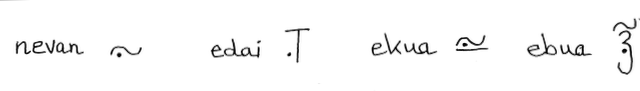Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
..... The 7 types of word
..
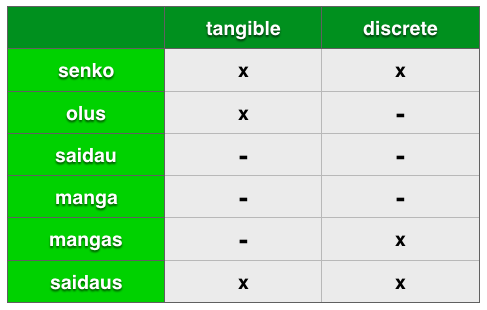
All words belong to one of the following 7 categories ...
..
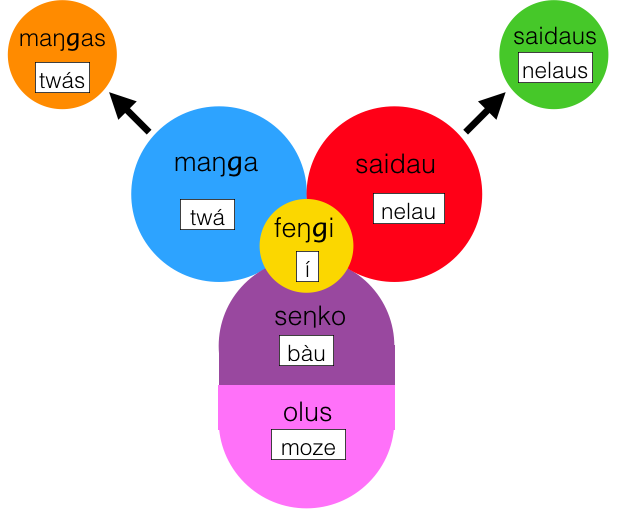
1) feŋgi = particle ... this is a sort of "hold-all" category for all words (and affixes) that don't neatly fit into the other categories. Interjections, numbers, pronouns, conjunctions, determiners and certain words that would be classed as adverbs in English, are all classed as feŋgi.
An example is Í .. the preposition indicating the dative.
..
..
2) seŋko = object
An example is bàu ... "a man"
..
3) olus = material, stuff
An example is moze ... "water"
..
4) saidau = adjective
An example is nelau ... "dark blue"
..
5) maŋga ... It is the basic form of the verb. Not considered or a noun or a verb (however the verbs built up from it by adding suffixes ARE considered full verbs.
An example is twá ... "to meet"
..
6) maŋgas = a noun derived from a verb. A maŋgas is derived from a maŋga just by suffixing -s. The maŋgas means one instance of the activity denoted by the maŋga. For example ...
twá = "to meet" ...... twás = "a meeting" ...... nò twás = meetings
holambu = "to explode" ..... holambus = an explosion ..... nò holambus = explosions
Also a game, a thought, a song, a run
..
7) saidaus = a noun derived from an adjective. A saidaus is derived from a saidau just by suffixing an -s. The saidaus means one object possessing the property denoted by the saidau.
An example is nelaus = a/the dark blue one ....... nò nelaus = a/the dark blue ones
..
..
... Seŋko
..
seŋko => noun OR noun phrase
seŋko baga => noun
seŋko kaza => noun phrase
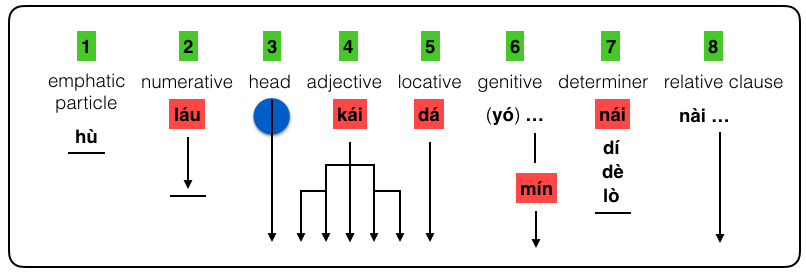
seŋko can have upto 8 elements.
Below is shown the order in which they must occur.
..
..
Elements 1, 2, and 7 have restricted membership, if fact element 1 has only one possibility, the word hù. The words with red background convert the noun phrase (or indeed the sentence in which the NP is embedded) into a question. A blue circle indicates the only mandatory element. Branching arrows indicate multiple possibilities.
3) ... the head \ seŋko baga
4) ... the adjective
More than one adjective is allowed. For example ... bàu gèu tiji = the little green man
kái "what type" can appear in this slot. In which case it turns the whole noun phrase (or sentence) into a question. For example ...
bàu gèu kái = what kind of green man ? ... noun phrase question
bàu gèu kái glà timpori = what kind of green man hit the woman ? ... sentence question
5) ... the locative. For example ... bàu gèu tiji pobomau = the little green man on top of the mountain
A locative comprises of a noun plus a locative pilana ... also the pilana meaning "from" ... so in total "noun" + pi la mau goi ce dua bene komo ?e fi
dá "where" can appear in this slot. In which case it turns the whole noun phrase (or sentence) into a question. For example ...
bàu gèu dá = where is the green man ?
6) ... the genitive. For example jwado gèu nambomau yó jene = Jane's big green bird on top of the house
Note that the particle yó is usually dropped when the possessor is next to the head. However as other elements intervene, the likelihood that yó is used increases.
If mín (who) is used instead of jene in the above ... then we would have a question ...
jwado gèu nambomau yó mín = Whose big green bird on top of the house ? = Whose's the big green bird on top of the house ?
7) ... the determiner
There are two determiners ... dí (this) and dè (that). For example ...
bàu gèu tiji pobomau dé = that little green man on top of the mountain.
The primary meaning is for comparing two objects that can be seen. Perhaps accompanied by gestures, dé will be appended to the further of the two objects and by way of distinction, dí will be appended to the nearer one.
nái (which) can appear in this slot. In which case it turns the whole noun phrase (or sentence) into a question. For example ...
bàu gèu tiji nái = which little green man ? ... noun phrase question
bàu gèu tiji nái glà timpori = which little green man hit the woman ? ... sentence question
Also lò "other" appear in this slot ... bàu gèu tiji lò = "the other little green man" or "another little green man"
Note ... dían => here, dèn => there ... not *dà dí and *dà dè
Note ... dí dè never appear independently as they do in English and many other languages. For example "this is good" => nèn dí r bòi .... literally "this THING is good"
Actually the above expression usually amalgamate to one word ... nendi r bòi "this is good" ... nende r bòi "that is good"
Note ... nò nendi is further contracted to => nodi' and nò nende' => node
2) ... the numerative
Any number can go in here ... also jù "no" and nò "plurality particle".
láu (how many) can appear in this slot. In which case it turns the whole sentence into a question. For example ...
láu bàu r pobomau = How many men are on top of the mountain ?
With more complex seŋko baga it is usual to break it up in order to specify exactly which element is being questioned. For example ...
láu bàu gèu tiji pobomau nài doikura = " How many little green men on the mountain that are walking? " ... would be re-phrased as ...
wò bàu gèu tiji pobomau _ láu doikura = w.r.t. the little green man on top of the mountain, how many are walking ? ... or ...
wò bàu tiji pobomau nài doikura _ láu r gèu = w.r.t. the little man on top of the mountain who are walking, how many are green ?
8) ... the relative clause
Relative clauses "RC" work pretty much the same as English relative clauses. The relativizer is nài (that, who). Here are some examples ...
yiŋkai nài doikore = the girl that has walked
bàu nài glás timpore = the man whom the woman has hit
glá nàis bàu timpore = the woman who has hit the man
bàu nàin glás fyori yiŋkaiwo = the man to whom the woman told about the girl
glá naiji bàus bundore nambo = the woman for whom the man has built a house
All the pilana can be appended to the relativizer to specify what roll the noun would have in the relative clause if it was a simple clause.
1) ... the emphatic particle is hù.
hù is used where we would use what is called "right dislocation" in English. For example ...
bàus hù glán nori alha = It is the woman to whom the man gave flowers.
bàus hù glán nori alha @ = Is it the woman to whom the man gave flowers ?
hù might be used in exasperated when somebody can not see something. For example ...
| hù nendi | "this one !" | hù nende | "that one !" |
| hù nodi | "these ones!" | hù node | "those ones !" |
This can also used as a sort of vocative case ... not obligatory but can be used before a persons name when trying to get their attention. For example ...
hù jene = Hey, Jane
hù gì = Hey, you
..
... Olus
..
The olus kaza has the same stucture as seŋko kaza except for the second element
the second element is replaced with three elements ... call them elements (9), (10) and (11)
(9) is a numerative, (10) is called "holder" and (11) is the particle yó
we have come across yó before. it indicates possession, in this case no actual possession but a sort of "extention" of possession. For example ...
ifa hoŋko yó ʔazwo pona = two cups of hot milk
where element (9) is ifa "two", element (10) is hoŋko "cup" and element (11) is yó
Note ... just as yó is often dropped from seŋko kaza, (11) is often dropped if olus kaza is short. For example ...
ifa hoŋko ʔazwo = two cups of milk
Nouns denoting quality are olus through derived originally from saidau. For example ...
nelaumi = blueness (from nelau "dark blue") and geumai = greenness (from gèu "green")
..
... Saidau
..
The saidau has two uses in the béu. It can either be part of a NP or it can be a copular complement. For example ...
bàu gèu = a/the green man
bàu r gèu = a/the man is green
..
... Maŋga
..
Not really a verb or a noun. Maybe corresponds to what is called "infinitive" or "masDar" in other languages.
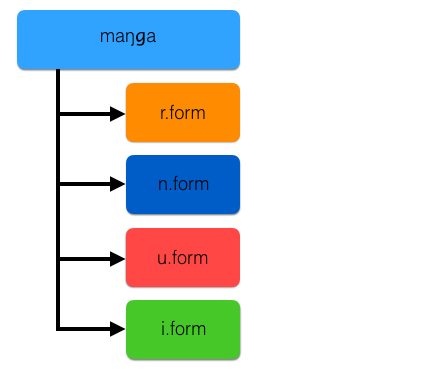
Lets take the solbe to explain these different forms. solbe is a maŋga and it would be found in the dictionary ... and if it was an English/ béu dictionary ... the translation "to drink" would lie alongside it.
An example of one of its (many) r.forms is solbori = He/she/it drank ....... so the r.form corresponds to a verb in indicative mood.
An example of one of its (handful of) s.forms is gò solban = I wish I could drink ....... corresponds to a sort of subjunctive mood.
The u.form (only one u.form per word) is solbu = drink ! ....................... so the u.form corresponds to a verb in imperative mood.
The i.form (only one i.form per word) is solbi ... this is the fornm used in verb chains and will be explained later.
We will go into a lot more detail about all these forms in the next chapter.
..
..
WHAT ABOUT THE ORDER OF MANGA KAZA ???
... Maŋgas
..
maŋgas => noun OR noun phrase derived from a verb
maŋgas baga => noun
maŋgas kaza => noun phrase
maŋgas can have 8 possible elements.
These elements are exactly the same as the ones detailed in the seŋko section above ... of couse the third element would be a maŋgas baga instead of a seŋko baga.
..
... Saidaus
..
saidaus => noun OR noun phrase derived from a adjective.
saidaus baga => noun
saidaus kaza => noun phrase
saidaus can have 8 possible elements.
These elements are exactly the same as the ones detailed in the seŋko section above ... of couse the third element would be a saidaus baga instead of a seŋko baga.
Actually saidaus can be derived from "locatives" and "genitives" as well as from saidau. For example ...
pobomaus = the one on top of the mountain
yós jene = the one belonging to Jane
..
... Other ... to be thought about more
..
What about taking more question words out of the big NP as I done in "numerative" ?
What about when dì and dè are the head. Of course the determiners are disallowed when dì and dè are in this slot ???
What about when pronouns are the head.
I still haven't resolved the ANY question.
bàu gèu tiji pobomau nái = which little green man on top of the mountain.
bàu gèu tiji pobomau kái = what type of little green man on top of the mountain.
Go into locatives more ... are they restricted to the pilana ? ... are they full blooded adjectives ?
Furthermore a maŋga can also be expanded into what is called a maŋkas*. Maybe best translated as "gerund phrase". The structure of a maŋkas can be derived from the structure of helkas ... Oh wait a minute, we haven't said what a helkas is yet ...
Just as a maŋga can be expanded into a maŋkas, by adding elements ... and the seŋko into a seŋkas ... a helgo can be expanded into a helkas .. "a clause".
OK ... now that we know what a helkas is we can go back to the maŋkas. Mmmhhh ... maybe the best way to explain it is just to do an example ...
falaja jonos jene timpuri pobomau "John hit Jane in the afternoon on top of the mountain" .... this is a helkas
The corresponding maŋkas would be jono timpa jene pobomau falaja ... "John's hitting Jane in the afternoon on top of the mountain"
The above maŋkas could appear in a clause as S, O or A argument.
..
Opening a door to the harem, revealing 67 scantily clad houries
1) You can fuck any one.
2) You can fuck every one.
NOT SAME
..
For uncountable nouns ( sand fandaunyo ) as opposed to countable nouns ( brick fandaunyo ) the construction is a bit different. See below ...
Another way in which this construction differs from a "brick" fandaunyo is that there is a magnifier slot. This can be filled with just one word ... well two words if you count hè's derived polar opposite uhe as a separate word.
Now as hè also qualifies other parts of speech, we have some ambiguity here. For example ...
moze pona hè can mean either a lot of hot water or very hot water. One can disambiguate by saying moze pona hè . moze hè / moze pona . moze hè meaning a lot of hot water or moze pona hè . pona hè / moze pona . pona hè meaning very hot water.
..
maŋkas
maŋga => maŋkas
[ Note ... lailas = one art of singing, Champaign Supernova would be called a ???? ]
..
..
..
If there is any entry in this slot, the head noun will be singular.
I call it the numerative slot instead of just number slot, because some entries allowed are not strictly numbers.
..
Some trivia ...
If one were to say ...
Roger is bla bla bla, Jack is bla bla bla and Charlie is Roger is bla bla bla. All three are bla.
In béu you would not say "all three", but rather "the threesome" (leume) ... which is a head noun rather than a number. OK ... when talking about mathematics we come across it, but otherwise you do not find numbers occurring by themselves.
In a similar manner, "no three" = jù leume and "any three" = ʔài ʔài leume
.. ..
..
..
MORE ON THE SENKO SECOND ELEMENT .... to think about ???
If there is any entry in this slot, the head noun will be singular.
I call it the numerative slot instead of just number slot, because some entries allowed are not strictly numbers.
All numbers can go in this slot of course. Also the particle nò ("number") can go in this slot.
ʔà = one. So also ...
ʔà = some (for singular noun)
ʔài = some (this makes the noun plural)
ʔà ʔà = any (for singular nouns)
Also we can have ...
| ú | all | jù | no | ||
| hài | many | yahai | a moderate number | iyo | few |
| haige | more | iyoge | less | ||
| haimo | most, a/the majority | iyomo | least, a/the minority |
haige and iyoge can also be qualified by a number (to qualify exactly how much the increase or decrease should be). In béu the number comes last. For example ...
haige hói = two more ... In actual fact, although this is permitted, it is very very rare. Usually it is hè hói. For iyoge followed by a number, there is no such contraction.
MORE ON THE SENKO EIGHTH ELEMENT ... to think about ???
As English has restrictive relative clauses and non-restrictive relative clauses "NRRC" ... so has béu.
a) ... RNC ... yiŋki nài r doikala nambon sùr hauʔe = the girls that are walking home are pretty
b) ... NRRC ... yiŋki _ nài r doikala nambon _ sùr hauʔe = the girls, that are walking home, are pretty ... (a pause (gap), I represent by "_" )
In b) the NRRC is giving us extra information about the girls.
[ Some thoughts ... I guess a RC is a bit like an adjective and it directly qualifies a noun. A NRRC is a bit like the second element in apposition. It is giving us extra information about the noun (which might otherwise be given in a separate utterance). Both NRRC and the second elements in apposition are isolated using pauses. ]
In English you get what is sometimes called a headless relative clause "HRC" or a free relative clause ... I guess "free from a noun" is the thinking behind the second term.
"What you see is what you get" is an example of a HRC ... well two examples to be precise.
We have exactly the same in béu ...
hù bwáir or hù màir = what you see is what you get
[You could also say ... dè hù bwáir or dè hù màir ... but this would be considered a bit stiff, a bit pedantic
NDONESIAN
Note ... even though we have no word "of" ... there is no ambiguity. If the above was two fandaunyo, there would either be a pause between hoŋko and ʔazwo (for example if one was A and one was the O argument), or they would be separated by "and" lé if they were separate fandau.
In this respect béu takes after Indonesian. For example ... five big bags of this black rice = lima tas besar beras hitam ini (literally ... five bag big rice black this)
three bags rice brown three bags big (full) wrt rice brown
(5 bag big) (rice black this) .... Usually languages have a linker, particular when the phrases are long. For example Chinese "de", English "of", Japanese "no". béu has no linker (similar to Indonesian) ... (however à or fí could be pressed into service if needed ??? )
(SideNote) ... ʔazwe = to suck ... ʔazweye = to suckle, to offer the breast
..... helkas
helgo => helkas ..
Another important word category is helgo .. "finite verb". That is .. a verb in its r.form, s.form, u.form or i.form.
So helgo are derived from manga. [related words ... helga = "to live" and helgi = "alive"]
..... More details about maŋkas and colwaikas
..
As we know, the main elements in a helkas are free. That is the S, A and O arguments can appear either side of the verb. However in other areas word order is not so free. For example in copula clauses. Also maŋkas does not have free word order. So how exactly is it done ... how do we derive maŋkas which has fixed word order from seŋkas which has free word order. Well the element that is marked on the helkas by the vowel just before the "r", comes immediately to the left of the maŋga. Also note that even though this is often dropped in seŋkas it can not in maŋkas*. The O argument (naked noun) of the helkas must come immediately after the maŋga in the maŋkas. Any other peripheral arguments are stuck on at the end.
The helkas = solbari saco he? moze pona = I drank some cold water very quickly
Derived maŋkas = pà solbe moze pona sacowe ... which can be an argument in another helkas or copula clause ...
pà solbe moze pona sacowe r kéu = my drinking the cold water quickly was bad
..
.*Well actually it is dropped in certain circumstances. For example ...
ʔár solbe moze = I want to drink water
..
If you see a maŋga surrounded by other elements, how do you know if you have a maŋkas or a seŋkas. Well in the maŋkas the manga can not be plural or have any possessors for one thing. For another thing a maŋkas can only take a subset of the pilana. While a seŋkas can take all 17 pilana a maŋkas is restricted to 7 ... là, máu, gòi, tú, jì, só and wò.
dói = month, doiwe = monthly
..
..... Pronouns
..
Here, for a transitive clause, "that which initiates the action" is called the A argument, and "that which is affected by the action" the O argument. Also, for an intransitive verb, the noun is called the S argument. It is convenient to make a distinction between all three cases. I follow the linguist RMW Dixon in using this terminology.
In most languages the S argument is marked the same way as the A argument. However in some languages the S argument is marked the same way as the O argument. These are called ergative languages. béu is one of these ergative languages. About a quarter of the world languages are ergative or partly ergative.
Below are the béu pronouns for the S and O arguments. This form can be considered the "unmarked form".
..
| me | pà | us | wìa | inclusive |
| us | yùa | exclusive | ||
| you | gì | you | jè | |
| him, her | ò | them | nù | |
| it | ʃì | them | ʃì |
..
Below are the pronouns for the A arguments ( the ergative arguments ).
Pronouns differ from nouns in that their tones change between the ergative and the non-ergative form. This is in addition to the normal suffixing of -s when a noun becomes marked as ergative.
..
| I | pás | we | wías |
| we | yúas | ||
| you | gís | you | jés |
| he, she | ós | they | nús |
| it | ʃís | they | ʃís |
..
jè and jés are the second person plural forms.
There is one other pronoun ... the reflexive pronoun tí. This is always an O argument. Notice that it is the only O argument with a high tone.
There is a strong tendency for it to come after the A argument. For example ...
jonos tí timporja jindin = john has not yet hit myself
This particle can be amalgamated to the infinitive to give a reflexive infinitive. For example ...
timpa = to hit ... ti.timpa = "to self-hit"/ "to hit oneself"/"to hit yourself"
[ A dot is used to show that the word comprises two separate elements. I suppose most linguists would use "=" to show cliticization. The dot makes no difference to the pronunciation ]
I suppose I should also mention the reciprocal particle bèn at this point. It always follows the verb. For example ...
jonos jenes timpur bèn = John and Jane hit each other.
The plural pronouns above can also combine with specifiers (and number) to make pronoun phrases.
Below is a table with nù "them".
The other plural pronouns pattern in a similar way. That is ... yùa, wìa, jè and ʃì
..
| jù nù | none of them | ù nù | all of them | ||
| í nù | any of them | é nù | one of them | éu nù | some of them |
| hài nù | many of them | iyo nù | few of them | ||
| haige nù | more of them | iyoge nù | less of them | ||
| haimo nù | most of them | iyomo nù | a minority of them |
..
Notice that nò uhai haizo and haizmo are 4 specifiers that are never used with pronouns. I don't know why.
..
..... Word order
..
In English it is the order of the verb and the arguments that shows who is the doer and what is the "done to". Namely the A and S argument come before the verb and the O argument after.
[ English is a non-ergative language and hence the A and S argument get treated in the same way. ]
In béu, to show who is the doer and what is the "done to", the suffix -s is appended to the A argument. For example ...
glás bàu timpra = The woman has hit the man
glá bàus timpra = The man has hit the woman
bàu r doikala = The man is walking
[ béu is an ergative language and hence the O and S argument have the same form. ]
But even though béu doesn't use word order to show who is the doer and what is the "done to", it does use word order for another purpose. Namely to show if an argument is definite* or not. For example ...
bàu doikr = The man walks
doikr bàu = A man walks
So we see ... an argument coming before the verb is definite and one coming after the verb is indefinite.
[ *And when we say definite, we mean that the person being spoken to can identify X as one particular X instead of some X or any X. ]
In English only 2 orders are found. Namely ... SV and AVO ... (V = verb). However in béu you have what is called "free word order". This means that you can come across the following 8 orders ... SV, VS, AVO, AOV, VAO, OVA, OAV and VOA.
But actually in a piece of discourse, it is most likely that the S or A argument are old information and probably the topic (the thing that you have been going on about for some time). In béu an established topic is usually dropped and so the 8 sentence types shown above collapse into 3 sentence types. Namely ... V(s), O V(a) and V(a) O
[ V(s) represents a verb marked for the person/number of the S argument and V(a) represents a verb marked for the person/number of the A argument ]
..
..... The Case System
..
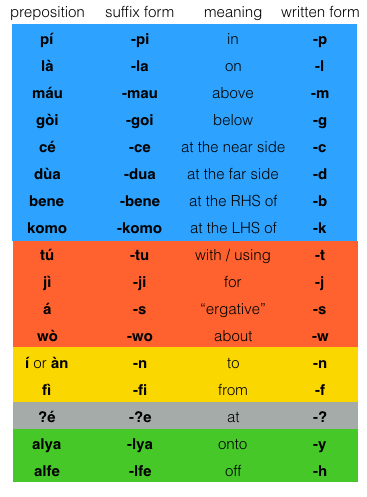
We have just mentioned the ergative case. In total there are 17 cases of course (if you were to include the unmarked case as well you have 18 different forms). They are called the pilana.
These are attached to a noun and show the relationship of that noun with respect to the rest of the sentence.
The word pilana is built up from ;-
pila (v) = to place, to position
pilana (a, n) = positioning, the positioner
..
..
The pilana are either realized as affixes or as stand-alone prepositions. If they are realized as affixes then, in the béu script uses a sort of shorthand. That is the affix is represented as one letter.
Whether the pilana appears as an suffix or a preposition depends on the noun phrase ... if the NP is only one word => suffix : NP more than one word => preposition. For example ...
nambodua = beyond the house
dùa nambo yinkai hauʔe = beyond the house of the pretty girl
[Also for pilana 11 and 13 .... a preposition is used if the noun ends in a consonant]
..
![]() ........................................... Specific Location ...................................................
........................................... Specific Location ................................................... ![]()
The first 8 define location.
1) -pi = in
2) -la = on
3) -mau = above, over, on top of
4) -goi = below, under, underneath, beneath
5) -ce = this side of
6) -dua = beyond, at the far side of
7) -bene = right, at the right hand side of
8) -komo = left, on the left hand side of
These are used to give a location with respect to some object. For example …
nambopi = in the house
nambomau = on the house, over the house
[ Note ... in a lot of situations, where "on" would be used in English, "above" is used in béu. For example ...
"John is on the mountain" = "jono r pobomau" not "jono r pobola" ]
.............................................................................................................................................. ![]()
 ...................................................... Roll .............................................................
...................................................... Roll ............................................................. 
The next 4 define the roll that the noun plays in the sentence.
9) -tu = with, using
He/she works as a doctor = kodor moltai.tu
He/she exercises by running = xxxor jaŋkastu
10) -ji = for, for the benefit of
11) -s = “the ergative case”
12) -wo = about, with respect to
bàus glaji nambo bundore kontotu = the man has built the house for the woman with a hammer
gala bauwo catur = the women talk about the man
![]() ...........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................... ![]()
![]() ......................................................... Motion .......................................................
......................................................... Motion ....................................................... ![]()
The next 2 specify motion.
13) -n = to
14) -fi = from
Now these are used to give a motion with respect to some object. For example …
nambon = to the house
nambofi = from the house
The prepositional form of 13) varies. If the NP begins with a vowel, then àn is used, if the NP begins with a consonant, then í is used.
 .............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................. ![]()
![]() ............................................. General Location ...................................................
............................................. General Location ................................................... ![]()
The next is a “general locative”.
15) -ʔe = at, on, in
glá (yó) pà r namboʔe = My wife is at home
flovan gì r pazbaʔe = Your food is on the table
boloŋgai r flovanʔe = the flies are at the food (some buzzing around and some crawling on the surface of the food)
boloŋga r flovanʔe = the fly is at the food (sometimes buzzing around and sometimes crawling on the surface)
boloŋga r flovanla = the fly is on the food (i.e. its legs are touching the food)
![]() .............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................. ![]()
![]() .................................... Hybrids of motion & position ........................................
.................................... Hybrids of motion & position ........................................ ![]()
The last two define motion AND position. They are sort of hybrids of the second pilana and the pilana of motion.
16) -lya = onto
17) -lfe = off
![]() ...............................................................................................................................
............................................................................................................................... 
.. As parts of speech
..
pilana of location phrases (i.e. nouns with 1 -> 8 or 15) can be considered adjectives if they come after a noun and adverbs if they come after a verb. They must come after a noun or a verb. Sometimes they come after the copula*. In this case they are adjectives. Now often the copula is dropped ... but if this dropping results in any ambiguity it can be readily "undropped".
pilana of motional phrases (i.e. nouns with 13, 14, 16 or 17) can be considered adverbs. They can come in any position because it is understood that they are qualifying the verb.
pilana phrases defining sentence rolls (i.e. nouns with 9, 10, 11 or 12) can come anywhere. They are considered nouns.
* [ Notice that in English, you can either say ... "a bird is in the tree" or "in the tree is a bird"
In béu only jwado r ʔupaiʔe is valid ... also note that in this case jwado is not definite because it is left of the verb. That rule doesn't work with the copula. ]
..
..... Punctuation and page layout
..
The letters in a word are always contiguous, that is there is always a line running right through the word. Writing is firstly from top to bottom and secondly from left to right.
Between words there is a small break in the line. The break should be 25% the height of a letter.
When telling somebody how to spell a succession of words, this small break would be indicated by dù
Between some words there is a gap. This represents a pause. A pauses in English is represented by a comma, a colon or a semicolon. Whenever an orator draws breath, this will be reflected in the writing by a gap. Also there are occasions where the grammar of béu demands a gap. A gaps hould be 75% the height of a letter. When such a gap is required I will represent in in my transcription as an underscore. (I could have used a comma, however I prefer not too ... presumable in English, commas originally were always used for pauses in speech. However nowadays in English many pauses are not represented in any way (presumably in these cases when it is not necessary for reading comprehension. Also in English, in a surprising amount of text commas are found where they shouldn't be. In béu gaps in a textblock have a one-to-one correspondence to a pause in speech).
*When listing items, béu is similar to English ... there is pause between every item except the last two items. Between these items, béu has lé, English has "and".
..
suna_dunu_celai lé àu = "orange, brown, pink and black" ... notice the two gaps and then the two breaks in the béu script above.
By the way, this would be spelled out as ... ‘’’sadu sanu nùa sana jù_duzu sanu nùa sanu jù_compa sane lata sanai dù_lata dite dù_sanau dù dù’’’
..
When telling somebody how to spell a succession of words, the gap is indicated by saying jù
Single gaps are very common. Occasionally you can have "double gaps" and even "treble gaps". These rare creatures represent "pregnant pauses" which are sometimes used for comic effect.
When telling somebody how to spell a succession of words, a "double gap" is rendered by bauva ??? , a treble gap by baiba ???.
Note the single point used in the "double gap" and the pair of points used in the "treble gap".
For a "double gap" there should be 75% letter height space above and below the dot. For a "treble gap" it is the same plus a 25% letter height space between the two dots. ..
..
There is also a punctuation mark called the "sunmark" ( kòi = sun ). This is basically a full-stop. The "sunmark" has double the diameter of omba (omba means "circle" and is used as a decimal point).
..
There are also punctuation marks called "moonmark" ( dèu = moon ). These are basically brackets. The opening one is called "moonmark" damau and the closing one is called "moonmark" dagoi. Direct speech is enclosed in "moonmarks". These bits of direct speech are also highlighted. Usually the first speaker's words are highlighted in blue and the second speaker's words are highlighted in yellow. The highlighted area is lozenge shape. Every "textblock" the protagonists are reset ??. In a story, after the scene is set ... that is the time of speaking and the identity of the speakers have been established, then their names are dropped from the text and the kloi "speak" is also dropped. However somebody reading the text out loud would give this information from their understanding of the situation.
..
..
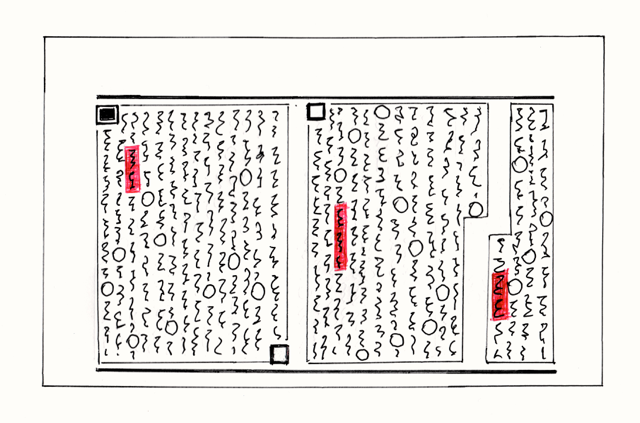
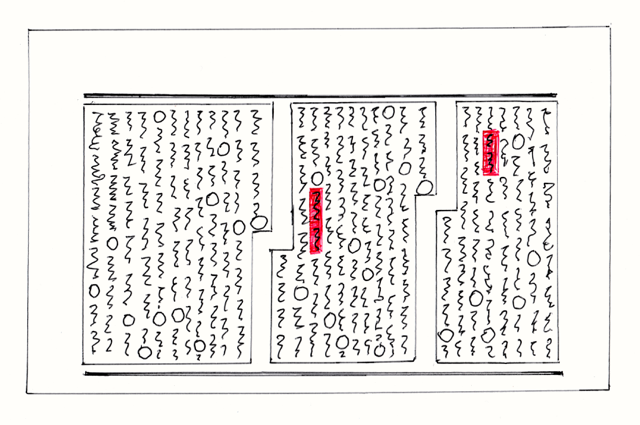
In a normal narrative, everything is written in "textblocks".
(Please note ... the light lines surrounding the "textblocks" are not real. They are just there to assist me drawing)
..
This is the first page in a "chapter". Notice the symbol at the top left hand side of the first "textblock". This is called a "heavy tile".
Textblocks fit in between "rails" about 4 inches apart. The width of a block should be between 60% and 90% * of the block height. Of course it is best to start a new block when the scene of the narrative changes or there is some discontinuity of the action, but this is not always possible. Then you just must arbitrarily split the text into two blocks. The standard practice is to stretch the text a bit so that the tops and bottoms of every column line up with their neighbours. XXXXXX
There is no way to split a word between two lines (as we can do in the West by using two hyphens). A "sunmark" must be next to the last word in a sentence (it can not go to the start of a new column by itself) However if a "sunmark" fall next to the bottom rail, then the next column will begin with a "sunmark". This is purely due to a love of symmetry.
The first text block starts at the top left (as you would expect). The second textblock starts below where the first text block stops. In fact the vertical space between the stop and the start of the two textblocks is equal to the horizontal "interblockspace" (see the figure above).
If the last "sunmark" of a "textblock" falls next to the bottom rail (as indeed happens with the very first "textblock" of the "chapter", then this "sunmark" is changed into a symbol called a "bottom tile". If a "textblock" ends in a "bottom tile", then what is called a "top tile" will appear before the first word of the next "textblock". This is purely due to a love of symmetry. Note that the "top tile" is exactly the same as the "bottom tile". (Actually in modern printing techniques, the text in complete "textblocks" can be stretched to prevent the final "sunmark" falling on the bottom rail)
When you come to the end of the page (you will have some sort of margin of course and not go all the way to the edge), you simply continue the block on the LHS of the next rail (or page). Below is the second page of the chapter. This page continues on from the page above.
..
..
In every textblock, one word or short noun phrase is highlighted in red. The shape of the highlighted area is rectangular with rounded edges. Usually a noun is chosen and the more iconic the better. Statistically these highlighted words tend to come towards the beginning of the "textblock".
..
There are two sizes for books. For all hardback books the size is about 8 inches by about 11 inches. For all paperback books the size is about 5 inches by about 8 inches. They are stored as shown in the figure below.
..
..
Unlike books produced in the West, these books are held with the spine horizontal when being read. The hardback page has two "rails" per page (i.e. three dark lines).
On the paperback book, the title is written on the spine and on the front of the book. On the hardback book the title is written on the front, also there is a flap that slides into the spine. However when the book is stored on a shelf, it is pulled out and hangs down. Hence the hardback books can be easily located, even when they are in the bookshelf.
A book will be divided into chapters. A chapter will have a number and usually a title as well. Either at the end of the book or just after the chapter, there will be a page, in which all the highlighted words for a chapter are listed in order. Instead of referencing things by page number, things are reference by chapter and textblock (indictated by the highlighted word(s) ).
Any particular word in a book can be reference by 5 parameters ...
1) "title of book"
2) number of the chapter
3) the highlighted word(s)
4) the number of the sunmarks counted. Actually they are counted backwards ... from the final "sunmark" of the "textblock". Note ... all "sunmarks" are counted, even the ones next to the top rail.
5) the number of the word. This is also counted backwards (i.e. the final word of the sentence is word "1" ... and so on)
* Occasionally very narrow blocks can not be avoided. And of course in mathematical/scientific tracts the tracts are all over the place ... interspersed with diagrams and what have you.
..
..... Noun totality ... collective and individually
..
Sometimes we want to talk about all members of the category "noun" acting (or being acted upon) COLLECTIVELY.
For this we use the particle ú before the plural of the noun. For example ...
moltai = a/the doctor
moltai.a = doctors
ú moltai = all doctors
Note ... the same word, when appended to a noun, means "the whole" or "entire". For example ...
falaja ú = all morning
..
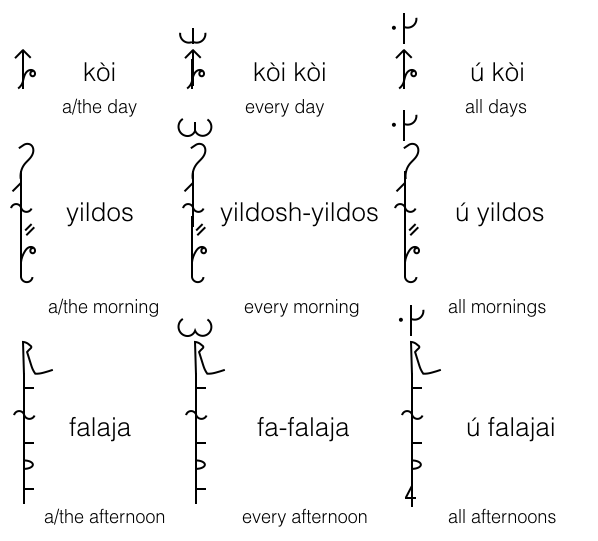
The opposite of the above, is when all members of the category "noun" is acting (or is being acted upon) INDIVIDUALLY.
By doubling the noun (or the first part of a noun) you give what can be called a distributive meaning.
Some examples ...
kòi = day
kòi kòi = every day
moltai = doctor
moltai moltai = each doctor
falaja = afternoon
fa falaja = every afternoon
Notice that for words over two syllables, only the first syllable is prefixed.
..
The "word-hood" of these duplications is murky. I am writing them here as two separate words ... i.e. fa falaja. But maybe fafalaja or fa-falaja would be more appropriate.
Single syllable words retain there tone when duplicated ... which indicates two separate words. However you also get phonological processes that are usually only word internal. That is to say, these structures show "sandhi".
For example ...
yildos yildos (every morning) would be pronounced / jildoʃ jildos /
bàu bàu (every man) could be pronounced / bàu vàu /
Anyway ... these constructions are never written out in full. Instead a special symbol is placed above the simple noun. This symbol can vary a bit, depending on the font being used : it can vary from a lower half circle bisected by a vertical stroke to a shape that looks a bit like the Arabic shaddah.
For example ...
It some contexts, semantically, it does not matter whether the individual or the collective form is used. When this is the case, the default choice is "individual" structure. ú tends to be used with tangible nouns more, it is hardly ever used with nouns denoting periods of time.
Note (as in English) the plural verb form is used for the collective structure, the singular verb form for the individual structure. For example ...
ú bàu súr = all men are
bàu bàu sór = every man is
TO THINK ABOUT ...
?à ?à bàu hù ?ís = any man that you want ( ?ís ... "you would want" ???? )
?ài ?ài bàu hù ?ís = any men that you want
?ài bàu = some men
..
..... lé .... lú .... lò
..
Earlier we have seen that when 2 nouns come together the second one qualifies the first.
However this is only true when the words have no pilana affixed to them. If you have two contiguous nouns suffixed by the same pilana then they are both considered to contribute equally to the sentence roll specified. For example ...
jonos jenes solbur moze = "John and Jane drink water"
In the absence of an affixed pilana, to show that two nouns contribute equally to a sentence (instead of the second one qualifying the first) the particle lé should be placed between them. For example ...
jenes solbori moʒi lé ʔazwo = "Jane drank water and milk"
jonos jenes bwuri hói sadu lé léu ʔusʔa = John and Jane saw two elephants and three giraffes.
[ Compare the above two examples to á jono jene solbori moze = Jane's John drank water ... i.e. The John that is in a relationship with Jane, drank water ]
This word is that is never written out in full but has its own symbol. See below ...
..
Note ... in the béu script, the "o" before "r" is always dropped. This is just a sort of short hand thing.
..
The following construction is also found.
lé moze lé ʔazwo = "both water and milk"
The above construction emphasizes the "linking" word lé
Another linking word is lú meaning "or".
jenes blor solbe moze lú ʔazwo = "Jane can drink water or milk"
The following construction is also found.
lú moze lú ʔazwo = "either water or milk"
The above construction emphasizes the "linking" word lú
There is another word that corresponds to the English "or". This is ʔala and it is a question word. For example ...
ʔís moze ʔala ʔazwo = "would you want water or milk"
And the answer expected of would be either "water" or "milk"
Say you were asking somebody if they were thirsty and you had only water or milk to give them. Then you would say ... ʔís moze lú ʔazwo ʔai@
The expected answer to the above question would be either "yes" or "no" (as is always the case when you have @ ( @ is pronouced a bit like ʔai but has contour tone instead of a normal high tone, it has a special symbol and I am using "@" to represent this symbol in my transliteration)).
Now if the question was "would you want water or milk, or both" you should say ...
ʔís mose ʔala ʔazwo ʔala leume
But sometimes (either because of the laziness of the speaker or because the likelyhood was not considered) ... ʔís moze ʔala ʔazwo ʔala leume comes out as ʔís moʒi ʔala ʔazwo.
So ʔís leume (I would like both) is an acceptable answer to the question ʔís moze ʔala ʔazwo
If the questioner would like to rule out the answer ʔís leume he would use the construction .
ʔís ʔala moze ʔala ʔazwo
So ʔala before the first item does exactly the same as lé or lú before the first item : it emphasizes the linking word.
..
... "no"
..
In béu, jù corresponds to "no".
"neither water nor milk" would be translated as jù moʒi jù ʔazwo
..
... lists
..
So far we have restricted ourselves to two items. We can summarize the system for two items as below ...
..
| lé | giving | 2 | items | |||||
| lú | giving | 1 | item | ..... | ʔala | asking for | 1 | item |
| jù | giving | 0 | items |
..
However we can join up more than two items. When more than two items are joined by the above 4 linking words, it is considered good style to have the linking word before the first item and the last item, before each item (except the first and the last) should be a slight pause (I call it a gap ... see "punctuation and page layout" earlier on this page).
For example ...
jenes bwori lé ifa sadu _ uba ʔusʔa _ ega moŋgo lé oda gaifai falaja dí = Jane saw two elephants, three giraffes, four gibbons and five flamengos this morning.
..
... other
..
lò = other
lòi = others
kyulo = again
welo = otherwise
..
..... Correlatives
..
| juvan | nothing | juda | nowhere | juku | never | jubu | nobody |
| ivan | anything | ida | anywhere | iku | anytime | ibu | anybody |
| evan | something | eda | somewhere | eku | sometime | ebu | somebody |
| uvan | everything | uda | everywhere | uku | always | ubu | everybody |
These correlatives are always written in their shorthand form. See the chart above.
The first column is a contraction of jù fanyo, í fanyo, é fanyo and ù fanyo (fanyo = thing)
The second column is a contraction of jù dà, í dà, é dà and ù dà (dà = place)
The third column is a contraction of jù kyù, í kyù, é kyù and ù kyù (kyù = time/occasion)
The last column is a contraction of jù glabu, í glabu, é glabu and ù glabu (glabu = person)
The non-contracted forms are still used, usually when emphasis is wanted.
There is another row in the above table.
This is the plural equivalent of the third row of the table above. The emphatic form of the above series would be ...
è fanyo, è dá, è kyù and è glabu .... if these elements were under* the main verb, it would be more normal to use ...
fanyoi, nò dá, nò kyù and glabua .... and actually, if any word from the third row of the main table came under the main verb, you could just use ...
fanyo, dá, kyù and glabu ... in this position you have probably a 50% chance of coming across evan and a similar chance to come across fanyo ... the same with eda, eku and ebu.
One interesting point is ... well for example ubu can mean "each person" and "all the people". If ubu was the S or A argument there could be one of two verbs in a SVC. One would have the meaning "to do together"/"to cooperate" and the other would have the meaning "to work alone". If ubu was the O argument or has some other roll in the sentence there is a partical that can be put in above* ubu. This particle means something like "individual" or "independent" and would disambiguate the meaning of the béu sentence.
*I was going to say 'after" and "before", however as the béu writing system is vertical I thought I should get in the spirit of things and use "under" and "above".
..
... Index
- Introduction to Béu
- Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds
- Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
- Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
- Béu : Chapter 4 : Adjective
- Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
- Béu : Chapter 6 : Derivations
- Béu : Chapter 7 : Way of Life 1
- Béu : Chapter 8 : Way of life 2
- Béu : Chapter 9 : Word Building
- Béu : Chapter 10 : Gerund Phrase
- Béu : Discarded Stuff
- A statistical explanation for the counter-factual/past-tense conflation in conditional sentences