 1
- Béu : Chapter 8 : Way of life 2
- Béu : Chapter 9 : Word Building
- Béu : Chapter 10 : Gerund Phrase
- Béu : Discarded Stuff
- A statistical explanation for the counter-factual/past-tense conflation in conditional sentences