Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
..... The Solid Verb
..
I call it the "solid" verb. Sometimes called an infinitive ... maSdar in arabic ... whatever.
A verb in its solid form (its most basic form) is called a maŋga
About 32% of multi syllable maŋga end in "a".
About 16% of multi syllable maŋga end in "e", and the same for "o".
About 9% of multi syllable maŋga end in "au", and the same for "oi", "eu" and "ai".
To form a negative infinitive the word jù is placed immediately in front of the verb. For example ...
doika = to walk
jù doika = to not walk .... not to walk
The solid verb can be followed by an A or S argument (with a yó in front), then an S argument (with a wò in front*), then any other arguments (these arguments taking there normal affixes or prepositions to show the arguments roll) ... to make a sort of nominalized clause.
*In formal speach ... yó and wò are always used. However in less formal registers it is possible to drop one or two of them ... as long as no ambiguity arises.
A maŋga can be an argument in a clause ... just as a seŋko can. For example ...
The kitten playing with the string and the monkey eating the cake was very amusing. ???
(a noun would have the determiner "this", maŋga has the determiner "thus" wedi(if you demonstrate the action)or wede (if someone else demonstrates the action))
???
..
..... The Main Verb
..
To make a verb in the indicative mood, you must first deleted the final vowel from the infinitive. Then add affixes that indicate "agent", "indicative", "tense/aspect" and evidentiality. We will refer to these as slots 1, 2, 3 and 4 respectively. Only the first three slots are mandatory.
..
... Slot 1
..
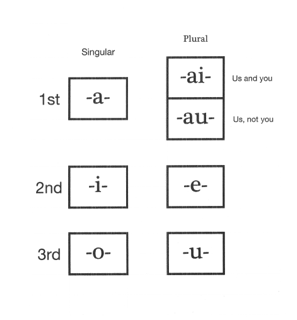
Slot 1 is for the agent ..
One of the 7 vowels below is must be added. These indicate the doer..
Notice that there are 2 entries that represent the 1st person plural subject (i.e. we). The top one represents first person inclusive and the bottom one represents first person exclusive.
Note that the ai form is used when you are talking about generalities ... the so called "impersonal form" ... English uses "you" or "one" for this function.
The above defines the "person" of the verb. Then follows an "r" which indicates the word is an verb in the indicative mood. For example ...
doika = to walk
doikar = I walk
doikair and doikaur = we walk
doikir = you walk
doiker = you walk
doikor = he/she/it walks
doikur = they walk
..
... Slot 2
..
Slot 2 is for the indicative marker.
..
At this point we must introduce a new sound and a new letter.
This letter has not been mentioned so far because it doesn't occur in any words as such. It only occurs in grammatical suffixes and it indicates the indicative mood.
If you hear an "r", you know you are hearing the main verb of a clause.
..
... Slot 3
..
Slot 3 is for tense and aspect markers
..
There are 7 tense/aspect markers in béu
1) doikara = I am walking
This is the present tense
2) doikaro = I walk
This is the aortist tense. It actually encompasses past, present and future. Used for generic statements, such as ... "birds fly".
Actually the final o is always dropped unless there is an n or an s in the evidentiality slot.
So doikaro => doikar = I walk
3) doikaru = I will walk
This is the future tense
4) doikari = I walked
This is the past tense
5) doikare = I have walked
This is the perfect aspect.
6) doikarai = I had walked
This is the past perfect.
7) doikarau = I will have walked
This is the future perfect.
..
The perfect tense, logically doesn't differ that much difference from the past tense,. but it is emphasizing a state rather than an action. It represents the state at the time of speaking as the outcome of past events. We have this tense/aspect in English and it is realized as "have -en".
For example if you wanted to talk to John and you went to his office, his secretary might say "he has gone to lunch, this emphasizes the absence of John as opposed to "he went for lunch". The latter is just an action that happened in the past, the former is a present state brought about by a past action.
For another example ... "she read the book on geometry"
This doesn't specify whether she read it all the way thru or whether she just read a bit of it. Whereas ...
"she has read the book on geometry", implies she read the book all the way thru, but more importantly the connotation is that at the present time she has knowledge of geometry.
..
... Slot 4
..
Slot 4 is for the evidential markers (well three out of four are evidential markers)
..
The final slot (slot 4) is for the evidential marker
There are three markers that cites on what evidence the speaker is saying what he is saying. However it is not mandatory to stipulate on what evidence you are saying what you are saying. In fact most occurrences of the indicative verb do not have an evidence marker.
The markers are as follows ...
1) -n
For example ... doikorin = "I guess that he walked" ... That is the speaker worked it out from circumstances/clues observed.
2) -s
For example ... doikoris = "They say he walked" ....... That is the speaker was told by some third party(ies) or overheard some third party(ies) talking.
3) -a
For example ... doikria = "he walked, I saw him" ...... That is the speaker saw it with his own eyes.
Note that the above evidential only co-occurs with the past tense.
Now there is a forth possibility for this slot ... and it is not actually an evidintial. Furthermore it has the same form as 3).
4) -a
For example ... doikorua = "he intends to walk" ... the agent in this case, of course, must be a sentient being (i.e. human).
Note that the above only co-occurs with the future tense.
..
..... The Side Verb
..
Let me introduce three dependent clause types here ... the "when" clause, the reason clause and the purpose clause.
1) ... the "when" clause is intoduced by the particle kyù (it is also a generic noun meaning "occasion"/"time" by the way). For example ...
kyù twaru jene ʃì òn fyaru = When I see Jane I will tell her.
Usually the English conditional particle "if"* is also translated as kyù
So ... "if I see Jane I will tell her" => kyù twaru jene ʃì òn fyaru also.
Now let's give the example sentence a habitual meaning ... say Jane fervantly supports Manchester United and the speaker always hears the latest results before Jane. So we have ...
*kyù twár jene ʃì òn fyaru = When I see Jane I will tell her.
Only that the main verb form is not allowed in these three dependend clauses ... if the verb has a final r it must be changed to a final s.
So the proper way to say "when I see Jane I will tell her" => kyù twás jene ʃì òn fyaru
[Now the question is "why substitute final r in a dependent clause, with s ... and it is a difficult question to answer. Maybe it is in recognition that in many natural languages, the verbs in dependent clause have a reduced number of possible forms (refer to what Sonja Cristofaro has written in chapters 125 -> 128 in WALS). Also I find utterance final s more pleasing than utterance r ]
*Other languages to conflate ? "when" and "if" are German (wenn) and Dutch (als). Actually if you really needed to disambiguate in béu you could use jindu meaning "as soon as" or fesʔa meaning "case"(as you can disambiguate in German, by using "sobald" and "falls")
* In English, there is another function for "if" ... it introduces a complement clause when the main clause verb is an "asking" verb. "whether" can also fulfill this function. The particle in béu that fulfills this function is wai.a. wai.a has only this function.
2) ... the reason clause is intoduced by the particle tà. (tà = "because")
XXXXXXX
3) As part of stand alone clauses ...
doikas = "should I walk" or "let me walk" or "how about me walking" or "can I walk" or "maybe I should walk"
doikis = "maybe you should walk" or "why don't you walk" or "how about you walking"
doikos = "let him walk"
doikos jono = "let John walk"
For transitive verbs ...
timpos baus waulo = let the man hit the dog
The negative subjunctive is formed by adding bù (or should that be jù). For example ...
bù doikos = best not to let him walk
They locked him up so that he would starve to death
They let him out at night so that he would not starve to death
..
..... The imperative verb
..
This is used for giving orders. When you utter an imperative you do not expect a discussion about the appropriateness of the action (although a discussion about the best way to perform the action is possible).
For non-monosyllabic verbs ...
1) First the final vowel of the infinitive is deleted and replaced with u.
doika = to walk
doiku = walk !
For monosyllabic verbs u is prefixed.
gàu = to do
ugau = do it !
The negative imperative is formed by putting the particle kyà before the infinitive.
kyà doika = Don't walk !
..
..... Examples of short verbs
..
In a previous lesson we saw that the first step for making an indicative, subjunctive or imperative verb form is to delete the final vowel from the infinitive. However this is only applicable for multi-syllable words.
With monosyllabic verbs the rules are different.
..
For a monosyllabic verbs the indicative endings and subjunctive suffixes are simply added on at the end of the infinitive. For example ...
swó = to fear ... swo.ar = I fear ... swo.ir = you fear ... swo.or = she fears ... swo.usk = lest they fear ...... etc.
..
For a monosyllabic verb ending in ai or oi, the final i => y for the indicative and subjunctive. For example ...
gái = to ache, to be in pain ... gayar = I am in pain ... gayir = you are in pain ... etc. etc.
..
For a monosyllabic verb ending in au or eu, the final u => w for the indicative and subjunctive. For example ...
ʔáu = to take, to pick up ... ʔawar = I take ... etc. etc.
..
..... Special short verbs
..
The above is the general rules for short verbs, however the 37 short verbs below the rules are different.
Their vowels of the infinitive are completely deleted for the indicative and subjunctive verb forms. For example ...
pòr nambo = he enters the house ... not *poi.or nambo
| ʔái = to want | |||
| mài = to get | myè = to store | ||
| yái = to have | |||
| jò = to go | jwè = to undergo, to bear, to endure, to stand | ||
| féu = to exit | fyá = to tell | flò = to eat | |
| bái = to rise | byó = to own | blèu = to hold | bwí = to see |
| gàu = to do | glù = to know | gwói = to pass | |
| día = to arrive, to reach | dwài = to pursue | ||
| lái = to change | |||
| cùa = to leave, to depart | cwá = to cross | ||
| sàu = to be | slòi = to flow | swé = to speak, to say | |
| kàu = to fall | kyò = to use | klói = to like | kwèu = to turn |
| pòi = to enter | pyá = to fly | plèu = to follow | |
| té = to come | twá = to meet | ||
| wòi = to think | |||
| náu = to give | nyáu = to return | ||
| háu = to put |
The imperative prefix is -u for all* short verbs. For example ...
unyau nambo = go home !
uzwo = fear !
ugai = be in pain !
uʔau ʃì = take it !
.* All short verbs apart from one that is. jò "to go" has the imperative form ojo.
Some nouns related to the above ... yaivan = possessions, property, flovan = food, gauvan = products, myevan = reserves, nauvan = tax, tribute, gwàu = things that must be done, gwài = things that have been done, deeds, acts. gò = actions, behavior.
A particle related to the above ... yó ... a particle that indicates possession, occurs after the "possessed" and before the "possessor.
..
..... 9 important verbs
..
| pòi | to enter, to join | poinau | to put in |
| féu | to exit, to leave | feunau | to take out |
| bwí | to see | bwinau | to show |
| glù | to know | glunau | to tell |
| pyà | to fly | pyanau | to throw |
| jó | to go | jonau | to send |
| tè | to come | tenau | to summon |
| bái | to rise | bainau | to raise |
| kàu | to fall | kaunau | to lower |
..
pyà _ jó _ tè _ bái and kàu are intransitive.
..
..... 4 slots before the verb
..
We have already covered the indicative with the 4 slots for "agent", "tense/aspect", " r " and "evidentiality" at the end of the denuded infinitive. As well as the nuances given by these post verbal slots, there are a set of nine particles which give further nuances to the basic indicative verb. These are called (near-standers ?). These particles occur in 4 pre-verbal slots. However these particles are independent word, not affixes.
These are shown (along with the 4 post-verbal slots) below ...
... Slot 1
..
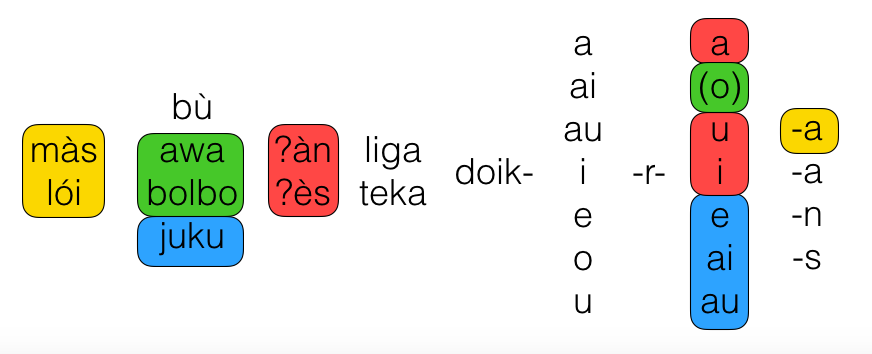
These two particles indicate probability.
màs = possibly
lói = probably
Of course they cover a wide probability range but the average probability gleaned from hearing màs would probably be around 50 %, and for lói, maybe up near 90 %.
..
... Slot 2
..
bù is a negative particle which has scope over the entire sentence ... equivalent to "not" in English.
awa gives a "habitual but irregular" (maybe best translated as "now and again" or "occasionally" or even "not usually") meaning to the main verb. Possibly related to the verb awata ? which means "to wander".
bolbo gives a "habitual and regular" (best translated as "normally" or "usually" or "regularly") meaning to the main verb. Possibly related to the verb bolboi which means "to roll".
OK ... but if you are only allowed one of these five, how would you translate .. "I don't usually come to these parent-teacher meetings but ...."
Well you wont say ... awa tár to these parent-teacher nò twás _ ...."
..
... Slot 3
..
These are called aspectual operators or aspectual particles.
..
In English the nearest translations* are ʔàn = "still" and ʔès = "already".
Many many languages have equivalents to these two particles. For example ...
..
| English | still | already |
| German | noch | schon |
| béu | ʔàn | ʔès |
| French | encore | déjà |
| Mandarin | hái | yîjing |
| Dutch | nog | al |
| Russian | eščë | uže |
| Serbo-Croatian | još | već |
| Finnish | vielä | jo |
| Swedish | än(nu) | redan |
| Indonesian | masih | sudah |
..
ʔàn indicates ...
1) an activity is ongoing
2) the activity must stop some time in the future, possibly quite soon.
3) there is a certain expectation* that the activity should have stopped by now.
Possibly related to the verb ʔanto which means "to continue".
ʔès indicates ...
1) an activity is ongoing
2) the activity was not ongoing some time in the past, possibly quite recently.
3) there is a certain expectation** that the activity should not have started yet.
Possibly related to the verb ʔesto which means "to start".
..
A very interesting thing about these two words is their negation. Either the particle plus verb can be negated (shown by one bar above the two word) or the verb by itself can be negated (shown by a bar above the verb).
If the verb is negated ... then, on the diagram ... the yellow place becomes white and the white space becomes yellow.
If the particle plus verb is negated ... then, on the diagram ... the dashed line representing now, is translated to the other side of the barrier that represents onset/cessation of activity.
..
..
As you see by above ... by changing whether the negator act on the verb plus the operator or whether the operator acts on the negator plus the verb, negative sentenced with ʔàn and ʔès give diametrically opposite meanings*** (the proper technical term is to call them "dual operators").
Note that there are 4 possible negative cases to choose from and a language only needs 2. I guess a language (to cover all negative cases) should have either "(a) and (c)" or "(b) and (d)" or "(a) and (b)" or "(c) and (d)".
For example, all Slavic languages prefer verb negation, hence they tend to have (c) and (d). In German, only (a) and (c) are allowed in positive declarations. Nahuatl has negation of the operator so uses (a) and (b). It can be said that English is an a/b language also. However in the negative English uses suppletive forms for the two operators ... "yet" for "already" and "anymore" for "still" ... hence "not yet" and "not anymore".
In béu, bù negates the whole sentence**** (or maybe I should say ... the whole clause). So béu is an a/b language as well.
..
* However the English pattern is a bit irregular in that it has the particle "yet" which corresponds to ʔàn in some circumstances and to ʔès in other circumstances.
** I believe that this expectation is a connotation that will inevitable develop if you have prolonged usage of a particle with meaning 1 and 2.
*** I find this stuff very interesting. If you want to know more, read "The Meaning of Focus Particles" by Ekkehard König.
**** In béu the particle jù negates one element in a sentence (the element immediately following it). So instead of using (a) and (b) we might have had (c) and (d) in the form ... *?àn jù doika and *?ès jù doika.
..... A speaker of béu ... while recognizing the logic of *?àn jù doika and *?ès jù doika, would deem them ungrammatical.
..
... Slot 4
..
liga makes verbs which in themselves are quite compact timewise, more spread out. For example ...
..
| koʕia | to cough | liga koʕia | "to be coughing", "to have a coughing fit" |
| timpa | to hit | liga timpa | "to be hitting" or "to assault" |
..
liga is never used with verbs that typically have an inherent long time duration. For example ...
- liga glarua beuba kewe would be translated as "I intend to be knowing the language of béu well" ... Not really good English either.
lglarua beuba kewe = "I intend to know the language of béu well" ... is more felicitous in both languages.
..
liga gives an imperative slant to the main verb. Possibly related to the verb ligai which means "to stay" or "to lie". Now in the very best register of béu this particle is used for a certain poetic effect, it is used sparingly and is not necessary for understanding what is being said. However people that are L1 speakers of a language having a perfective/imperfective tend to over-use liga. This is not really a problem, it just shows that they are not L1 béu speakers. Conversely people that are L1 speakers of language that lacks this distinction tend to not use liga enough. Again ... no real problem.
..
teka is the opposite of liga. It means "momentarily". Possibly related to the verb telka which means "to slip a little bit". While in theory it can be used with almost any verb, it tends to be used disproportionately with a dozen or so verbs. For example ...
..
| bwí | to see | teka bwí | to catch a glimpse |
| wòi | to think | teka wòi | to think for a moment |
| ʕái | to want | teka ʕái | for a moment, to want |
..
... Restrictions
..
..
Certain members of slots 1,2 and 3 can only co-occur with a subset of the affixes in post-verbal slots 3 and 4.
YELLOW ... if you have màs or lói then in post-verbal slot 4 you can only have the -a that follows the future tense u (that is, the one that isn't really an evidential). However all affixes in slot 4 are not compulsary.
GREEN ... if you have awa or bolbo then in post-verbal slot 3 you can only have the aortist tense (the one that is the null affix).
RED ... if you have ʔàn or ʔès then in post-verbal slot 3 you can only have the present, future and past tenses.
BLUE ... we introduce another particle here ... juku meaning "never". It is a more emphatic negative than bù, but can only be used with the 3 perfect aspects in slot 3.
..
Most of the above restrictions don't need much comment. Hoewver in English there appears to be some conflation between "already" and the perfect aspect. For example "I've done it already". Maybe the reduced phonological prominence of the aspectual marker (i.e. "v") is a major contributing factor of this conflation. In béu ʔès and the three perfect aspectual markers are two different things.
1) When you use ʔès (or ʔàn) you are concerned about the onset/cessation of an event ... probably in the recent past or near future.
2) When you use the perfect aspect you are concerned about the state of the subject (A or S) which has resulted from some event that might be quite far in the past ... impinging on this is a stong "experential" connotation. For example ... if John has read a book on geometry, you can assume he has some knowledge of this subject. If he has been to London, you can assume he has many sounds and sights of London stored away in his memory.
..
Not to be confused with lò = "other" and kyulo = "again" These two particles come just in front of the verb. They are only used with the indicative verb and the maŋga.
..
..... Tying two clauses together
..
In béu we have live clauses and dead clause.
The head of a live clause is a verb in its declarative form.
The head of a dead clause is a verb in its declarative form.
A live clause has its main elements in any order, the S term is marked as the ergative. The A and O terms are unmarked.
A dead clause has word order VS or VAO, the O term being marked as the dative. The A and S terms are unmarked.
tàin = before
jáus = after
ʔéu = while, as
kyun = until
kyuvi = ever since
If the subjects (that is S or A) of two clauses are different then they can be conjoined timewise by using one of the above stand-alone particles. For example ...
1) jenes bwori jono ʔéu jonos fori nambo tí = Jane saw John as he was leaving his house.
Also ... as in English we can have the two clauses in the other order ...
2) ʔéu jonos fori nambo tí_jenes bwori ò = As John was leaving his house, Jane saw him
Notice that in this sentence, the second jono has been replaced by the pronoun ò ... in actual fact ... in 1) the chances are that jonos would be replaced by ós ... but this makes the sentence ambiguous.
John whistled as he left his house = jono wizori ʔéu ò fori nambo tí = *jono wizori ʔéu féu í nambo tí
---
Now if the subjects of two clauses are the same, one of the clauses can becomes a dead clause. Only a very short and simple clause can become a dead clause ... both ...
A) Any time,place or manner adjuncts will stop a clause collapsing to a dead clause.
B) An O argument that is longer than a single word.
When the above requirements are met ....
A) S or A is dropped completely.
B) The linker word is appended to the infinitive.
C) if there is an O it immediately follows the infinitive and has the dative marker -n affixed.
1) S while S ................... jono wizori ʔéu ò huzori ... (pronoun used in second clause)
=>jono wizori huzuaʔeu = John whistled while smoking ... (must drop S, the linker must be appended to the infinitive)
2) A O while A O ..... jonos timpori jene ʔéu ós huzori ʃiga ... (pronoun used in second clause)
=> jonos timpori jene huzuaʔeu ʃigan ... (must drop A, the linker must be appended to the infinitive. O must be a single word)
3) A O while S .......... jonos timpori jene ʔéu ò huzori ... (pronoun used in second clause)
=> jonos timpori jene huzuaʔeu ... (must drop S, the linker must be appended to the infinitive)
4) S while A O ........... jono huzori ʔéu ós timpori jene .... (pronoun used in second clause)
=> jono huzori timpaʔeu jenen .... (must drop A, the linker must be appended to the infinitive. O must be a single word)
John left his house whistling = Jonos fori nambo tí ʔéu wiʒia
wiʒia = to whistle
koʔia = to cough
huzua = to smoke
..
... Introducing Verb Chains
..
béu has a technique that integrates two clauses even further. It is called the "verb chain".
In certain situations it is considered unnecessary to include person-tense information on an active verb. If there are a number of verb concepts that can be thought of as partaking in sort of "composite" activity, then only the initial verb gets person-tense-evidentiality information. The non-initial verbs have the final verb of their base form deleted and the vowel i added. For example ... slanje (to cook) => slanji. If the verb only has one syllable, then the final verb of their base form (the only vowel) is replaced with a schwa and the word looses its tone. For example ... flò (to eat) => flə.
Below are three verb chains ... each one having a different time structure.
..
... Similtaneous Time
..
John walked along the road whistling => jono doikori komwe plə wiʒi*
..
to whistle = wiʒia
to walk = doika
to follow = plèu
road = komwe
..
We can also say ...
"John walked along the road whistling" => jonos komwe plori doiki wiʒi.
In fact there are six ways in which the three verbs can be arranged. The meaning of the sentence would be exactly the same in all six cases.
Note that "John" appears "naked" or in his "s-marked" form depending on whether the first verb is transitive or intransitive. The first verb has the full verb train ( it is "r-form" however later verbs in the chain are in their reduced form (i.e. their "i-form")
*Actually this sentence is more likely to be expressed as jono doikori komwewo wiʒi
..
... Interleaved Time
..
All afternoon I was writing reports and answering the telephone => falaja ú kludari fyakas sweno nyauʒi
..
afternoon = falaja
to write = kludau
report(noun) = fyakas
telephone(noun) = sweno
to answer = nyauze
..
Note .... in the first example the times of the different verbs were similtaneous, in this example the times of the different verbs are randomly interleaved throughout the afternoon.
It would also be possible to render the above as falaja ú sweno nyauzari kludi fyakas ... means the same thing.
Notice that in this example we have two verb-object-pairs, (kludau, fyakas) and (sweno, nyauze). While an object must stay next to its verb, there is a tendency for it to precede the verb when it is definite and to follow it when indefinite).
[ And with a change of tense ... "All afternoon I have been writing reports and answering the telephone" => falaja ú kludar fyakas sweno nyauʒi ]
..
... Sequential Time
..
Yesterday John caught, cooked and ate three fish => jana jonos holdori slanji flə léu fiʒi
..
yesterday = jana
to catch = holda
three = léu
fish = fiʒi
..
In this example, the three verb concepts happened in a definite order, and must be expressed in that order.
A verb chain must be contained in one clause. However the verb form used in a verb chain (the i-form ... both slanji and flə are considered the i-forms of the verbs slanje and flò ... even though there is no "i" in the form flə) can be used over multiple clauses. For example ...
"Yesterday John caught three fish, then cooked then and then ate them" => jana jonos holdori léu fiʒi _ slanji _ flə .... actually, is this a good idea (i-form over multiple clauses) ???
You can continue adding "i-form" verbs indefinitely. However if the subject changes, you have to go back to an "r-form". Also if the internal time structure of the composite action was to change, then one must revert to an "r-form". jana jonos holdori léu fiʒi _ slanji _ flə is definitely three clauses because of the mandatory intonation breaks. The object of the last two clauses is the same as the object of the first clause. However this need not be the case ( I can not think of a good example at the moment ??? ).
[ Note ... Although the verb chain is the common way to express when two actions happen at the same time, another method is possible. That is to make one of the verbs into an adjective. And then by placing this directly behind another verb you get an adverb. For example ... wizari doikala = I whistled while I walked] .... ???
Note that in these three examples, that the internal time structure of the composite action (i.e. simultaneous, interleaved and sequential) are never formally stated. Rather they are known due to the listeners knowledge of the situation being described.
The internal time structure of a situation is not always clear. But if it is thought necessary to clarify it one can always fall back to conjoining clauses with conjunctions.
..
... Motion Verb Chains
..
Verb chains are used a lot for verbs of motion. In certain languages (for example Cantonese, verbs do the job that prepositions do in European languages. Now béu does have a set of prepositions (the pilana). So for defining exactly what non-core NP's are doing in a sentence (that is everything that is not S, A or O) ... in béu this task is shared about equally between prepositions and minor verbs.
The rules are the same as stated in the previous section. But for common minor verbs there is a set order in which they must occur. This is shown below ...
..
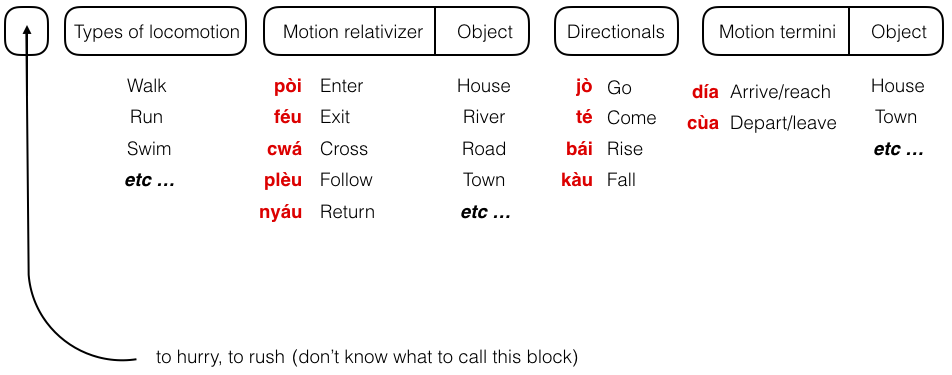
... The directionals
..
Often jə or tə / bə or kə are tagged on at the end of a motion clause. Like a sort of afterthought. They give the utterance a bit more clarity ... a bit more resolution. For example ...
 .............................. jaŋkori tə = "he ran towards us"
.............................. jaŋkori tə = "he ran towards us"
Note ... in the script the schwa is simply left out, so if you see a consonant standing by itself, you know that you have part of a verb chain.
If two directionals were to be used, jə or tə would follow bə or kə.
Obviously these 4 verbs often occur independently. In which case they are in their r-form.
this section is nothing to do with verb chains, just a bit to do with the usage of té and jò----
té is always intransitive. jò can be transitive or intransitive. For example ...
I am going to London => (pás) jar london ... however if the destination is not immediately after the verb í london (pás) jar
"I am going" or "I will go" => (pà) jaru
By the way ... if you go to meet somebody, jò and twá form a verb chain. For example ...
jò twə jono => to go and meet John
ojo twə jene => go and meet Jane (notice the irregular imperative)
..
..
* In contradistinction, when a origin comes immediately after the verb dwé "to come" the pilana -fi is never dropped.
..
HERE----------<---------LONDON
tè londonfi = to come from London
tè jonovi = to come from John
..
..
He is lowering John down the cliff-face to the ledge => ós gora jono cliff gìa ledgeye ??
I dragged the dog along the road ??
joske pòi nambo = let's not let him go into the house ... there are 2 verbs in this chain ... jòi and pòi
jaŋkora bwá nambo dwía = he is running out the house (towards us) ... there are 3 verbs in this chain ... jaŋka, bwá and dwé
doikaya gàu pòi nambo jìa = Walk (command) down into the house (we are in the house) ... there are 4 verbs in this chain ... doika, gàu, pòi and jòi
Extensive use is made of serial verb constructions (SVC's). You can spot a SVC when you have a verb immediately followed (i.e. no pause and no particle) by another verb. Usually a SVC has two verbs but occasionally you will come across one with three verbs.
*Well maybe not always. For example jompa gàu means "rub down" or "erode". Now this can be a transitive verb or an intransitive verb. For example ...
1) The river erodes the stone
2) The stone erodes
With the transitive situation, the "river" is in no way going down, it is the stone. Cases where one of the verbs in a verb chain can have a different subject are limited to verbs such as erode (at least I think that now ??). Also the verbal noun for jompa gàu is not formed in the usual way for word building. Erosion = gaujompa
gaujompa or gajompa a verb in its own right ... I suppose that this would happen given time ??
I work as a translator ??? ... I work sàu translator ??
"want" ... "intend" ... etc. etc. are never part of verb chains ?? ..........................................
........... Unbalanced
..
Now all the above were examples of "one off" or "balanced" verb chains ( "balanced" in the sense that all the verbs have about the same likelihood ). A more common type of verb chain is one in which some common verb is appended to a clause to give some extra information. Examples of these verbs are ... "enter", "exit", "cross", "follow", "to go through", "come", "go", etc. etc. etc.
................. enter and exit
..
When in verb chains, these 2 verbs tend to be the main verb. They are used where "into" and "out of" are used in English.
pòi = to enter
féu = to exit
nambo féu tə = to come out of the house
nambo pòi jə = to go into the house
nambo pòi tə = to come into the house
nambo féu jə = to go out of the house
féu nambo tə = to come out of a house
féu nambo jə = to go into a house
pòi nambo tə = to come into a house
féu nambo jə = to go out of a house
nambo féu jaŋki tə = to run out the house (towards us)
féu nambo jaŋki tə = to run out a house (towards us)
..
............... across & along & through
..
When in verb chains, these 3 verbs tend to be the main verb.
kwèu = to cross, to go/come over
plèu = to follow, to go/come along
cwá = to go/come through
komwe kwèu = to cross the road
komwe kwèu doika = to walk across the road
kwèu komwe doiki = to walk across a road
kwèu komwe doiki tə = to walk across a road (towards the speaker)
plèw and cwá follow the same pattern
Note ... some postpositions
komwe kwai = across the road = across a road
pintu cwai = through the door = along a road
Above are 2 postpositions ... derived from the participles kwewai and cwawai
komwe plewai = along the road
..
............ .............. ascend and descend
..
When in verb chains, these 2 verbs tend to be the auxiliary verb. They are used where "up" and "down" are used in English.
bía = to ascend
kàu = to descend
CLIMB ʔupai kə = to climb down a tree
ʔupai CLIMB kə = to climb down the tree
CLIMB ʔupai bə = to climb up a tree
THROW toili kə = to throw down a book ???
These are also often inserted in verb chains to give extra information. The usually precede "come" and "go" when "come" and "go" are auxiliary verbs in the chain.
jò kə pə nambo = to go down into the house
jaŋkor kə pə nambo jə = he runs down into the house (away from us)
jaŋkor pə nambo kə tə = he runs down into the house (towards us)
The two above sentences could describe the exact same event. However there is some slight connotation in the latter that the descending happened at the same time as the entering (i.e. the entrance of the house was sloping ... somewhat unusual)
..
.............. here and there
..
awata = to wonder
jaŋka awata = to run around
..
............. bring and take
..
kli.o = a knife
kli.o ʔáu jə = to take the knife away
kli.o ʔáu tə = to bring the knife
ʔáu kli.o jə = to take a knife away
kli.o uʔau jə nə jono = take the knife and go give to John
kli.o uʔau tə nə jono = bring the knife and give to John
If however the knife was already in the 2nd person's hand, you would say ...
ute nə jono kli.o = come and give john the knife ... or ...
ute nə kli.o jonon = come and give the knife to john
Note ... the rules governing the 3 participants in a "giving", are exactly the same as English. Even to the fact that if you drop the participant you must include jowe which means away. For example ...
nari klogau tí jowe = I gave my shoes away.
Note ... In arithmetic ʔaujoi mean "to subtract" or "subtraction" : ledo means "to add" or "addition".
Note ... when somebody gives something "to themselves", tiye = must always be used, no matter its position.
..
....... for and against
..
HELP = to help, assist, support
gompa = to hinder, to be against, to oppose
FIGHT = to fight
FIGHT jonotu = to fight with john ......... john is present and fighting
FIGHT HELP jono = to fight for John ... john is present but maybe not fighting
FIGHT jonoji = to fight for John ...........probably john not fighting and not present
FIGHT gompa jono = to fight against John
..
.......... to change
..
lái = to change
kwèu = to turn
lái sàu = to change into, to become
kwèu sàu = to turn into
The above 2 mean exactly the same
Note ...
paintori pintu nelau = he has painted a blue door
paintori pintu ʃìa nelau = he has painted a door blue
..
??? How does this mesh in with clauses starting with "want", "intend", "plan" etc. etc. ... SEE THAT BOOK BY DIXON ??
??? How does this mesh in with the concepts ...
"start", "stop", "to bodge", "to no affect", "scatter", "hurry", "to do accidentally" etc.etc. ... SEE THAT BOOK ON DYIRBAL BY DIXON
..
..
... IA and UA
..
... Consequence Couplets
..
... The copula
..
The three components of a copular clause have a strict order. The same order as English in fact. Also the copula subject is always unmarked.
The copula is sàu.
However the indicative mood is not derived from the infinitive in the usual method.
.*sàr = I am
.*sàir = we are
.*sàur = we are
.*ʃìr = you are
.*sèr = you are
sòr = he/she/it is
sùr = they are
The indicative mood is invariably* shortened to simply r and appended directly to the copula subject. For example ...
jono r jini tè tomo r tumu = "John is clever but Thomas is stupid"
Note that r loses its tone as it is phonologically part of the last word of the subject NP ... it is an enclitic.
This "r" can build up tense/aspect and evidecial affixes as a normal verb. For example ...
jene gáu rìs hauʔe = "They say old Jane used to be beautiful"
Note that in this case the copula does not loose its tone. It is an independent word.
Also note that for copular clauses, the subject pronoun can never be dropped, because the pronoun information is gone (that is there is no component to the left of the "r").
wài r wikai tè nù r yubau = "we are weak but they are strong"
ʃì r broken = "it is broken"
*Well not invariably. If a copular subject doesn't end in a vowel and the copula has the aortist tense (i.e. no vowel), then we get the forms or and ur. or for a singular copular subject and ur for a plural copular subject. Again ... these forms are phonologically enclitics and have no tone.
..
Often the O argument of a V2 is dropped if it is considered too trivial be to worth bothering about. For example solbe (to drink) is a transitive verb but often the O argument can be unceremoniously dropped. The copula subject in certain situations is also dropped. These situations largely correspond to when English used the dummy subject "it". The reason for dropping the copula subject is almost the mirror image with respect to the dropping of the O argument. Whereas the O argument is thought too "trivial" or "predictable" the dropped copula subject is thought "all encompassing" or "so obvious that no need to mention it".
In these situations ... sòr (or occasionally sùr) is used.
Often used for talking about the weather (as in English).
This construction is used in particular with the words neʒi, boʒi, fain and aufain.
neʒi ... an adjective = "necessary" ... neʒis = a necessity
boʒi ... an adjective = "best" .... boʒis = the optimum ... boʒizgan = calculus ??
fàin ... an adjective = "fitting", "appropriate", "a good"(course of action)
and of course ufain is the opposite of fain. So ... for example ...
sòr neʒi tà .... = "you need to ..."
sòr boʒi tà .... = "best if you ..."
sòr fàin tà .... = "you had better ..."
xxxxxx which method is the best ??
ʃì r neʒi tà .... = "you need to ..."
ʃì r boʒi tà .... = "best if you ..."
ʃì r fàin tà .... = "you had better ..."
[the copula would be sùr if two course of action were being proposed]
Now these three have a pretty fine degree of distinction between their meanings.
Of course people will not always pick the absolute correct word for every occasion. But there are nuances of meaning between the 3 words ...
fàin should be used when the advantage that the proposed course of action brings, is for the benefit of a third party and/or the proposed course of action will be approved of by society at large.
boʒi should be used when the benefits of the proposed course of action is mainly to the speaker or the speakee.
neʒi ... when followed by a clause in the past or perfect tense, means that from things apparent now, the course of action contained in the clause, must have happened in the past [i.e. so it is not a hundred miles away from the n evidential in the verb train]. When followed by a clause in the aortist or future tense ... then the meaning is not a hundred miles away from the modal sentences introduced by yái or byó.
And we have one other word that is commonly used with the above construction. That is maible. For example ...
sòr maible tà .... = "it's possible that ..."
sòr maible hè tà .... = "it's probable that ..."
Of course this usage is equivalent to using the particles màs and lói. The copula construction would be used when the main point of the utterance is to indicate the probability. màs and lói are used when the probability information is just an optional extra that was thrown in.
In careful speach the copula is retained in the above constructions. However in rapid informal speech, you will hear the copula dropped also.
..
There is another verb that also looses its subject for the same reason. yái is a normal V2 in every respect [i.e. its A argument takes the s-marker, it can be put in the passive form] apart from the fact that when its subject is missing it acts as an existential verb. For example ...
yór dèus = "there is a God", "God exists"
This is negated by negating the noun rather than negating the verb. For example ...
yór jù dèus = "there is no God", "God doesn't exists" .... not .. *yorj dèus
This existential construction often has a location incorporated into it. For example ...
yór yiŋki hè swedenʔi = "there are many attractive girls in Sweden" ... [the word here order is fixed].
The above means pretty much the same is the copula sentence ...
yiŋki hè r swedenʔi ... [and remember, all copula sentences are fixed word order].
Which in turn means pretty much the same as the normal transitive clause ...
swedenes yór yiŋki hè ... [free word order]
..
..
... Index
- Introduction to Béu
- Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds
- Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
- Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
- Béu : Chapter 4 : Adjective
- Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
- Béu : Chapter 6 : Derivations
- Béu : Chapter 7 : Way of Life 1
- Béu : Chapter 8 : Way of life 2
- Béu : Chapter 9 : Word Building
- Béu : Chapter 10 : Gerund Phrase
- Béu : Discarded Stuff
- A statistical explanation for the counter-factual/past-tense conflation in conditional sentences