Olivarian: Difference between revisions
m (→Diacritics: fixed typo) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
:*The circumflex accent (<ê> and <ô>) appears in the roots of some verbs. They don't indicate word stress, but when that vowel becomes stressed (in some persons of the present, for example), then it indicates a low vowel (/ɛ/ and /ɔ/). | :*The circumflex accent (<ê> and <ô>) appears in the roots of some verbs. They don't indicate word stress, but when that vowel becomes stressed (in some persons of the present, for example), then it indicates a low vowel (/ɛ/ and /ɔ/). | ||
:*The diaresis (over ''ü'') appears in the digraph ''qü'' before ''e'' or ''i'' and indicates a voiced labiovelar approximant (/w/) in standard pronunciation. Over the dialects, it can also be silent or pronounced as [v], especially in Lenòmia. | :*The diaresis (over ''ü'') appears in the digraph ''qü'' before ''e'' or ''i'' and indicates a voiced labiovelar approximant (/w/) in standard pronunciation. Over the dialects, it can also be silent or pronounced as [v], especially in Lenòmia. | ||
:*T-comma ‹ț› represents the voiceless alveolar affricate (/ts/). | :*T-comma ‹ț› represents the voiceless alveolar affricate (/ts/). S-comma <ș> represents the voiceless post-alveolar fricative (/ʃ/). | ||
===Digraphs=== | ===Digraphs=== | ||
Revision as of 18:31, 30 May 2013
| Vulgariano | |
| Pronunciation: | [vulgaɾiˈano] |
| Spoken in: | Vulgaria, Sea of Sardinia |
| Coordinates : | (may not appear in some maps) [1] |
| Total speakers: | 80,000 |
| Language family: | Romance language |
| Distribution: | 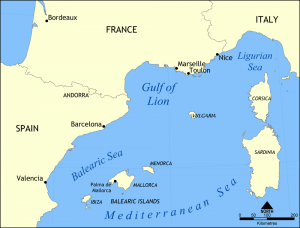
|
Vulgarian (or lingua vulgariana) is a Romance language spoken as a native language by about 80 thousand people in the Island of Vulgaria, in the Sea of Sardinia.
Vulgarian derives diachronically from Latin. It is extremely conservative in comparison to some other Romance languages.
Writing system
Alphabet
Vulgarian is written with the 26 letters of the Latin alphabet, with four diacritics appearing on vowels (circumflex accent, acute accent, grave accent, diaeresis), the t-comma (ț) and the s-comma (ș).
Letters typically have the same values as in the International Phonetic Alphabet. Further details are explained below.
Diacritics
- The acute accent and the grave accent indicate that a vowel is stressed, and also the quality of the accented vowel, more precisely its height: é (/e/), í (/i/), ó (/o/), ú (/u/), and ý (/i/) are stressed high vowels, while à (/a/), è (/ɛ/), and ò (/ɔ/) are stressed low vowels.
- The circumflex accent (<ê> and <ô>) appears in the roots of some verbs. They don't indicate word stress, but when that vowel becomes stressed (in some persons of the present, for example), then it indicates a low vowel (/ɛ/ and /ɔ/).
- The diaresis (over ü) appears in the digraph qü before e or i and indicates a voiced labiovelar approximant (/w/) in standard pronunciation. Over the dialects, it can also be silent or pronounced as [v], especially in Lenòmia.
- T-comma ‹ț› represents the voiceless alveolar affricate (/ts/). S-comma <ș> represents the voiceless post-alveolar fricative (/ʃ/).
Digraphs
- CH: voiceless velar plosive (/k/).
- GH: voiced velar plosive (/g/).
- GU: represents the voiced velar plosive plus (/g/) plus a voiced labiovelar approximant (/w/) before vowels. Elsewhere, it is pronounced /gu/.
- LH: palatal lateral approximant (/ʎ/).
- NH: palatal nasal (/ɲ/).
- PH: voiceless labiodental fricative (/f/).
- QU: occurs before e and i and represents the voiceless velar plosive (/k/).
- QÜ: occurs before e and i and represents the voiced velar plosive plus (/k/) plus a voiced labiovelar approximant (/w/).
- RR: occurs between vowels and represents the alveolar trill (/r/).
- SS: occurs between vowels and represents the voiceless alveolar sibilant (/s/).
- TH: represents the voiceless alveolar plosive (/t/).
- ZZ: represents the voiceless alveolar affricate (/ts/).
Double letters
With exception of rr, ss, and zz, mentioned above, double letters are pronounced as if they were single letters.
Letters whose pronunciation depend on adjacent letters in the word
- C: voiceless postalveolar affricate before e and i (/tʃ/); voiceless velar plosive elsewhere (/k/).
- G: voiced postalveolar affricate before e and i (/dʒ/); voiced velar plosive elsewhere (/g/).
- QU: voiceless velar plosive followed by a voiced labiovelar approximant (/kw/), except in the combinations <que> and <qui>, pronounced /ke/ and /ki/.
- R: alveolar tap (/ɾ/) after vowels; alveolar trill elsewhere (/r/).
- S: voiced alveolar sibilant (/z/) between vowels; voiceless alveolar sibilant elsewhere (/s/).
Other letters that differ from IPA
- H: when it is not part of a digraph, it is silent.
- J: voiced postalveolar fricative (/ʒ/).
- W: voiced labiovelar approximant (/w/) or close back rounded vowel (/u/).
- X: velar plosive plus alveolar sibilant. Voiced between vowels (/gz/), unvoiced elsewhere (/ks/).
- Y: palatal approximant (/j/> or close front unrounded vowel (/i/).
- Z: voiced alveolar affricate (/dz/).
Stress and accentuation
The default stress is on the penultimate (next-to-last) syllable on words that end in a vowel, ‹n› or ‹s› and on the final syllable when the word ends in any consonant other than ‹n› or ‹s›. Words that do not follow the default stress have an accent over the stressed vowel. Such an accent can be acute, for low vowels, or grave, for high vowels.
Vulgarian rules count syllables, not vowels, to assign written accents. A syllable is of the form XaXX, where X represents a consonant, permissible consonant blend, or no sound at all and a represents a vowel, diphthong, or triphthong. Diphthongs and triphthongs are any combination of two and three vowels, respectively. Hence, Vulgarian writes familia (ending with a diphthong) but línea (the default stress would be on e as it does not form a diphthong).
Furthermore, the high vowels è and ò always have a grave accent in stressed position, even when the stress is understood, as in pède or nòvo. If not specifically marked, the stressed vowels e and o are otherwise low by default.
Phonology
In this section, the phonology of the standard dialect is described.
Vowels
| Front | Back | |
|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u |
| Close-mid | e | o |
| Open-mid | ɛ | ɔ |
| Open | a | |
- While Vulgarian contrasts close-mid (/e o/) and open-mid (/ɛ ɔ/) vowels in stressed syllables, they are in free variation when unstressed.
Consonants
| Bilabial | Labio- dental |
Dental/ Alveolar |
Post- alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | |||
| Plosive | p b | t d | k g | |||
| Fricative | f v | s z | ʃ ʒ | |||
| Affricate | ts dz | tʃ dʒ | ||||
| Approximant | j | w | ||||
| Trill | r | |||||
| Tap | ɾ | |||||
| Lateral | l | ʎ |
- Nasals assimilate to the point of articulation of whatever consonant they precede. For example, /nɡ/ is realized as [ŋɡ].
Dialects
| IPA | Consonants | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Dòssia | Lenòmia | Ucòsia | S. Telcapòlia | N. Telcapòlia | Pecesamia | W. Hurtòmia | E. Hurtòmia | Examples | |
| b | b | bocca | ||||||||
| b, v | v | β, v | β | trabalho | ||||||
| v | v | v | levare | |||||||
| b, v | b | vacca | ||||||||
| p | p | b | β | sapere | ||||||
| p | p | padre | ||||||||
| d | d | d | d | dulce | ||||||
| ð | nido | |||||||||
| t | t | vita | ||||||||
| t | tecto | |||||||||
| f | f | fícato | ||||||||
| k | k | k | câne | |||||||
| g | ɣ | laco | ||||||||
| g | g | pedagogo | ||||||||
| g | gallo | |||||||||
| l | l | l | l | l | luna | |||||
| ɫ | sole | |||||||||
| l, ɫ | palma | |||||||||
| ʎ | j | ʎ | ʝ | palhacio | ||||||
| j | j | iate | ||||||||
| j | acţione | |||||||||
| m | m | madre | ||||||||
| n | n | nòstro | ||||||||
| ɲ | ɲ | nj | ɲ | banho | ||||||
| r | ʀ, ʁ, r | ɾ | r | r, ʁ, x, h | r | ratto | ||||
| ɾ | ɾ | ɾ | ɾ | puro | ||||||
| ɾ, ɹ, ʁ, x, h | pòrta | |||||||||
| s | s | s, ʃ | ʃ | s | s, h | pasta | ||||
| s | s | similare | ||||||||
| z | z | s, z | z | z | casa | |||||
| z | z, ʒ | ʒ | z, ʒ | z, h | metesmo | |||||
| (d)ʒ | ʒ | dʒ | ʒ | ʒ | x, h | generale | ||||
| (j)ʃ | is | (p)s | ʃ | (j)ʃ | lajxare, cojxa | |||||
| (t)ʃ | z | tʃ | z | s | θ | dícere | ||||
| s | ʃtʃ | ʃ | s, ʃ | ʃs, ʃ | s, ʃ | pesce | ||||
| tʃ | s | cèlo | ||||||||
| (t)s | ts | cânţione | ||||||||
| (d)z | z | dz | z | dz, z | zelare | |||||
| w | Ø | v, Ø | w, Ø | qüestione | ||||||
| IPA | Vowels | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | Ucòsia | S. Telcapòlia | N. Telcapòlia | Pecesamia | Dòssia | Lenòmia | Hurtòmia | Examples | |
| a | a | a | a | a | a | casa | |||
| ɐ̃ | ɑ̃ | ɨ | ângelo | ||||||
| a, ə | ə | a, ə | gallina | ||||||
| ɛ | jɛ | ɛ | ɛ | jɛ | je | pède | |||
| ɛ | ɛ | tèrra | |||||||
| ẽ | tèmpo | ||||||||
| e | e | e | e | censo | |||||
| e | e, ɛ | erro | |||||||
| e, i | ɨ | ə | gente | ||||||
| i | i, e | i | i | i, ə | i, e | i | primario | ||
| ɨ | restrîngere | ||||||||
| i | i | i | amico | ||||||
| ĩ | cinqüe | ||||||||
| ɔ | wɔ | ɔ | ɔ | ɔ, ø, œ | wo | scòla | |||
| ɔ | còsta | ||||||||
| õ | ɔ̃ | cònto | |||||||
| o | o | o | o | ponto | |||||
| o | o, ɔ, ø | pollo | |||||||
| o, u | u | u, ə | o, u, ə | o, u | o | voluto | |||
| u | u | u | u | u, y | u | cubo | |||
| ũ | u | un | |||||||
Grammar
Sentences and word order
Verbs
Every Vulgarian verb belongs to one of three form classes, characterized by the infinitive ending: -are, -ere, or -ire— sometimes called the first, second, third and the fourth "conjugations", respectively.
Nouns
Articles and determiners
Adjectives
Adverbs
Prepositions
Pronouns
Examples
Sample texts
Declarațione Universale de'llos Direċtos Humanos
Artículu Unu
Totos illos èsseres humanos nascont líberos et eguales in dignitate et in direċtos. Sunt dotatos de rațione et de conscienția et debent comportar-se illos unos cun illos altros in spíritu de fraternitate.
Articulu Duos
Totas las personas se possont prevalere de'llos direċtos et las libertates proclamatos in ella presente Declarațione, sin nulla distincțione, notatamente, de rața, de colore, de sexu, de lingua, de religione, de opinione política oud qualsía altra, de orígine naționale oud sociale, de fortuna, de nascența oud qualsía altra situațione. Fòra de acuéstu, non seràt facta nulla distincțione fundata in illu statutu políticu, jurídicu oud internaționale de'llu paese a'llu quale una persona appertènet, sía acuéstu paese oud territoriu independente, subtu tutela, non autònomu oud subiectu ad qualsía altra limitațione de suberanitate.
Artículu Trés
Totu individuu hat direċtu a'lla vita, a'lla libertate et a'lla securitate de sua persona.
Artículu Quattro
Nulla persona seràt mantenuta in sclavitúdine oud in servitúdine; la sclavitúdine et illu commerciu de sclavos sunt prohibitos subtu totas las suas formas.
Artículu Cinque
Nulla persona seràt submissa ad tortura oud tractamentos oud ad puniționes crudeles, inhumanos oud degradantes.
Artículu Sex
Totu individuu hat illu direċtu, in totos locales, a'llu reconnoscimentu de sua personalitate jurídica.
Artículu Septe
Totos sunt eguales abante la lege et haunt direċtu, sin distincțione, ad eguale protecțione de'lla lege. Totos haunt direċtu ad una eguale protecțione contra qualsía discriminațione que viòlet la presente Declarațione et contra qualsía provocațione ad tale discriminațione.
Artículu Oċto
Tota persona hat direċtu ad un recursu effectivu abante las juristicționes naționales competentes contra illos actos que viòlent illos direċtos fundamentales reconnoscutos per la constituțione oud per la lege.
Artículu Noue
Nulla persona pòtet èssere arbitrariamente arrestata, detenuta oud exiliata.
Artículu Dèce
Tota persona hat direċtu, in condiționes de plena egualitate, ad èssere equitativa et publicamente audita per un tribunale independente et imparțiale, per la determinațione sía de suos direċtos et obligaționes, sía per illu examen de qualsía accusațione in matèria penale contra élla.
La Turren de Babel
Intunque tota la terra habeva una sola lingua et las metísimas parablas. Quando partieront de'llu oriente, incontraront una planura in illu paese de Senar et allà se stablieront. Et dísseront illos unos a'llos altros: Venitis, fàciamos bloccos et còcamo-los cun fòcu. Et illos bloccos lis servieront de pètra et illu bitume de cementu. Appòst dísseront: Venitis, constrúamo-nos una ciutate et una turren, illu cúlmine de'lla quale arribet a'llu cèlu, et fàciamo-nos famosos, ad fine de vedere la ciutate et la turren que illos filĭos de'llos hòmines construevant. Et illu Senĭore disset: Illes sunt un solu pòpulu et parlant una sola lingua: acuéstu est illu que comințiaront fàcere. Ahora nullu los restrigeràt de fàcere totu que se proponant. Intunque descèndamos et confúndamos lòru lingua, ad fine de que non compreendant mais la lingua illos unos de'llos altros. Et illu Senĭore los dispersaut de allà supre tota la terra; et cessaront de constrúere la ciutate. Per acuéstu, acuésta ciutate se clamaut Babel, per que allà illu Senĭore confuset la lingua de tota la terra, et de allà illu Senĭore los dispersaut supre tota la terra.
Illu Diminutu Príncipe
Quando habeva sex annos, vedui, una vece, una magnífica imàgine, in un libru supre la foresta vírgine que se clamabat "Històrias Vivutas". Acuéstu representabat una serpente boa que ingluttibat una fèra. Acuésta èst la copia de'llu designu:
Se diceva in illu libru: "Las serpentes boas ingluttont lòru preda tota intègra, sin masticar-la. Appòst non possont mais mover-se et dormont durante illos sex meses de lòru digestione".
Reflexi multu intunque supre las adventuras de'lla jungla et, ad mea vece, reexíi, cun un làpize de colore, ad tracciare meun primu designu. Èra assí:
Monstrai mea òpera maistra a'llas personas grandes e lis questionaba si meun designu lis faceva pavore.
Éllas me respònseront: "Per que un capellu farea pavore?"
Meun designu non representabat un capellu. Representabat una serpente boa que digerevat un elephante. Intunque disegnai illu interiore de'lla boa, per que las personas grandes potuissent compreèndere. Sempre necessitant explicaționes.
Sànscritu
La lingua sànscrita, qualsía sua antiquitate, est de una structura meravilĭosa; mais perfecta ca illu grècu, mais rica ca illu latine et mais exquisitamente refinata que totas las duas, sibenque hat cun las duas una affinitate mais forte, tantu in las radices de'llos verbos quanto in ellas formas de grammàtica, ca potereat habere statu productu per accidente. Tan forte, in factu, que nullu philòlogu potereat examinare totas las trés, sin crédere que se originaront de una fonte commune que, pòte èssere, non mais existe. Ivi hat una raţione similare, sibenque non tan forte, per pressupónere que tanto illu gòthicu quanto illu celta, sibenque mesclatos cun una lingua multu differente, habiant illu metísimu orígine que illu sànscritu; et illu antiquu persa poterea èssere aggregatu a'lla metísima familia.