Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
..... Person/Tense/Evidence
..
Also called the r-form or the indicative.
..
To make a verb in the indicative mood, you must first deleted the final vowel from the infinitive. Then add affixes that indicate "agent", "indicative mood", "tense", "evidentiality" and "perfectness". We will refer to these as slots 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 respectively. All these affixes together are known as the verb tail. The "agent", "indicative mood", "tense" are mandatory ... however one tense, the aortist is a null morpheme.
..
... Seven Persons
..
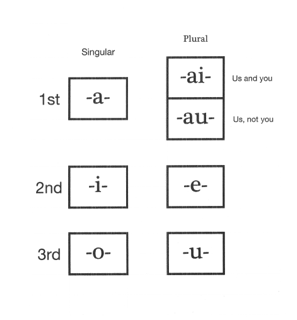
Slot 1 is for the agent ..
One of the 7 vowels below is must be added. These indicate the doer..
Notice that there are 2 entries that represent the 1st person plural subject (i.e. we). The top one represents first person inclusive and the bottom one represents first person exclusive.
Some people might have difficulty remembering whether to use ai or au. The diagram below might help some ...
..
..
Mathematically it is as if ... ai = me + you ... and ... au = me + they ....... (sort of)
The vowels of the first person plural inclusive pronoun magi are reflected in the infix -ai-.
As are the vowels of the first person plural exclusive pronoun manu are reflected in the infix -au-.
..
Note that the ai form is used when you are talking about generalities ... the so called "impersonal form" ... English uses "you" or "one" for this function.
The above defines the "person" of the verb. Then follows an "r" which indicates the word is an verb in the indicative mood. For example ...
doika = to walk
doikar = I walk
doikair and doikaur = we walk
doikir = you walk
doiker = you walk
doikor = he/she/it walks
doikur = they walk
..
... One Mood
..
Slot 2 is for the indicative mood marker.
..
At this point we must introduce a new sound and a new letter.
This letter has not been mentioned so far because it doesn't occur in any words as such. It only occurs in grammatical suffixes and it indicates the indicative mood.
If you hear an "r" you know you are hearing the main verb of a clause.
..
... Five Tenses
..
Slot 3 is for tense markers. There are 5 tense markers in béu
..
1) *doikaro => doikar = I walk (habitually)
I call this the aortist tense. The word comes from Ancient Greek and means "indefinite" as it was the unmarked tense/aspect. (Actually thIs unmarked form had a past & nondurative meaning in Ancient Greek). I call this form aortist because it is usually represented by a null morpheme. In béu it has a sort of timeless tense (sometimes it is habitual) used for generic statements. For example ...
ngur jwadoi = "birds fly"
Actually you can say this tense has an underlying o which appears again if there is an n or s in slot 4.
2) doikaru = I will walk
This is the future tense
3) doikari = I walked
This is the past tense. This means that the action was done before today (by the way ... the béu day starts at 6 in the morning).
4) doikare = I walked
This is the near-past tense. This means that the action was done earlier on today (a good memory aid is to remember that e is the same vowel as in the English word "day")
5) doikara = I am walking
This is the present tense ... it means that the action is ongoing at the time of speaking.
..
It can be seen that béu is more fine-grained, tense-wise than most of the world's languages ... http://wals.info/chapter/66 and http://wals.info/chapter/67
..
... Two Evidentials
..
Slot 4 can have one of the evidential markers a, a, n, s or it can be empty. Actually the first a defines the subjects attitute rather than any evidentiality, however all 4 are usually just called evidential markers.
..
There are three markers that cites on what evidence the speaker is saying what he is saying. However it is not mandatory to stipulate on what evidence you are saying what you are saying. In fact most occurrences of the indicative verb do not have an evidence marker.
The markers are as follows ...
1) -n
For example ... doikorin = "I guess that he walked" ... That is the speaker worked it out from circumstances/clues observed.
I will mention waron here. It means "I think so" and is nearly as common an answer as aiwa "yes"
2) -s
For example ... doikoris = "They say he walked" ....... That is the speaker was told by some third party(ies) or overheard some third party(ies) talking.
3) -a
For example ... doikoria = "he walked, I saw him" ...... That is the speaker saw it with his own eyes.
Note that the above evidential only co-occurs with the past tense and near-past tense. Actually when used with the near-past tense, *ea => ia so the distinction between "past" and "near-past" is lost for this evidential.
Now there is a forth possibility for this slot ... and it is not actually an evidintial. Furthermore it has the same form as 3).
4) -a
For example ... doikorua = "he intends to walk" ... the agent in this case must be a sentient being of course.
This evidential marker only co-occurs with the future tense.
If the speaker doesn't know the evidential or deems it unimportant then this slot can be left empty. According to corpus studies in béu, 60% - 70% of r-form have nothing in this slot.
..
So the complete verb prefix system is ...
..
It can be seen that the béu evidentiality inventory is quite substantial compared to other languages ... http://wals.info/chapter/78
Also it appears that 4 or 5 categories being appended to the verb is typical of languages of the world. See ... http://wals.info/chapter/22 [If I have understood the chapter properly]
..
... For brevity
..
We have seen that in the verb tail, o is not pronounced if it comes final (the aortist tense).
The reason for this is brevity of speech.
For brevity of writng, every occurrence of o is not written (in the verb tail). For example ...
..
..
... Probability/Aspect/Negation
..
We have already covered the 4 slots for "agent", r, "tense" and "evidentiality" at the end of the verb. As well as the nuances given by these suffixes, there are particles which add further information to the basic verb. These are called (near-standers ?). These particles occur in three pre-verbal slots..
..
..
... Two Probabilities
..
The two particles in slot 1 show probability.
lói = probably
màs = possibly
If nothing is in this slot, one assumes probability is 100%.
The probability distribution for lói centres around 85 %.
The probability distribution for màs centres around 50 %.
One can indicate a probability distribution centred around 15 % by using lói + bù. For example ... lói bù doikor = He/she probably doesn't walk.
..
... Two Habituals
..
The 7 particles in slot 2 have to do with aspect in some way.
Aspect can be tricky.
Every verb can be considered to have a default probability distribution over time.
 .... By the way, don't worry too much about the time scale in these sketched.
.... By the way, don't worry too much about the time scale in these sketched.
..
timpa and nko have very simple default probability shapes. But the typical (possible) probability distribution for kludau toili is more complicated.
..
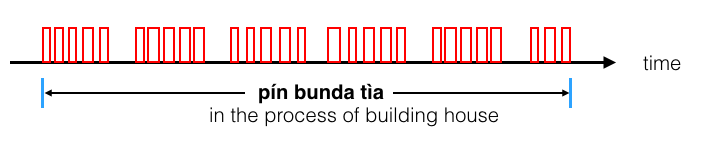
Likewise the typical (possible) probability distribution for bunda tìa.
We can group all verbs into 3 classes occording to their probability distribution over time.
1) Punctual event ... timpa
2) Steady state ....... nko
3) Process ............ kludau toili or bunda tìa
Now every verb (actually "very situation" would be more acurate) have a range of typical probability distributions associated with them. However the béu aspect markers IMPOSE a typical probability distributions on any verb they touch.
For example the particle awa imposes a probability distribution quite similar to kludau toili on ANY verb that it come in contact with.
awa* gives a "habitual but irregular" (maybe best translated as "now and again" or "occasionally" or even "not usually") meaning to the verbal block.
The particle bolbo* is similar to awa in a way. However it implies quite a bit of regularity. Maybe the regularity implied by ...
bolbo gives a "habitual and regular" (best translated as "normally" or "usually" or "regularly") meaning to the verbal block.
..
* awa is possibly related to the verb awata which means "to wander". bolbo is possibly related to the verb bolbolo which means "to roll". [by the way boloi means "to turn over" (as in "to turn over a mat"). boloi also means revolution [ boloi peugan means "social revolution" or boloi tun means "political revolution" ... i.e. the French Revolution ]. gwò is possibly related to the verb gwói which means "to pass (by)".
..
... The Perfect
..
The difference between bù and juku can best be explained with respect to a punctual verb such as timpa. For example, suppose we were discussing "John hitting Paul yesterday afternoon". That particular instance of "hitting" can be negated with bù. However suppose it is wished to widen what is negated. Suppose that you want to say that there has been no instances of "John hitting Paul" (up until the present time of course), then you would use juku to negate the proposition. This is equivalent to "never" in English and I consider it an aspect particle.
jonos polo bù timpori = John did not hit Paul
jonos polo juku timpori = John never hit Paul .... Notice that both timpori or timpore could be used. It depends upon what has been said before.
bù is purely negation. No probability distribution is imposed on the verb. Or you can say that the negated clause has the same probability distribution as the bare verb.
..
Now awa and bolbo impose a probability distribution over a period in time. juku, gwò* and jù gwò describe a probability distribution with respect to a point in time. In particular juku says that zero action has happened before a relevant point in time and gwò says that all the action has finished before a relevant point in time. For example ...
..
juku kludar toili dè = I have never read that book ... not one word
pín kludar toili dè = I have not completed that book (but I have read some of it)
gwò kludar toili dè = I have read that book .............. every word
..
..
It is not really possible to say *bù kludar toili dè. In this case the process of reading the book is being considered as a punctual process (which it really isn't). However by dropping the object you get bù kludar. This can be regarded as an event with a probability distribution over time, similar to nko. That is it is a sort of generic steady state event. For these sort of events bù is the normal negator. In a similar way constructions like "horses never fly" *fanfai juku ngur are frowned upon. "horses don't fly" *fanfai bù ngur is considered more felicitous.
..
gwò could be called an experiential perfect. béu also has a result perfect expressed with the copula sàu and the participle -in.
Overall the aspect distinctions available with béu are pretty fine-grained in some areas. It is not necessary to obsess too much on getting the exact form.
..
[ In Mandarin ... 没 méi or 没有 méiyǒu is used instead of 不 bù and the aspect marker 了 le is omitted ]
..
Some examples of usage ...
..
| gwò kodor | he has worked | juku kodor | he has never worked | juku kodora | he has never worked (up until now) |
| gwò kodori | he had worked | juku kodori | he had never worked | ||
| gwò kodore | he has worked (earlier today) | juku kodore | he hasn't worked (so far) today | ||
| gwò kodoru | he will have worked | juku kodoru | he will never have worked |
The aortist tense is negated using bù. i.e. bù kodor => he doesn't work
Let me explain the difference between juku kodor and juku kodora. The former is the unmarked form. In the latter the possibly of working in the future is given more prominence.
..
... The overlap couplet
..
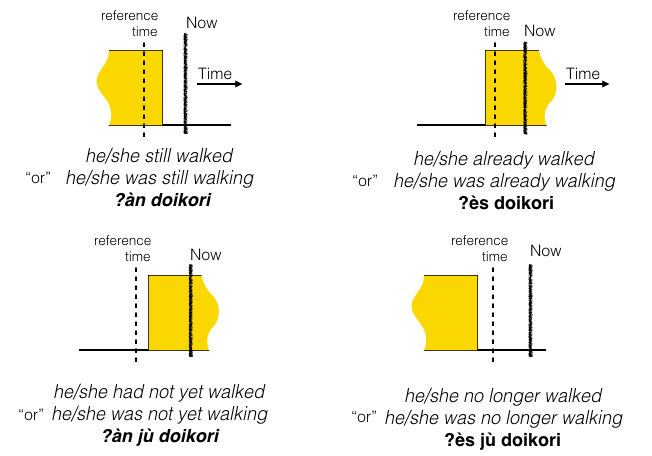
I call ʔàn and ʔès "overlap words".
You sometimes come across them referred to as "aspectual operators" or "aspectual particles" in the Western Linguistic Tradition.
Most languages have equivalents to these two particles ...
..
| English | still | already |
| German | noch | schon |
| béu | ʔàn | ʔès |
| French | encore | déjà |
| Mandarin | hái | yîjing |
| Dutch | nog | al |
| Russian | eščë | uže |
| Serbo-Croatian | još | već |
| Finnish | vielä | jo |
| Swedish | än(nu) | redan |
| Indonesian | masih | sudah |
..
ʔàn indicates ...
1) An activity is ongoing.
2) The activity must stop some time in the future, possibly quite soon.
3) There is a certain expectation* that the activity should have stopped by now.
ʔès indicates ...
1) An activity is ongoing.
2) The activity was not ongoing some time in the past, possibly quite recently.
3) There is a certain expectation* that the activity should not have started yet.
..
* Inevitably a connotation of "contrary to expectation" will develope to a certain degree. This is because if the situation was according to expectation often nothing would need be utterred. Hence ʔàn and ʔès are often found in contrary to expectation situation which in turn colours their meaning.
..
..
A very interesting thing about the overlap couplet is how they are negated cross-linguisticly. Either the particle can be negated or the verb can be negated. The first case I represent with a bar over the operator+verb. The second case with a bar over the verb only.
Notice ... compared to the positive case, if the operator+verb is negated ... the line that represents onset/cessation of activity is moved to the other side of the dashed line representing "now".
Notice ... compared to the positive case, if the verb is negated ... then the yellow place becomes white and the white space becomes yellow.
..
..
As you see by above ... by changing whether the negator act on the operator+verb or whether only on the verb give diametrically opposite meanings.
Note that there are 4 possible negative cases to choose from and a language only needs 2. A language (to cover all negative cases) should be either "(a) (b) type" or "(c) (d) type" or " (a) (c) type" or "(b) (d) type"
Cross linguistically there are interesting variations. All Slavic languages prefer verb negation, hence they are (c) (d) types.
In German, only (a) and (c) are allowed in positive declarations.
Nahuatl has negation of the operator so is (a) (b) type.
English is a bit tricky ... it has suppletion and uses "not yet" for situation (c) and "no longer" for situation (d). Now in English "yet" means pretty much the same as "still". I believe "yet" was the original particle but "still" over time largely usurped it in the positive case. However the form "not yet" ... if taken at face value would seem to negate the operator. But it doesn't. Logically it would make more sense if we said "yet not" instead of "not yet" [i.e. we have situation (c) rather than (b)]. I am sure there is a perfectly good explanation for this reversal but unfortunately I do not know it ... anyway ... nothing to worry about too much. [ The form "not work yet" seems more logical in its word order ... how can "not" in "not yet work" have "work" under its scope but not "yet" ... but apparently that is the way it works ]
In béu, bù negates the whole clause and jù simply negates the following word. In béu to negate a clause containing ?àn or ?ès, jù is always inserted immediately before the verb. It can be seen that it patterns with the Slavic languages.
..
| ʔàn | kod-a-r-a | dían |
|---|---|---|
| still | work-1SG-IND-PRES | here |
==> I am still working here
| ʔès | kod-a-r-a | dían |
|---|---|---|
| already | work-1SG-IND-PRES | here |
==> I already work here
| ʔàn | jù | kod-a-r-a | dían |
|---|---|---|---|
| still | not | work-1SG-IND-PRES | here |
==> I don't work here yet
| ʔès | jù | kod-a-r-a | dían |
|---|---|---|---|
| already | not | work-1SG-IND-PRES | here |
==> I no longer work here
..
These operators are usually used to specify overlap with present time ... (I call the present time, NOW, in the diagrams). I would think this is true of every language (notice that the above examples the tense is always -a). However it is a trivial matter to reference the time of onset/cessation of activity to a different time ... you just change the tense.
..
... Non-zero reference time
..
If the reference time is not NOW, we have an overlap-word clause, non-zero reference time.
The example below has a refernce time in the past. This is shown by having verb in the past tense. (Note to specify tense, person must first be specified ... I went for 3SG)
..
..
To have the reference time in the future, simply put the future tense on the verb.
Now when you have a reference time other than NOW, this reference time must be already understood by all or it must be explicitly stated. For example ...
| ʔès | kod-o-r-i | dían | kyù | baba ò | dai-o-r-i |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| already | work-3SG-IND-PAST | here | when | his father | die-3SG-IND-PAST |
==> He was already working here when his father died
..
In the above examples, the reference times are not NOW but are specified by another action (or state).
..
... When the overlap is specified
..
Sometimes the time of overlap between the reference time and the onset/cessation of activity is specified. I call this an overlap clause with absolutely specified overlap time.
By the way ... overlap clause, specified overlap time and a plain overlap clause have significantly different meaning ... ʔès and ʔàn clause are focused on the present time ... if an "offset time" is added then we focus on a period of past time extending into the present or a period of time extending from the present into the future. For example ...
| ʔàn | kod-a-r-u | dían | áus | euca | yìa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| yet | work-1SG-IND-FUT | here | period | seven | year |
==> I will work here for seven more years
| ʔès | kod-a-r-a | dían | áus | euca | yìa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| already | work-1SG-IND-FUT | here | period | seven | year |
==> I have worked here for seven years
Note ... If I wanted to give logical symmetry to the two case I could have used the present tense (kodara) for both. However the human mind treats past time and future time very different ... the future action is uncertain.
I thought this difference in treatment should be reflected in the grammar ... as in fact it is in most natural languages ... so ʔàn kodaru dían euca yìa instead of ʔàn kodara dían euca yìa
..
Negating the above
..
Now we have already said that béu is basically an (a) (b) type language.
However if we have a specified offset time it becomes (c) (d) type.
The negator used in this case is jù rather than bú.
To explain the reason for this .... well take the case of the English sentence ... "I have worked here for seven years" [ ʔàn kodara dían euca yìa ]
Now if we negate the English we get "I have not worked here for seven years"
However this is ambiguous ... does it mean "I have been idol for seven years" or "I have worked for a period of time different from seven years"
béu avoids this ambiguity by using the negative operator jù which only negates the element immediately following. So ...
"I have been idol for seven years" => ʔàn jù kodara dían euca yìa
"I have worked for a period of time different from seven years" => ʔàn kodara dían jù euca yìa
..
..
Note : the bottom left one is ?àn jù kodara euca yìa rather than *?ès jù kodara euca yìa
THIS IS BECAUSE ?
The rule is that bù is not allowed in a clause that has ʔès/ʔàn and an "specified offset time".
Note ... in English, one of the functions of the perfect is to indicate that an action started sometime in the past and is still going on. For example ... "I have worked here for seven years". In béu this is indicated by ʔès ...
..
While we are discussing this area I really should mention the béu non-overlap clause with duration and present tense.
If a time period is mentioned with a verb in béu the time period denote how long the activity went on for ... the duration of the activity (the duration usually follows the verb and no preposition ... like "for" ... is needed). However if ʔès/ʔàn are in the clause, the time period mentioned refers not to duration but to overlap. In this section we only talk about clauses with duration.
For the i, e and u tenses these constructions are self explanatory. For example ...
| kod-a-r-i | dían | áus | euca | yìa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| work-1SG-IND-PAST | here | period | seven | year |
==> I worked here for seven years (but I no longer work here).
However duration along with a present tense is worth mentioning.
| kod-a-r-a | dían | euca | yìa |
|---|---|---|---|
| work-1SG-IND-PRES | here | seven | year |
==> I will working here for seven years in total ............. I think this is disallowed
In the above example ... we are told that the total work period is seven years, but we get no information about how far we are through this seven year period. One doesn't hear this construction (present tense along with a time period) that often, but when you do hear it, its meaning is quite clear.
..
PS ... If you want to know more about aspect operators "The Meaning of Focus Particles" by Ekkehard König is the book for you.
..
... Restrictions
..
Let us discuss restrictions on these particles for a moment. Three rules to remember ...
1) lói and màs can co-exist with any particles from slot 2.
2) lói and màs can co-exist with bù from slot 3 but not with jù.
3) No particles from slot 2 can co-exist with bù.
4) Only ?àn and ?ès from slot 2 can co-exits with jù.
..
One usage of jù (slot 3) is mentioned above. Another usage is in certain SCV's. For example "listen not hear" ... "look not see" ... "try not succeed" where jù replaces the normal lé between the verbs.
[ ANY OTHER USAGE ? ]
..
... Other Verbal Moods
..
When people speak they have different intentions. That is they are trying to achieve different things by speaking ... maybe they are trying to convey information, or wanting somebody to do something, or not to do something, or they are just expressing their feelings about something. All these are examples of what is called moods. Different languages have different methods of coding their moods. Also the various moods of a languages cover a different semantic range compared to other languages.
There are 7 moods in béu ... 3 expressing themselves by changes to the root verb and 4 by periphrasis.
..
..
..
What are considered moods are shown by a green circle.
..
..
How the different moods and forms interact are shown above. [this will be explained in full later]
..
... The Infinitive
..
The maŋga is "the infinitive"
This is the base form of the verb ... not considered a mood. maŋga corresponds to what is called the "infinitive" in some languages or the "masDar" in Arabic.
About 32% of multi syllable maŋga end in "a".
About 16% of multi syllable maŋga end in "e", and the same for "o".
About 9% of multi syllable maŋga end in "au", and the same for "oi", "eu" and "ai".
Note that no maŋga end in "i", "u", "ia" and "ua"
"i" is reserved for marking verb chains, which will be explained later.
"u" is used for the imperative mood ... i.e. for commanding people.
"ia" is used for a past passive participle. For example ...
yubako = to strengthen
yubakia = strengthened ... as in pazba dí r yubakia => "this table is strengthened"
"ua" could be called the future passive participle I guess. For example ...
ndi r yubakua => these ones must be strengthened
To form a negative infinitive the word jù is placed immediately in front of the verb. For example ...
doika = to walk
jù doika = to not walk .... not to walk
..
... The imperative
..
You use the following forms for giving orders ... for giving commands. When you use the following forms you do not expect a discussion about the appropriateness of the action ... although a discussion about the best way to perform the action is possible.
..
For non-monosyllabic verbs ...
The final vowel of the maŋga is deleted and replaced with u.
doika = to walk
doiku = walk !
..
For monosyllabic verbs -hu is appended.
gàu = "to do"
gauhu = "do it" ... often só is added fot extra emphasis.
só gauhu = do it !
One verb has an irregular form.
jò = "to go"
ojo = "go" ... actually a bit abrupt, probably expressing exasperation, veering towards "fuck off" ... jò itself can be used as a very polite form.
..
The imperative cab be directed at second person singular or second person plural. When addressing a group and issuing a command to the entire group you sort of let your eyes flick over the entire group. When addressing a group and issuing a command to one person you keep your eyes on this person when issuing the command ... maybe saying their name before the command ... probably preseded by só which is a vocative marker as well as being an emphatic particle.
[ Note ... I think that in English, the infinitive usually has "to" in front of it, in order to distinguish it from the imperative. In béu too there is a need to distinguish between these two verb forms. However as the imperative occurs less often than the infinitive, I have decided to mark the imperative. ]
..
... The prohibitive
..
This is also called the negative imperative. Semantically it is the opposite of the imperative. It is formed by putting the particle kyà before maŋga.
kyà doika = don't walk
That is pretty much all there is to say about it.
..
... The optative
See Ch 3.??
... The suggestive
..
We have come across kái before. In chapter 2.10 we saw that it was a question word meaning "what kind of". It normally follows a noun being an adjective. For example ...
báu kái = what type of man ?
ò r báu kái = what type of man is he ?
ò r deuta kái = what type of soldier is he ?
nendi kái = this is what type ?
But just as a normal adjective can be a copula complement, so can kái.
ò r kái = what type is he ?
nendi r kái = this is what type ?
ʃì r kái = what type of thing is it ?
However when you see kái utterance initial you know that it has a slightly different function : it is introducing the "soliciting opinion" mood. For example ...
kái magi nyáu tìan jindi = How about we go home now ? OR Let's go home now.
Now ... as with the "optative", the "soliciting opinion" mood is usually orientated towards the future and uses maŋga. However their are circumstances where you solicit opinion about past events [for example a group of detectives on a crime scene discussing the possible steps taken by the perpetrator]. In these circumstances the r-form would be used preceded by the particle tà ... [see the table in the section above]
The main thing about this mood is that the speaker is asking for feedback/advice/approval or disapproval. But it overlaps with the field "gently suggesting a course of action" somewhat.
..
... The interrogative
..
Also called Polar Questions. A polar question is a question that can be answered with "yes" or "no".
..
To turn a normal statement ( i.e. with the verb in its r-form) into a polar question the particle ʔai? is stuck on at the very end.
It has its own symbol (and I transcribe it as ʔai?) because it possesses its own tone contour.
I have mentioned this particle in chapter 1 (if you look back you can see its exact tone contour). Here is its symbol again ... 
And here is an example of it in action ...
 ... jono jaŋkori ʔai? = Did John run ?
... jono jaŋkori ʔai? = Did John run ?
..
ʔai? is neutral as to the response expected ... well at least in positive questions.
To answer a positive question you answer ʔaiwa "yes" or aiya "no" (of course if "yes" or "no" are not adequate, you can digress ... the same as any language).
Here is an example of a positive question ...
glá r hauʔe ʔai? = Is the woman beautiful ?
If she is beautiful you answer ʔaiwa, if not you answer aiya*.
..
To answer a negative question it is not so simple. ʔaiwa and aiya are deemed insufficient to answer a negative question on their own. For example ...
glá bù r hauʔe ʔai? = Is the woman not beautiful ?
If she is not beautiful, you should answer bù hauʔe**, if she is you can answer either hù hauʔe or glá r hauʔe
I guess a negative question expects a negative answer, so a positive answer must be quite accoustically prominent (that is a short answer ("yes" or "no") is not enough)
..
We have mentioned só already ... in the above section about seŋko. This is the focus particle. It has a number of uses. When you want to emphasis one word in a clause, you would stick hù in front of it***.
Another use for só is when hailing somebody .... só jono = Hey Johnny
You can also stick it in front of someone's name when you are talking to them. However it is not a "vocative case" exactly. Well for one thing it is never mandatory. When used the speaker is gently chiding the listener : he is saying, something like ... the view you have is unique/unreasonable or the act you have done is unique/unreasonable. When I say unique I mean "only the listener" hold these views : the listener's views/actions are a bit strange.
When stuck in front of a non-multi-syllable verb you get an imperative. For example ... só nyáu = Go home
só can also be used to highlight one element is a statement or polar question. For example ...
Statement ... bàus glán nori alha = the man gave flowers to the woman
Focused statement ... bàus só glán nori alha = It is the woman to whom the man gave flowers.****
Unfocused question ... bàus glán nori alha ʔai? = Did the man give flowers to the woman ?
Focused statement ... bàus só glán nori alha ʔai? = It is to the woman that the man gave flowers ?
..
Any argument can be focused in this way.
..
*These words have a unique tone contour as well ... at least when spoken in isolation. I suppose I should have given these two words a symbol each ... if I wanted to be consistent.
**Mmm ... maybe you could answer ʔaiwa here ... but a bit unusual ... not entirely felicitous.
***In English, when you want to emphasis a word, you make it more accoustically prominent : you don't rush over it but give it a very careful articulation. This is iconic and I guess all languages do the same. It is a pity that there is no easy way to represent this in the English orthography apart from increasing the font size or adding exclamation marks.
****English uses a process called "left dislocation" to give emphasis to an element in a clause.
..
The other type of question ... the content question was covered in the last chapter.
..
... The conflative
..
Actually the verb itself is called an i-form verb. But a clause that has one or more i-form verbs is called a conflative clause.
I will only touch on this subject here ... in Ch 10 there is a section that goes into this verb form in exhaustive detail. But one quick example ...
..
jana jonos holdori nti flə léu sainyi => "yesterday John caught, cooked and ate three fish"
..
yesterday = jana
to catch = holda
to cook = ntu
to eat = flò
three = léu
fish = sainyi
..
totai timpə+ri jw+ daun = the child was hit and died (instantly) [Note to self : how to say "the child was hit and died later"]
totai = a/the child
timpa = to hit
jwòi = to undergo
dàu = to die
dàun = to kill
jwòi dàun = to be killed
..
In a conflative clause, the first verb is conjugated as normal. However the remaining verbs are in their i-form. That is ... the final vowel of the manga is deleted and replaced with "i". If the verb is monosyllabic, the final vowel is replaced with a schwa. Semantically thei-form verbs follow the first verb. That is nti means ntu.ori and flə means flori.
In conflative clauses, there can only be one subject but there can be more than one object. A conflative clause can consist of a mixture of H verbs and ɸ verbs. If the first verb is H then the subject is in its ergative form, otherwise it is in its base form. In the example given here, the three verbs have a definite time order, so the verb order is pretty much set. But we shall see in Ch 10 many examples where this is not the case.
..
Note ... in this example, all three verbs are intransitive and have the same object. So léu sainyi can not come between any of the verbs, but must come either before them all or after them all ... jana jonos léu sainyi holdori nti flə => "yesterday John caught, cooked and ate the three fish"
..
My motivation for having the conflative is to express meanings such as "through" or "into" by pure verbs ... i.e. "to go through", "to enter".
Also the béu verb tail can get pretty long so I didn't want it to be necessary to repeat it three or four times in quick succession.
Conflative clauses are very often used to describe situations involving motion. But no actual restrictions on what verbs can enter into a conflative clause (of course the verbs plus other arguments must represent a coherent subset of reality. That is the overall clause must make sense semantically).
..
..... Valency
..
In every language a particular verb can be associated with a number of nouns (we usually called these nouns arguments of the verb). For example ....
| jono-s | jene-n | slaigau | haun-o-r-a | eŋglaba-tu |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| John-ERG | Jane-DAT | calculus | teach-3SG-IND-PRES | English-INST |
==> John is teaching calculus to Jane in English
In the above example "teach" is associated with 4 nouns.
Now things can get a bit confusing here. It is said that it is easy to distinguish between "core arguments" which are essential and "peripheral arguments" which simply add more information. But this is not so. The consensus w.r.t. English seems to be that if an argument requires a preposition, then it is a "peripheral arguments", if no preposition required then it is a "core argument".
In the above example "English" can be dismissed as a peripheral argument because of "using". But what about "Jane". In the above example Jane's roll in the clause is defined by the prefix "to". But what if "John is teaching calculus to Jane in English" is re-arranged as "John is teaching Jane calculus in English"? Here you have three nouns not qualified by a prefix. In English "teach" is sometimes called a ditransitive verb (a verb that can take three essential arguments).
In beu no verbs are considered ditransitive ... Jane will always be marked by the dative suffix. Now you might argue that every instance of teaching involves "somebody getting taught" ... well this is true, but it is also true that every instance of teaching involves some language being used. At the end of the day ... the English verb "teach" means exactly the same as its béu equivalent ( haun ). It is just that there are two different conventions for talking about the verb in two different linguistic traditions. The béu linguistic tradition is the simplest.
The béu linguistic tradition divides all verbs in into two types .... H (transitive) and Ø (intransitive). In dictionaries all verbs are marked by the simbol H or Ø. H means a transitive verb ( called a "dash verb" ) and Ø means an intransitive verb ( called a "stroke verb" ). The rule is ...
..
A verb is H if it is ever associated with a noun that has the ergative marker "-s".
A verb is Ø if it is never associated with a noun that has the ergative marker "-s".
..
Now I will introduce the S A O convention which was devised by RMW Dixon. This convention is a useful way to refer to the arguments of transitive and intransitive verbs. The one argument of the intransitive verb is called the S argument. The argument of the transitive verb in which the success of the action most depends is referred to as the A argument. The argument of of the transitive verb is most affected by the action is called the O argument.
O was probably chosen from "object", A from "agent" and S from "subject" ( I find this useful to keep in mind as a memory aid). However O does not "mean" object and A does not mean agent and S does not mean subject. I (and many other linguists) use the word subject to refer to either A or S. Easier to talk about "subject" that to talk about "A or S" all the time.
[ In the béu linguistic tradition, the A argument is "the sadu noun", the O argument is the "the dash noun" and the S argument is the "the stroke noun".]
..
Now in English certain verbs appear to be Ø in some situations and H in others. These are called ambitransitive verbs.
..
1) The old woman knitted a sweater
2) The old woman knitted
"knit" is regarded as a "A=S ambitransitive". In (1) "old woman" is A ... in (2) "old woman" is S ... [ (2) is a smaller bite of the reality described by (1) ]
..
3) The old woman opened the door
4) The door opened
"open" is regarded as a "O=S ambitransitive". In (3) "the door" is O ... in (2) "the door" is S ... [ (4) is not inconsistant* to a smaller bite of the reality described by (3) ]
..
Now just as there are no "ditransitives" in béu, there are no "ambitransitives. "knit" is considered H but with the O argument being dropped when it is unimportant or unknown. Similarly "open" is considered H but with the A argument dropped** when it is unimportant or unknown.
bala "to open" is always H in béu. However, in English, "open" is sometimes transitive and sometimes intransitive.
Take pintu baləri*** "the door opened". In English the proper analysis is "door" = "S argument". Well it is subject because it comes before the verb, and as it is the only argument it must be S.
In béu the proper analysis is "door" = "O argument". We know bala "to open" is H becuse on occasion it can occur with A arguments. However in this case the only noun (pintu) is not marked for the ergative hence it must be the "O argument".
pintu baləri could also be translated as "the door was opened".
..
*(4) leave open the question whether human action brought about the action or it was due to some other cause. This question could be answered by rewriting (4) as either "The door was opened" or "The door opened by itself".
**Actually it would be possble to drop A arguments in English if the imperative was not the base verb. For example in English "knit a jersey" is a command ... but if English ... say ... suffixed "ugu" for the imperative, then the command would be "knitugu a jersey". That would allow "knit a jersey" to be interpreted as "jersey being knitted".
***We haven't come across the schwa before the "r" before. This will be explained very soon.
..
So in béu …. each verb is either H or Ø … no ambitransitives or ditransitives. Also “the passive” is not talked about … rather it is just considered a particular case of “dropping”. And actually “dropping” is not considered a bit deal … just an very obvious thing to do.
..
Now one problem with dropping arguments is that the subject (S or A) must be represented in slot "1" of the indicative verb. How should we know what to put in here ( see Ch3.1.2.1 ). One solution could be to use the 3 person plural suffix -u- ... chances are that it is a 3rd person agent and the plural is more generic than the singular. This is what Russian does to make a sort of a passive. Another solution would be to use a vowel not already appropriated for pronoun agreement. This is what béu does. The schwa is inserted in the slot just before the "r".
Everything collapses in ... to the schwa ... an impersonal schwa.
..
"the door opened" = "the door was opened" = pintu baləri (Actually I do not think the schwa symbol is visually distinct enough ... from now on I will use a cross) => pintu bal+ri
..
Here are some examples of this construction [ I will call it the impersonal construction from now on ]
beuba bl+r dían = "The language of béu is spoken here"
pí gaudoheu dè_blanyo g+r = "In this factory telephones are made"
toilia bù ost+r pí duka dí = "Books are not sold in this shop"
pintu by+r bala = pintu r balwa = the door has to be opened
pintu mb+r bala = the door can be opened ........... [ to understand this example and the one above it ... see Ch 4.7 ]
hala dè nyal+ryə = that rock is eroded .......... nyale = to erode, to wear
..
Note ... the schwa can not support any tone. And as it is only used in the grammer and not in any base words as such it was not introduced in Chapter 1 (as r was not). The schwa is represented in fact by a cross in the béu writing system ...
..
Note ... Some béu speakers pronounce "schwa" + "syllable final rhotic" as "ø" or "ør". These people also tend to give "ø" the proper tone. However the majority pronoun a schwa followed by a rhotic appoximant with neutral tone.
..
Now "door" is a man-made object and probably it exists in a place with many people around. So it is reasonable to expect there to be human volition involved when it opens. But what about when we get out into nature. When we see a river freezing. There is no agent to be seen behind this "freezing" ... it just happens. For this reason the verb "to freeze" doska is Ø.
But now we have become clever ... we hold dominion over nature. Hence we need to derive a word for freeze that is H. And that deriration is arrived at by appending -n.
Hence ...
doska = to freeze
moze doskori = the water froze
moze doskanaru = I will freeze the water
..
Actually any Ø can take this suffix and become H. Here are a few more examples ...
..
| ngeu | to fly | ngeun | to throw |
| jó | to go | jón | to send |
| tè | to come | tèn | to summon |
| bái | to rise | báin | to raise |
| kàu | to descend | kàun | to lower |
| dàu | to die | dàun | to kill |
| slài | to change | slàin | to change |
| diadia | to happen | diadian | to cause |
..
And here are a few more examples ....
| ʔoime | to be happy, happyness | ʔoimor | he is happy | ʔoimen | to make happy | ʔoimen | pleasant |
| heuno | to be sad/sadness | heunor | she's sad | heunon | to make sad | heunon | depressing |
| taude | to be annoyed | taudor | he is annoyed | tauden | to annoy | tauden | annoying |
| swú | to be scared, fear | swor | she is afraid | swún | to scare | swún | frightening, scary |
| centa | to be angry, anger | centor | he is angry | centan | to make angry | centan | really annoying |
| yode | to be horny, lust | yodor | she is horny | yoden | to make horny | yoden | sexy, hot |
| gái | to ache, pain | gayor | he hurts | gáin | to hurt (something) | gáin | painful |
| gwibe | to be ashamed/shame/shyness | gwibor | she is ashamed/shy | gwiben | to embarrass | gwiben | embarrassing |
| doimoi | to be anxious, anxiety | doimor | he is anxious | doimoin | to cause anxiety, to make anxious | doimoin | worrying |
| ʔica | to be jealous, jealousy | ʔicor | she is jealous | ʔican | to make jealous | ʔican | causing jealousy |
..
jài ?oime is an adjective meaning happy by nature.
Six H can also take -n as well. They are ...
..
| flò | to eat | flòn | to feed, feeding |
| mwé | to see | mwén | to show, showing |
| háu | to learn | háun | to teach, tuition |
| nko | to know | nkon | to inform, informing |
| pòi | to enter, to join | pòin | to put in, insertion |
| féu | to exit, to leave | féun | to take out, extraction |
..
In English, all the above except the last would be considered ditransitive verbs. "to take out" would not be considered ditransitive because one argument would be marked by the preposition "from". In béu they are all still H although they have undoubtedly one extra noun compared to their non-derived counter parts. Remember H and Ø were defined as ...
A verb is H if it is ever associated with a noun that has the ergative marker "-s".
A verb is Ø if it is never associated with a noun that has the ergative marker "-s".
(Note : fyá "to tell" means basically the same as nkon but is less formal. Also gàu means basically the same as diadian but is less formal. )
..
We have discussed bala and doska so far. The first is considered basically H and the second one basically Ø. There is a third type of verb ... for this type it is hard to say if it is more basic as Ø or more basic as H. So these verbs have two basic forms. For example ...
..
cwamo hulkori = the bridge broke
deutais cwamo helkuri = the soldiers broke the bridge
..
Actually for the first example .. the chances are that the breakage was due to wear and tear caused by human activity. But the important thing is that it is non-volitional. Also there might have been no humans around when the bridge actually did break. So we can talk about the bridge breaking by itself ... as if by an act of nature. And another example ...
..
jono wiltore = John woke up (earlier today)
jenes jone woltore = Jane woke up John (earlier today)
..
There are about 40 of these pairs. If the Ø has u the H will have e ... if the Ø has i the H will have o.
So lets summarize these three typre of verb ...
..
..
So to wrap it all up about verbs and arguments ...
No verbs are ambitrasitive. They are either Ø or H. However it is easy to drop the A or the O argument from a H clause if either of them is considered trivial or is unknown.
Now in béu any H can be given a Ø meaning ( grammatically the structure is still H ) by making the the O argument tái ... meaning himself, herself, yourself etc. etc. However only animate A arguments do this. Hence ...
bàus tái timpori = the man hit himself ................. acceptable
*pintus tái balori = the door opened itself ...... unacceptable
In English there are two ways to report on a door opening without mentioning any agent ... "the door opened" and "the door was opened"
In béu only one ... pintu bal+ri ... which is just a H clause with the A argument dropped. Comparable to how "the old woman knitted"(as this would appear in béu of course) is a H clause with the O argument dropped.
..
In béu you can make a "passive participle" by suffixing -ia.
If you come across something broken and you know it was broken by human volition ... you would call it helkia.
If you come across something broken and you did not know how it was broken ... you would call it hulkia.
If you come across something frozen you would call it doskia. There is no such word as *doskania.
..
In béu you can make the "general obligation participle" by suffixing -ua.
If you come across something that has to be broken ... you could refer to it as helkua.
If you come across something that had to be frozen ... you could refer to it as doskanua.
There is no such words as *doskua or *hulkua
..
The above method of presenting a verb like bala hints at human volition. To get rid of this connotation (to suggest that the event happened naturely) we must use tezau "to become" plus an adjective. This is demonstrated below ...
Consider geuko = "to turn something green" ... H ... derived from gèu "green"
1) báu tezori gèu = The man became green .. ........................ natural
2) báu geuk+ri = The man was made green .................... human volition
3) báus tái geukori = The man made himself green ......... human volition
..
Now consider bala = "to open" ... H
1) pintu tezori balya = the door became opened = the door opened .......... natural ................ [ here the agent could be anything ... the wind ... or even some fairy cái ... use your imagination ]
2) pintu bal+ri = the door was opened ............................................... human volition .... [ this one implies that the agent was human but is either unknown or unimportant and the action deliberate ]
Note ... there is no (3) here as a door is non-human.
..
In either of the (1)'s wistia "deliberately/carefully" or wistua "accidently/carelessly" can be added after* tezori. This automatically makes Agent => Human
The same for the (2)'s, but the incidence of wistua should greatly excede the incidence of wistia as "intention" is the default for this construction.
With (3) the connotation of intent is so strong that wistia/ wistua could be considered a bit infelicitous ... not impossible but indicative of an unusual situation.
* or wistiwe or wistuwe if not immediately after the verb. [by the way ... wisto = "mind/brain" by the way]
..
..... Six verbs of a kind
..
| bala | to open | kala | to shut/close |
| bana | to let go, to release, to free ... | kana | to connect, to make fast, to join |
| baza | to empty | kaza | to fill |
..
And we have six common adjectives derived from the above ...
..
| balya | open | kalya | shut/closed |
| banya | free, seperate | kanya | connected, joined |
| baʒya | empty | kaʒya | full |
..
| balo | an opening | kalo | a (window)shutter/valve |
| bano | padding | kano | link/connector |
| bazo | a void/vucuum |
The o suffix implies something solid. "connection", "association" or "relationship" would be covered by the manga ... kana.
bazda = desert ?? : kazda = ocean " kanda = an intersection ?? : balda = a gap
bano originally padding to separate a warriors leather armour from his tunic.
..
..... Shapes
..
Now béu has some justification for claiming to be an engelang. The paradigm above is quite engelangish as is the number system. The naming of shapes is also very engelangish. See below ...
..
Derived from dano dailo dauzo we have the adjectives danai dailai dauzai meaning "straight flat regular".
Derived from danai dailai dauzai we have the adjectives unai ulai uzai meaning "crooked/bent uneven/bumpy irregular".
..
Derived from dano dailo dauzo we have dante daite dauste meaning "a crooked line" "a rag"(also plate as in plate tectonics) "a lump"
The above may have some connection with dò "to move". The below may have some connection with kwè "to turn".
kwane kwaile kwauze = "a ring" "disc/plate/dish" "ball/sphere/globe" [Note kwante kwailte kwauste are imperfect manifestations of <= (kwauste=blob) ]
Also note ... si.anka = a testicle, si.ankau = a pair of testicles, si.ai = the earth (not used for other worlds), si.ana = a globe (a facsimile of <=)
{Note to self : should -ana derive other words ? taime = angle ? taume = solid angle ? ]
..
dalnoban = a triangle < uban dalno
dalnogan = a square < egan dalno
Note ... dailo is the usual word for square, dailo uzai would mean rectangle. However you might hear dalnogan in a mathematical context.
dalnodan = a pentagon < odan dalno
dalnolan = a hexagon < oilan dalno
etc. etc.
..
a tetrahedron = daizlogan < egan daizlo (i.e. a foursome of facets)
a cube = daizlolan < oilan daizlo
Note ... dauzo is the usual word for cube, dauzo uzai would mean block. However you might hear daislolan in a mathematical context.
an octahedron = daizlozan < aizan daizlo
a dodecahedron = daizlojain < ajain daizlo
an icosahedron = daizlojaizan < ajaizan daizlo
..
Note ... side as in flank is kebo ... face as in human/animal face is muka
..
..... Two verbal prefixes
..
In Dyirbal we have ... baŋga- "to paint" : baŋga-yarra- "to begin to paint".
In Russian we have ... бежать "to run" : побежать "to start running".
béu has something similar to the Russian example (except that voicing has been introduced) ...
doika = "to walk" : bodoika = "to start to walk" / "to set out"
bo- is an inflection rather than a derivation because it is applied automatically to all verbs.
..
In the Western Linguistic Tradition, bo- is called a marker of inchoative aspect.
..
béu also has the verbal prefix ke- which is opposite semantically from bo- ...
doika = "to walk" : kedoika = "to stop walking"
I don't think the Western Linguistic Tradition has a term for this (shame on you Western Linguistic Tradition)
..
Actually bo- and ke- are not symmetrical. ke- is a lot less common with the aspect particles yə and wə* taking up a lot of heavy lifting.
If the verb begins with e, then one of them is subsumed ...
eskua "to be angry" : keskua "to calm down" as opposed to ... bo.eskua "to get angry" ... which is the normal way béu handles vowels meeting up across inflectional boundaries.
A similar thing happens when bo- is prefixed to a verb beginning with o.
..
Some other examples ...
mauma = to sleep : bomauma = to fall asleep : kemauma = to wake up
kodai = to work : bokodai = to start to work : kekodai = to stop working / to down tools
sit .... stand ... lie ?
..
*See the section "IA & UA" in chapter 10.
..
..
..... To undergo
..
We have seen the subjectless verb form above where the vowel before the r becomes a schwa.`However there is another way to drop a subject ... by using the verb jwòi "to undergo" plus the infinitive. Of these two ways of dropping the subject, the former is overwhelmingly preferred. However for forming present participles and infinitives, the second method is necessary.
timp+ra = I am being hit : jwola timpa = being hit : jwòi timpa = to be hit
[Note to self .... sort out the below ... and also all the RUBBISH PARTICIPLE stuff I have]
mwari jono katala lazde = I saw John cutting the grass ....................... katala lazde is a saidau kaza ..... katala is a saidau baga
mwari lazde jwola kata = I saw the grass being cut ............................. jwola kata is a saidau kaza
mwari lazde jwola kata hí jono = I saw the grass being cut by John .... jwola kata hí jono is a saidau kaza
Note ... although the là suffix is probably connected to the second pilamo it should be recognized as a separate siffix here. If it was the pilamo we would have ... bwari lazde là jwòi kata
mwari lazde kataya = I saw the grass that has been cut
mwari lazde katawa = I saw grass that must be cut = I saw that the grass must be cut
lazde katawa mwari = I saw the grass that must be cut
mwari lazde nài r katawa
[Note to self .... explain exactly what pilamo can go on the manga ... everything can go on mangan I guess ]
..
..... The copula
..
The three* components of a copular clause usually have a strict order*** ... "copular subject" => "copula" => "copula complement". For example ...
..
| "copular subject" | "copula" | "copula complement" |
| jono | r | koduʒi |
|---|---|---|
| John | is | diligent |
| - | - | - |
| jono | r | moltai |
| John | is | doctor |
..
The copula's base form is sàu. You will see that it is listed among the 37 short verbs. However it patterns differently from the other 36. And indeed it patterns differently from all other verbs. Below are the r-forms of sàu ...
..
..
The copula form rule ... "When the copular subject noun (or noun phrase) is overtly stated, use the short form. At all other times, use the long form"
..
The short form is used when the copular subject noun (or noun phrase) is overtly stated. In other situations the full form is used. For example when the copular subject is a pronoun**, the long form must be used.
You can see in the above chart that the short form of the aortist tense has two forms. ró is used in two situations ...
1) If the copula subject ends in a consonant. For example ....
sòs rò hau?e = the snow is beautiful
2) If an evidential is tagged on. For example ...
tìa ròn hau?e = the house is beautiful (I guess)
..
r by itself is used in all other situations.it is a clitic attached the the last vowel of the copula subject. However it is always written as a separate word. For example ....
tomo r tumu = Thomas is stupid
It takes the tone of the copula subject.
..
The aortist form is the form corresponding to "am", "are" ans is in English. The present tense is "marked" (i.e. the unusual case that carries extra eaning). For example ...
..
sòs rò hau?e = snow is beatiful ….. a timeless truth
sòs rà hau?e = the snow is beatiful (for now) ... maybe the speakers are contemplating the snow melting and the consequent slush
..
And another example ...
..
jono r bòi = John is good (it is his nature)
jono rà bòi = John is being good ... maybe to impress somebody who is visiting.
Note ... to say jono rà bòi invalidates jono r bòi to a certain extent.
..
Because there is a strict word order, definiteness can not be expressed as it usually is with other verbs (S, O, A, dative ... left of verb if definite, right of verb if not). However the particles èn and ín can be drafted for this purpose.
[Note to self : should every pilamo defined argument act thus ... what about other arguments ? ]
It is only the r-form of the copula which is irregular. All other forms are perfectly normal. For example ...
sauhu bòi = be good ................................................................. u-form
kodor sə kludado = he works as a clark .................................... i-form
kodi sòr kludado = he/she works as a clark …........................… i-form .............. Actually, I think this way is better (change the rest of the website ?)
..
There is also the change of state copula, tezau. While tezau < té + sàu, I would not call it a calque on English "become", rather the deep semantic process that formed "become" in English, worked also in béu.
There is strict word order with this copula as well ...
..
| "copular subject" | "copula" | "copula complement" |
| jono | tezori | koduʒi |
|---|---|---|
| John | became | diligent |
| - | - | - |
| jono | tezori | moltai |
| John | became | doctor |
..
As you can see there is no erosion here.
Notice that for the two copulas the copuls subjects are always unmarked ... that is they never take the ergative suffix.
..
How to negate a copular sentence ? Some examples ...
jono bù r jutu = john isn’t big
bù sòr jutu = he/she isn’t big
ò bù sòr jutu = HE isn’t big (I am)
In the last example, it is not necessary to have the full copula form to show 3SG ... *ò bù r jutu ... would not be confusing. However we continue to abide by "the copula form rule"
..
* Well sometimes the copular subject is dropped so two components. It is dropped if the subject is "the world"/"the environment". Under the section "Valancy" we introduced the impersonal form of the verb ... normally used when the subject is "unknown"/"trivial". The copula also has an impersonal form. However now the reason is not because the subject is trivial : rather the opposite, the subject is all encompassing.
Note ... Other languages use "world" or "environment" as the subject in similar situations, English used "it".
As with English, this construction is often used for the weather ...
fona = rain : fonia = rainy/raining : fonua = dry (well not raining). So ...
s+ra fonia = it's raining
tez+ra fonia = it's starting to rain
..
**But actually to come across "pronoun" followed by "full copuls" is quite rare. As with all other verbs, ‘’’béu’’’ demands that the subject pronouns be dropped. Or at least you only hear them in exceptional circumstances.
For example, normally you would say ...
tìa bundari : "I built the house"
However upon hearing jono tia bundari (John built the house) you would say ...
aiya _ pás tìa bundari = No, I built the house
And another example, normally you would say
sar jutumo : "I am biggest"
However upon hearing jono r jutumo (John is biggest) you would say ...
aiya _ pà sar jutumo : "No, I am biggest"
..
***There are two exceptions to this rule.
..
1) If the copula subject is a manga or a manga phrase you have two possible orders.
..
| nyáu | r | bòi |
|---|---|---|
| to return | is | good |
==> To return is good
..
| sòr | bòi | nyáu |
|---|---|---|
| "is" | good | to return |
==> It is good to return
..
The more accoustic weight the manga phrase has, the bigger the tendency to use the second order ...
..
| sòr | bòi | nyáu | tìa | jindi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| "is" | good | to return | home-DAT | now |
==> It is good to return to home now
..
With the copula coming initially the short eroded form can never be used ... that is *r bòi nyáu or *rò bòi nyáu are illegal.
..
2) If copula subject is a clause**** with the particle gò at the front, you have only one possible order ... "copula" and then "copula complement" and then "copular subject".
| sòr | bòi | gò | t-o-r-e | heute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| "is" | good | that | come-3SG-IND-PAST | today |
==> It is good that he/she came today
..
tezau follows sàu when it comes to word order.
..
**** this construction is covered in the Ch 4 in the section "The particle gò "
The above has all you need to know about the copula's ... not much to them ... just a few rules.
However I am appending a bit about the adverb wautus to this section as nowhere else really seems appropriate.
wautus can be broken down into wáu "a pair of eyes" : 'tú "particle giving the intrumental case" : s "adverbial marker". It means "apparently" or "seemingly".
In English "by eye" usually means "by not measuring as such but roughly estimating (whatever) only using ones eyes". wautu does not mean this : it means "apparent".
More often come across in the form wautus "apparently".
jono boizor wautu = "John is OK apparently
wautus jono boizor = "John appears to be health"
jene r wautu maumala = "it seems as if Jane is asleep"
jene maumora_wautus = "Jane is asleep, apparently" ... Note, in the last example wautus was added as an afterthought so it needs the adverbial s (not usually necessary when an adjective follows a live verb).
..
... Existence
..
In the above section we saw how the impersonal form of sàu links an adjective to the universe at large (well at least to the local environment).
In a similar way, the impersonal form of yáu "to have on your person" links an noun to the universe at large.
..
But first let us run through some of the usages of yáu.
..
The basic usage is to link an object to a person.
jonos yór kli.o = John has a knike
..
The basic usage can be expanded and it can be used to link objects to a location.
| tunheu-s | y-o-r-e | yiŋki | hè | yildos |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| townhall-ERG | have-3SG-IND-PST | "attractive girls" | a lot | morning |
==>(1) the townhall had many attractive girls this morning
..
The above usage can become impersonalized (i.e. the locative subject is deleted and the person slot gets a schwa) and the meaning then becomes ... the physical object exists somewhere in the Universe. For example ...
..
y+r dèus = "there is a God" or "God exists"
This construction can be negated in two ways ...
bù y+r dèus = "there isn't a God" or y+r jù dèus = "there is no God"
So y+r is basically the béu existential clause. The English existential clause has "there is"/"there are".
Now the basic existential clause can be modified. For example ...
(2) y+r yiŋki hè = "There are many attractive girls"
Can be modified ... below we modify it with an "adjective phrase of location" tunheuʔe and an "adjective phrase of time" yildos
(3) y+re yiŋki hè tunheuʔe yildos = "there were many attractive girls at the townhall this morning"
..
Which actually means exactly the same as (1) above ... (i.e. tunheus yore yiŋki hè yildos)
Which in turn means pretty much the same as the copular sentence ...
(4) yiŋki hè rè tunheuʔe yildos = "many attractive girls were at the townhall this morning" ... so ... actually three ways to say the same thing ... (1), (3) and (4)
But note ...
*tunheuʔe rè yiŋki hè yildos = "at the townhall this morning were many attractive girls"
The above construction that is allowed in English, feels a bit strange in béu ... in the same way that "green is the man" feels a bit strange in English.
But three ways to say the same thing, should be sufficient ... don't you think ?
..
... Index
- Introduction to Béu
- Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds
- Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
- Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
- Béu : Chapter 4 : Adjective
- Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
- Béu : Chapter 6 : Derivations
- Béu : Chapter 7 : Way of Life 1
- Béu : Chapter 8 : Way of life 2
- Béu : Chapter 9 : Word Building
- Béu : Chapter 10 : Gerund Phrase
- Béu : Discarded Stuff
- A statistical explanation for the counter-factual/past-tense conflation in conditional sentences