Béu : Chapter 4
..... kolape
This is a complement clause construction. In English there are 7 types of complement clauses, in béu there are only 3.
A complement clause is call a kolape in béu. The three types are briefly summarised below and then each of the types is discussed in more detail.
1) I remembered writing the book ... this conveys that the whole process of locking the door is going thru the speakers mind ... ???ari pà kludau toili
The béu form above looks similar to the English "I remembered to write the book". However this is NOT the meaning.
To say "I remembered to write the book" in béu you would say ???ari tá toili (rà) kludu ... see the section about participles.
2) I thought that I wrote the book ... takes the same form in béu ... olgari tá kludari toili
3) He asked me whether I had written the book ??? ... askori (pavi) tavoi kludari toili
kolape jù
In béu the word order is usually free. This is not true in a kalope jù
jonoS rì kéu = John was bad
(pà solbe moze pona sacowe)S rì kéu = my drinking the cold water quickly was bad
Notice that pà solbe moze pona sacowe behaves as one element. It has the same function as "John" in the previous example.
The word order inside kolape jù is fixed. It must be S V or A V O for a transitive clause (any other peripheral arguments are stuck on at the end).
Also notice that the ergative marker -s which is usually attached to the A argument is dropped. Actually for pronouns it is not just the dropping of the -s, but a change of tone also, so this form is identical to the O form of the pronoun.
The kolape above, if expressed as a main clause would be.
(pás) solbari saco* moze pona = I drank the cold water quickly
Other examples ;-
wàr solbe (I want to drink) is another example. (wò = to want)
klori jono timpa jene (he saw John hitting Jane) ... (klói = to see)
kolape jù? can be considered as a noun phrase and the fixed ordering of elements can be seen as a reflextion of the strict order of elements in a normal noun phrase
Subject1 Head2 Object3(Peripheral arguments4 x n)
1) The "A" argument or the "S" argument.
2) The verb.
3) The "O" argument, which would of course be non-existent in an intransitive clause.
4) Adverbs and everything else.
A gomia such as solbe can be regarded as a proper noun** and can be the head of a cwidauza (see a previous section)
or it can be the head of a kalope jù. But these two constructions are always distinct. For example you couldn't append a determiner to a kalope jù ... (or could you ??)
* in a main clause the adverb can appear anywhere if suffixed with -we. But in kalope jù the adverb must come after the Subject, Verb and Object.
** A gomia never forms a plural or takes personal infixes in the way a normal noun does. Also it only takes a very reduced subset of pilana, so a gomia can be regarded as an entity half way between nounhood and verb hood. For that reason I consider gomia as a part of speech, standing alongside "noun" and "verb".
kolape tá
In this form the full verb* is used, not the gomia. Also we have a special complementiser particle tá which comes at the head of the complement clause.
wàr tá jonos timporu jene = I want John to hit Jane
klori tá jonos timpori jene (he saw that John hit Jane) ... (klói = to see)
*Well not quite the full form. Evidentials are never expressed.
kolape tói
This is equivalent to English word "whether".
sa RAF kalme Luftwaffe kyori Hitler olga tena => The RAF's destruction of the Luftwaffe, made Hitler think again. ... here a gomiaza acts as the A-argument.
*in the combinations where sacowe immediately followed solbe it is merely saco
Things to think about
what about "who" or "what" introducing a relative clause ?
what is a gomiaza
Can this be used for a causative construction ??
Verb chains
bawas bura nambo laulai halfai => The men go home singing and laughing
bawas bura nambo laulai lauloi?? halfai => The men go home singing songs and laughing
bawas bura nambo laulai halfai jono => The men go home singing and laughing about John
This is used when things happen at the same time and the subject of all the verbs is the same. Notice that the ai-forms can come after the r-form verb.
It is not really important which verb comes first, perhaps the one considered the most relevant/important should come first.
The three verbs above sort of amalgamate into a single verb. The actions should be considered a single event.
In the examples above the three constituent verbs of the verb chain happen at the same time but this is not always the case. In the example below the constituent verbs happen one after the other.
awes hufu bái kyái jono (take sheep go give John) = Take the sheep and give it to John.
Minor Verb "ai"
The small verbs constitute a subset of verbs. They always follow the r-form verbs.
It is very common to have the following verbs in their ai-form.
blià = to stay
bé = to go
kò = to come
= to ascend
= to descend
= to return
The most common use for this is when you want to fit another action, inside the act of walking. For example "I was walking to school when it started to rain". Occasionally this form is used when you simply want to emphasis that the action took a long time (well in béu anyway, not so much in English). For example "This morning I was walking 2 hours to school (because I sprained my ankle)".
láu = to become
I painted the house red = paintari nambo lái hìa
solboi ʔá dori uboi = Those drinks that she made are delicious
solboi ʔá dori lái uboi are all finished = Those drinks that she made delicious are all gone
Note we need to use lái or sometime we would get confusion d/t the béu habit of dropping the copula.
bwò = to receive, to get, to undergo
bwaru timpa = I will be hit
bài bwài timparu = I will be being hit ??
kye = to give
kyari òye solbe
(pás) kyari oye timpa glá = I made him hit the woman
gain only one verb and it is transitive. There are two ways that we can make an intransitive clause.
1) pintu lí mapa = The door became closed ... this uses the adjective form of mapa and the "copula of becoming" láu.
Agent => Anything ... It could be that the agent was the wind ... or even some evil spirits ... use your imagination.
2) pintu bwori mapau = The door was closed ... this is the standard passive form.
Agent => Human and the action deliberate ... It strongly implies that the agent was human but is either unknown or unimportant.
Let us go back to gèu and consider gèu in an intransitive clause. As above we have 3 ways.
1) báu lí gèu = The man became green ... this uses the adjective form of gèu and the "copula of becoming" láu. This form has no implication as to the humanness of the agent.
Agent => Anything and the action could be accidental.
2) báu bwori geuldu = The man was made green ... this is the standard passive form. It strongly implies a human agent but the agent is either unknown or unimportant.
Agent => Human and the action deliberate
3) báu tí geuldori = The man made himself green ... this form implies that there was some effort involved.
Agent => The man and the action deliberate
= to come
= to go
= to rise ... sái : to raise ... slái
= to descend ... gàu : to lower ... glàu
= to enter ... poi : to put in ... ploi
= to go out
= to follow
= to cross
= to go through
= to pass
= to return
= to do something in a haphazard manner, to do something in an unsatisfactory manner
= to scatter about
= to hurry
= to do accidentally ??
The above are often stuck on the end of an utterance ... like a sort of afterthought. They give the utterance a bit more clarity ... a bit more resolution.
See what Dixon has in Dyirbal.
ai-form only with r-form or can also go with n-form, etc. etc.
You can add as many verbs as you want. The added verbs are understood to have the same protagonists, gwomai and evidentiality as the r-form verb.
passorla singai kite flyai = He is passing by singing and flying a kite
WHAT ABOUT SEPERATE OBJECTS ON THE TWO VERBS ?
WHEN WE INTRODUCE "ALONG" (FOR EXAMPLE) WE ARE INTRODUCING A NEW OBJECT IN THE CLAUSE ???
The causative construction
(pás) dari jono dono = I made john walk
(pás) dari jono timpa jene = I made John hit Jane ... in this sort of construction, jono, timpa and jene must be contiguous and jono should be to the left of jene.
To give and to receive
kyé means to give and bwò means to receive or get.
1) jonosA kyori toiliO jeneye = John gave a book to Jane"
Note that (as with all béu main clauses) the arguments can be in any order.
2) jeneA bwori toiliO (jonofi) = Jane got a book (from John)
O.K. the above is the usage normal usage of kyé and bwò. They sort of describe the same action but from two different perspectives.
The passive construction
3) jonosA timpori jeneO = John hit Jane
4) jeneS bwori timpa (jonotu) = Jane was hit (by John)
4) is the passive equivalent of 3) ... used when the A argument is unknown or unimportant.
If the agent is mentioned, he or she is marked by the instrumentive pilana.
The reciprocal construction
jono jene timpuri kyebwo = "John and Jane hit each other" = "John and Jane hit one and other"
kyebwo the reciprocal particle (usually comes immediately after the verb) is obviously derived from the phrase kyé bwò
Notice that normally we would have -s on both John and Jane ... however not in the reciprocal construction.
Also note that é(and) is not used between proper names.
Ambitransitive verbs
fompe is an intransitive and a transitive verb (S and A)
jene fompori = Jane tripped
jonos fompori jene = John tripped Jane
halka is an intransitive and a transitive verb (S and O)
pintu halkori = the door broke
jonos pintu halkori = John broke the door
To recognize as a transitive clause you must look for the ergative -s, if no -s then we have an intransitive clause.
Or alternatively you must look for the particle kyebwo
Tom Jerry halkuri = Tom and Jerry broke
Tom Jerry halkuri kyebwo = Tom and Jerry broke one and other.
MUST THINK ABOUT THE BELOW
Other examples ...
jene bwori du dono = Jane was made to walk
(pás) bwari du solbe moze (jonotu) = I was made to drink the water (by John)
moze bwori solbe (jenetu) = The water was drunk (by Jane)
(pás) dari jono jene flompe = I made John trip Jane
Changing transitivity
béu has 2 morphological ways to make all these type of verbs into transitive verbs ( see -at- and -az- causatives).
-AT- and -AZ-
tonzai = to awaken
tonzatai = to wake up somebody (directly) i.e. by shaking them
tonzazai = to wake up somebody (indirectly) i.e. by calling out to them
henda = to put on clothes
hendata = to dress somebody (for example, how you would dress a child)
hendaza = to get somebody to dress (for example, you would get an older child to dress by calling out to them)
The above methods of making a causative only apply to intransitive verbs. To make an transitive clause onto a causative the same method is used as English used. That is the entire transitive clause becomes a complement clause of the verb "to make".
In addition to the causative infixes shown above, there are many verb pairs such as poi = to enter, ploi = to put in, gau = to rise, glau = to raise, sai = to descend, slai = to lower
and in multisyllable words ... laudo = to wash (oneself), lauldo = to wash (something). The above are not really considered causatives. The infixing of the l is by no means productive. In fact you can not call it "infixing". Also in many cases the transitive verb out of the pair is more common than the intransitive one.
Note;- The way you say "allow" or "let" in béu is to use the gambe along with the hái "give".
I let her go => hari liʔa oye
.
..... The Calendar
The béu calendar is interesting. Definitely interesting. A 73 day period is called a dói. 5 x 73 => 365.
The phases of the moon are totally ignored in the béu system of keeping count of the time.
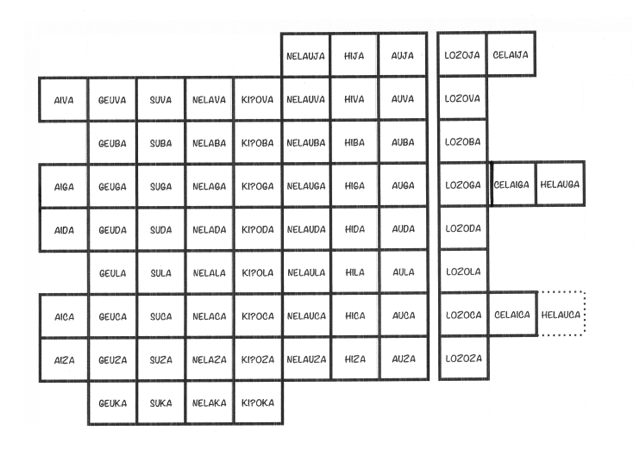
The first day of the dói is nelauja followed by hija, then auja lozoja celaija and then aiva etc. etc. all the way upto kiʔoka.
The days to the right are workdays (saipito) while the days to the left are days off work (saifuje). Each month has a special festival (hinta) associated with it. These festivals are held in the three day period comprising lozoga, celaiga, helauga. The five "months" are named after the 5 planets that are visible to the naked eye. The 5 big festivals that occur every year are also named after these planets.
| mercury | ʔoli | Month 1 | doiʔoli | Xmas... on 21,22,23 Dec | hinʔoli |
| venus | pwè | Month 2 | doipwe | festival on 4,5,6 Mar | himpwe |
| mars | gú | Month 3 | doigu | festival on 16,17,18 May | hiŋgu |
| jupiter | gamazu | Month 4 | doigamazu | festival on 28,29,30 July | hiŋgamazu |
| saturn | yika | Month 5 | doiyika | festival on 9,10,11 Oct | hinyika |
hinʔoli ... This is the most important festival of the year. It celebrates the starting of a fresh year. It celebrates the stop of the sun getting weaker. It is centred on the family and friends that you are living amongst. Even though eating and drinking are involved in all the five festivals, this festival has the most looked-forward-to feasts.
himpwe ... People gather at various regional centres to compete and spectate in various music and poetry competitions. Sky lanterns are usually released on the last day of this festival. On the first two days of the festival, what is called the "fire walk" is performed. This is to promote social solidarity. Each locality comprising up to 400 people build a fire in some open ground. These people are divided into 2 sections. One section to walk and one section to receive walkers. The walkers are further divided into groups. Each group is assigned another fire to visit and they set of in single file. Each of them carries a torch (a brand) ignited from the home fire. Upon arriving at the fire that they have been assigned (involving a walk of, maybe, 5 or 6 miles) they throw their brand into the fire as their hosts sing the "fire song". After that the visitors are offered much drinks and snacks by their hosts. There is considerable competition between the various localities to be the most generous host. The routes that people must go have been chosen previously by a central committee, but the destination is only revealed to the walkers just before they set out. On the second day the same thing happens but the two sections, the walkers and the receivers of the walkers, swap over rolls.
hiŋgu ... It is usual to get together with old friends around this time and many parties are held. Friends that live some distance away are given special consideration. Often journeys are undertaken to meet up with old acquainances. Also there is a big exchange of letters at this time. The most important happenings of the last year are stated in these letters along with hopes and plans for the coming year.
hiŋgamazu ... This festival is all about outdoor competitions and sporting events. It is a little like a cross between the Olympics games and the highland games. People gather at various regional centres to compete and spectate in various team and individual competitions. However care is taken that no regional centre becomes too popular and people are discouraged from competing at centres other than their local one. Also at this festival, a "fire walk" is done, just the same as at the "himpwe" festival.
hinyika ... Family that live some distance away are given special consideration. Often journeys are undertaken for family visits and ancestors ashboxes are visited if convenient. This is the second most important festival of the year. People often take extra time off work to travel, or to entertain guests. Fireworks are let of for a 2 hour period on the night of helauga. This is one of the few occasions where fireworks are allowed.
By the way, when a year changes, it doesn't change between months, it changes between lozoga and celaiga.
Every 4 years an extra day is added to the year. The doiʔoli gets a helauca.
béu also has a 128 year cycle. This circle is called ombatoze. There is a animal associated with every year of the ombatoze.
These animals are ;-
| wolf | weasel/ermine/stoat/mink | bullfinch | badger |
| whale | opossum | albatross | beautiful armadillo |
| giant anteater | lynx | eagle | cricket/grasshopper/locust |
| reindeer | springbok | dove | gnu/wildebeest |
| spider | Steller's sea cow | seagull | gorilla |
| horse | scorpion | raven/crow | python |
| rhino | yak | Kookaburra | porcupine ? |
| butterfly | triceratops | penguin | koala |
| polar bear | manta-ray | hornbill | raccoon |
| crocodile/alligator | wolverine | pelican | zebra |
| bee | warthog | peacock | capybara |
| bat | bear | crane/stork/heron | hedgehog |
| frog | lama | woodpecker | gemsbok |
| musk ox | chameleon | hawk | cheetah |
| lion | frill-necked lizard | toucan | okapi |
| dolphin | aardvark | ostrich | T-rex |
| kangaroo | hyena | duck | driprotodon(wombat) |
| shark | cobra | kingfisher | gaur |
| dragonfly | mole | moa | chimpanzee |
| turtle/tortoise | N.A. bison | black skimmer | panda |
| jaguar | snail | cormorant/shag | Cape buffalo |
| rabbit | colossal squid | vulture | glyptodon/doedicurus |
| beetle | seal | falcon | pangolin |
| megatherium | woolly mammoth | flamingo | baboon |
| elk/moose | squirrel | blue bird of paradise | lobster |
| tiger | gecko | grouse | seahorse |
| jackal/fox | octopus | swan | lemur |
| elephant | swordfish | parrot | auroch |
| giraffe | ant | puffin | iguana |
| mouse | crab | swift | mongoose/meerkat |
| smilodon | giant beaver | owl | mantis |
| camel | goat | hummingbird | walrus |
Each of these animals above is a toze, which can be translated as "token", "icon" or "totem ". omba means a circle or cycle. So you can see where the name for the 128 year period comes from.
The very last helauca of every ombatoze is dropped.
ombatoze is sometimes translated as "life", "generation" or "century"
xxx means a 4 year period. It also means "calendar".
The start of time
Year 2000 had 365.242,192,65 days
Every year is shorter than the last by 0.000,000,061,4 days
By adding one day every 4 years we get a 365.25 day year
If we then drop one day every ombatoze we get a 365.242,187,5 day year (actually very close to the actual year length)
Before 2084, the actual year will be bigger than the calendar year – after 2084 the actual year will be smaller than the calendar year
For this reason midnight, 22 Dec 2083 is designated the fulcrum of the whole system. That day will be time zero.
At the moment we are in negative time.
..... Index
- Introduction to Béu
- Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds
- Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
- Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
- Béu : Chapter 4 : Adjective
- Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
- Béu : Chapter 6 : Derivations
- Béu : Chapter 7 : Way of Life 1
- Béu : Chapter 8 : Way of life 2
- Béu : Chapter 9 : Word Building
- Béu : Chapter 10 : Gerund Phrase
- Béu : Discarded Stuff
- A statistical explanation for the counter-factual/past-tense conflation in conditional sentences