Béu : Chapter 5
The parish
béu country is divided into "parishes". These are rural communities of 10,000 -> 50,000 people (urban areas have are distinct from rural areas and have a very different administrative structure).
The parish boundaries follow geographical features, such as streams and ridges etc. However the shape of a parish approximates to a hexagon. In fact in a total featureless landscape it would be a hexagon.
The rim banners
Each parish has 6 banner-rows along its boundaries. A banner-row consists of 17 banners about 10 m apart. Each banner is made from a pole about the girth of an adults arm or leg. Each pole is about 7.5 m high and the top 5 m of the pole has an orange banner. The cloth of the banner is about 1/3 m wide. When about half the original cloth has been weathered away the cloth should be replaced, best to do an entire banner-row at on time. These banner-rows are normally placed in prominent positions. They can be anywhere along a boundary, but it isn't considered good to have the gap too small or too big between any neighbouring banner-rows.
In sparsely populated areas you get what is called a super-parish. They are around 10 times the size of a normal parish (but their population falls within the 10,000 -> 50,000 limit). These super-parishes have 2 barrier-rows per side(that is 12 in total), and each banner-row has 19 banners. All these banner dimensions are about 15% to 20% bigger than normal.
The outer spoke banners
About 2/3 of the way out from the parish centre there are what are called the spoke banners arranged in banner-rows. There are 4 of these banner-rows and each has 11 banners. Again these are in prominent positions and/or well visible from roads. Again they should be quite spread out from each other.
Each of there banner-rows, instead of delineating the parish boundary, point towards the administrative centre of the parish, the toilido.
(For a super-parish there are 8 banner-rows with 13 banners each)
The inner spoke banners
About 1/3 of the way out from the parish centre there are what are called the spoke banners arranged in banner-rows. There are 3 of these banner-rows and each has 7 banners.
Again each of these banner-rows is pointing to the toilido.
(For a super-parish there are 5 banner-rows with 7 banners each)
The parish hall
The town clock
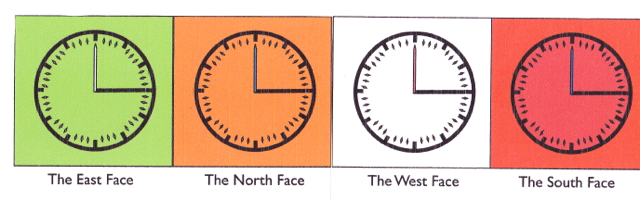
Every town has a clocktower and the clocktower has 4 faces, which are aligned with the cardinal directions. The street pattern is also so aligned : that is the four biggest streets radiate out from the clock in the cardinal directions.
Each face displaying a clock similar to the one below.
The above figure shows the time at exactly 6 in the morning. You notice that the main (hour hand) hand is pointing to the right : it starts from the horizontal. This hand sweeps out one revolution in 24 hours and it moves anti-clockwise
Notice that secondary (minute hand) starts from the vertical and sweeps out a revolution in 2 of our hours. It moves clockwise. And actually when it passes the main hand, there is a clever mechanism to stop it being hidden. It stops 3.75 minutes at one side of the main hand, and then moves directly (2 steps) to the other side of the main hand and stops there for 3.75 minutes. After that it does a step and waits 2.5 minutes, etc. etc. ... until it encounters the main hand again.
The red and the black arms do not move continuously but move in steps. The primary arm moves 3.75 degrees every 15 minutes, and the secondary arm moves 7.5 degrees every 2.5 minutes.
The clocktower is surmounted by a green conic roof (actually not really conic ... the roof slope decreases as you get nearer the bottom). Lighting from under the roof could be provided for each face. Either that or the faces could be illuminated from within at night. The faces are not exactly vertical but the top slightly overhangs the bottom.
There is never any numbering on the face.
The clock also emits sounds. Every 2 of our hours the clock makes a deep "boing" which reverberates for some time. Also from 6 in the morning to 6 at night, the clock emits a "boing" every 30 of our minutes. The first "boing" has no accompaniment. However the second "boing" is followed (well actually when the "boing" is only .67 % dissipated) by a "sharper" sound that dies down a lot quicker : "teen". The third "boing" has 2 "teen"s 0.72 seconds apart. The fourth has 3 "teen"s. The fifth one is back to the single "boing" and so it continues thru the day.
The secondary hand and the 36 diamonds should be ...
East face => white or even better, silver
North face => light blue
West face => green
South face => dark blue
(The drawing is a bit out in this respect).
The time of day
dé = day
The béu day begins at sunrise. 6 o'clock in the morning is called cuaju
The time of day is counted from cuaju. 24 hours is considered one unit. 8 o'clock in the morning would be called ajai (normally just called ajai, but cúa ajai or ajai yanfa might also be heard sometimes).
| 6 o'clock in the morning | cuaju |
| 8 o'clock in the morning | ajai |
| 10 o'clock in the morning | uvai |
| midday | ibai |
| 2 o'clock in the afternoon | agai |
| 4 o'clock in the afternoon | idai |
| 6 o'clock in the evening | ulai |
| 8 o'clock in the evening | icai |
| 10 o'clock at night | ezai |
| midnight | okai |
| 2 o'clock in the morning | apai |
| 4 o'clock in the morning | atai |
Just for example, let us now consider the time between 4 and 6 in the afternoon.
16:00 would be idai : 16:10 would be idaijau : 16:20 would be idaivau .... all the way up to .... 17:50 which would be idaitau
Now all these names have in common the element idai, hence the period from 4 o'clock to 6 o'clock is called idaia (the plural of idai). This is exactly the same as us calling the period from 1960 -> 1969, "the sixties".
The perion from 6 o'clock to 8 o'clock in the morning is called cuajua. This is a back formation. People noticed that the two hour period after the point in time ajai was called ajaia(etc. etc.) and so felt that the two hour period after the point in time cuaju should be called cuajua. By the way, all points of time between 6 a.m. and 8 a.m. MUST have an initial cuaju. For example "ten past six in the morning" would be cuaju ajau, "twenty past six" would be cuaju avau and so on.
If something happened in the period from 4 o'clock to 6 o'clock, it would be said to have happened idaia.pi
Usually you talk about points of time rather than periods of time. If you arrange to meet somebody at 2 o'clock morning, you would meet them apaiʔe.
But we refer to periods of time occasionally. If some action continued for 20 minutes, it will have continued nàn uvau, for 2 hours : nàn ajai (nàn means "a long time")
In English we divide the day up into hours, minutes and seconds. In béu they only have the yanfa. The yanfa is equivalent to 5 seconds. We would translate "moment" as in "just a moment" as yanfa also.
Index
- Introduction to Béu
- Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds
- Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
- Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
- Béu : Chapter 4 : Adjective
- Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
- Béu : Chapter 6 : Derivations
- Béu : Chapter 7 : Way of Life 1
- Béu : Chapter 8 : Way of life 2
- Béu : Chapter 9 : Word Building
- Béu : Chapter 10 : Gerund Phrase
- Béu : Discarded Stuff
- A statistical explanation for the counter-factual/past-tense conflation in conditional sentences