Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds: Difference between revisions
| Line 902: | Line 902: | ||
Numbers are never written out in full. Always the method given above is used. It is as if in a body of English text you never came across the "seven" but only "7". | Numbers are never written out in full. Always the method given above is used. It is as if in a body of English text you never came across the "seven" but only "7". | ||
With fractions, cardinal numbers and numbers denoting group size, there is the choice of writing 7<sup>th</sup> or seventh. That is you can either use the symbols given below or you can write out in full ... in this example '''suga''', '''nuga''' and '''buga'''. | |||
.. | |||
[[Image:TW_385.png]] | [[Image:TW_385.png]] | ||
Revision as of 00:24, 21 April 2016
..... The sounds of béu
..
The full range of sounds heard in béu are given below according to the conventions of the I.P.A. (International Phonetic Alphabet)
..
| labial | labiodental | alveolar | postalveolar | palatal | velar | glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stops | p b | t d | k g | ʔ | |||
| fricatives | f (v) | s z (ð) | ʃ ʒ | (ɣ) | h | ||
| affricates | tʃ dʒ | ||||||
| nasals | m | n | ŋ | ||||
| liquids | r l | ||||||
| glides | w | y |
tʃ dʒ are the initial sounds of "Charlie" and "Jimmy" respectively. From now on they will be represented by c and j.
ʔ represents a glottal stop (the sound a cockney would make when he drops the "tt" in bottle). In béu this is a normal consonant ... just as real as "b" or "g" in English.
The sounds "b" and "v" are in free variation when inside a word and between two vowels ... henceforth just referred to as b in this document.
The sounds "d" and "ð" are in free variation when inside a word and between two vowels ... henceforth just referred to as d in this document.
The sounds "g" and "ɣ" are in free variation when inside a word and between two vowels ... henceforth just referred to as g in this document.
z is an allophone of s when inside a word and between two voiced* sounds.
ʃ is also an allophone of s when before the front vowel i or before the consonant y. ʃ is found in English and is usually represented by "sh" (as in "shell")
ʒ is an allophone of s when the above two conditions apply at the same time. ʒ turns up in English in one or two words. It is the middle consonant in the word "pleasure".
ŋ is an allophone of n when followed by k or g. ŋ is found in English and is usually represented by "ng" (as in "sing").
l is a clear lateral in all environments.
r is an approximant in all environments.
p, t and k are never aspirated. And on the other hand b, d and g are more voiced than in English (i.e. the voice onset time is a lot earlier)
* Actually all the phonemes are voiced, apart from p, t, k, s, f, h and ʔ.
The béu phoneme inventory is shown below.
..
| labial | labiodental | alveolar | postalveolar | palatal | velar | glottal | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| stops | p b | t d | k g | ʔ | |||
| fricatives | f | s | h | ||||
| affricates | tʃ dʒ | ||||||
| nasals | m | n | |||||
| liquids | r l | ||||||
| glides | w | y |
There are 5 basic vowels ... a, e, i, o, u plus ə. However the schwa is only used in the grammar and does not appear in any actual words. There are 6 diphthongs ... ai, au, oi, eu, ia and ua. Note that while the sounds ia and ua are possible sound combinations in English, they each are realised as two syllables. In béu the two components are more intertwined ... the flow into each other more. And they each represent only one syllable. Certain people pronounce e and o more open, when in an open syllable, but for others, e and o are the same in all environments.
..
béu differentiates between words using tone. All single syllable words have either a high tone (for example pás = "I") or a low tone (for example pà = me). All multi-syllable words lack tone (or can be said to have neutral tone). If a single syllable word, receives an affix making it into a multi-syllable word, its tone will become neutralised. If a word count was done on a typical béu text, it would be found that around 17% of words have a high tone, 33% have a low tone and 50% have the neutral tone.
..
All non-monosyllables have stress on the first syllable. If this initial syllable is light (i.e. no initial consonant cluster, no diphthong and no coda) then the vowel will have nearly twice its normal length. For example, take the words mulu (beatle) and huŋgu (swan) and kludau (to write). The initial u in mulu is a lot longer than the other 4 instances of u. However it doesn't receive any special marking. This extra length is totally predictable from its location.
NB ... no minimal pair can be found to differentiate uu from u.
..
Don't let the tones put you off learning béu. The chances are vanishingly small that you will cause a misunderstanding by pronouncing one of the short words wrong. And even if you speak the language and put absolutely no effort into getting the tones right ... no problem, it will just mark you out as a non-native speaker, you will be understood virtually all the time.
..
In the béu writing system a small dot is placed to the right of the word if it has a high tone. If single syllable words are come across that do not have a dot .... well then you know that they must be low tone.
..
..... Some interjections
..
All languages have a small set of interjections. Often these words fall outside the normal phonology of the language ; béu is no exception. These words are normally elucidated singly. Also they usually have a set pitch contour. The pitch contours of the interjections below are shown by the red lines.
..
..
Apologies ... I haven't worked out how to represent IPA in Keynotes yet. So I must give the actual exclamations below ...
(a) ... iʃʃ ..... ʃ usually only occurs before i ... it has double length
(b) ... xaa ... where "x" is the sound in "loch" ... a has double length
(c) ... aiʔdo ... the glottal stop is usually not syllable final
(d) ... ohoo ... the final o has double length plus ... the initial o has single length plus.
..
(e), (f) and (g) are not interjections. But are included here as they are break the normal rules in some way.
..
(e) ... ʔaiwa meaning "yes". When said in isolation (i.e. nearly always) it takes a definite tone conture.
(f) ... aiya meaning "no". When said in isolation (i.e. nearly always) it takes a definite tone conture.
(g) ... ʔai is a sentence final yes/no question particle. Now other mono-syllables have either a high tone or a low tone. This one has a tone conture.
ʔaiwa and aiya are written as words normally are. However ʔai with its rising contour is given a special sign. Call it a shorthand sign if you want ...  ... as you can see, it looks a bit like a "2".
... as you can see, it looks a bit like a "2".
And above is shown how to represent the other 6 words.
..
..... Consonant clusters
Word initial
The following consonants and consonant clusters can begin a word;-
| ʔ | |||
| m | my | ||
| y | |||
| j | jw | ||
| f | fy | fl | |
| b | by | bl | bw |
| g | gl | gw | |
| d | dw | ||
| l | |||
| c | cw | ||
| s/ʃ | sl | sw | |
| k | ky | kl | kw |
| p | py | pl | |
| t | tw | ||
| w | |||
| n | ny | ||
| h |
Word medial
. .
The following consonants and consonant clusters can be found in the middle of a word ;-
| lʔ | lm | ly | lj | lf | lb | lg | ld | lc | lz/lʒ | lk | lp | lt | lw | ln | lh | |
| ʔ | m | j | f | b | g | d | l | c | z/ʒ | k | p | t | n | h | ||
| nʔ | ny | nj | nf | mb | ŋg | nd | nc | nz/nʒ | ŋk | mp | nt | mw | nh | |||
| sʔ | zm | ʒy | zb | zg | zd | zl | sk | sp | st | zw | zn | sh |
Above are 58 medial consonants/consonant-clusters. Actually there is a zero option as well. For example kli.o (knife). So we can say there are 59 possibilities.
..
And also there are actually 38 possible initial consonants/consonant-clusters as there are some words that start with a vowel.
..
Word final
..
The consonants n, s and r can occur word finally.
..
..... Vowel clusters
..
The vowels and diphthongs are ... ai e eu u ua a ia i oi o and au
When I write béu words using the latin alphabet, I will sometimes insert a dot "." to indicate syllable breaks. For example ...
iyo.ito (itsy-bitsy, tiny) is a 4-syllable word. If I had written it without the dot it would have been a 3-syllable word. Of course when written in the béu script there is no ambiguity.
..
..... The plural and dual
Regular plurals
..
Most multi-syllable nouns end in one of the vowels e u a i or o.
To show plurality, these are changed into eu ua ai ia and oi respectively. For example ...
..
nambo = house, namboi = houses
..
The normal way for single-syllable nouns to show plurality is to put the word nò in front of the noun.
nò means number (well it does when it is not qualifying another noun). For example ...
..
húa = head, nò húa = heads
..
A very small number of multi-syllable nouns end in ai or au. For plurality they add a (that is another syllable ... a ... is suffixed to the word). For example ...
..
nandau = word, nandau.a = words
moltai = doctor, moltai.a = doctors
..
The dual
..
There are a few nouns (mostly body parts) that have a dual form as well as a plural form. All the word that can take a dual end in a. The dual form is made by changing the a to au.
..
| wá | eye or eyes | wáu | a pair of eyes | nò wá | eyes |
| elza | ear or ears | elzau | a pair of ears | elzai | ears |
| duva | arm/hand | duvau | a pair of arms/hands | duvai | arms/hands |
| poma | leg/foot | pomau | a pair of legs/feet | pomai | legs/feet |
| gluma | breast or breasts | glumau | a nice pair | glumai | breasts |
| jwuba | buttock or buttocks | jwubau | an arse | jwubai | buttocks |
| ploka | cheek or cheeks | plokau | cheeks | plokai | cheeks |
| olna | shoulder or shoulders | olnau | a pair of shoulders | olnai | sholders |
| kloga | shoes or shoe | klogau | a pair of shoes | klogai | shoes |
..
Actually the plural forms of the above are hardly ever encountered. For these words, the dual form is by far the most commonly encountered form.
..
There is one word that doesn't end in a that has a dual form ...
glabu = "person" and has the regular plural form glabua, however it also has a dual form ...
glabau = "two people" or "a couple" (not necessary married but the word gives a very strong connotation that the couple are intimate/having sexual relations)
..
Irregular plurals
..
Three single-syllable words have irregular plurals. These are ;-
..
| bàu | man | bawa | men |
| glá | woman | gala | women |
| nò | number | nòi | numbers |
..
Also there are 7 nouns for which the basic form has a collective meaning and to refer to "one member of" the final vowel must be deleted and replaced with ai
| toti | children | totai | a child |
| bode | small birds | bodai | a small bird |
| fiʒi | fish | fizai | a fish |
| alha | flowers | alhai | a flower |
| ʔupo | trees | ʔupai | a tree |
| yinki | crumpet | yinkai | a young unmarried woman, an attractive girl, a virgin |
| wazbia | distance | wazbai | 3,680 m (the unit used for measuring distance) |
..
Note ... alhabu = a bunch of flowers, a bouquet ... fizbu = a school of fish ... bodebu = a flock of birds ... pobu = forest
..
..... Thread writing
..
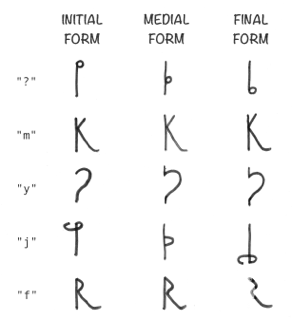
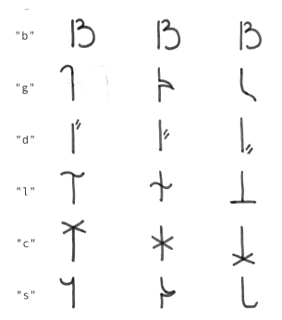
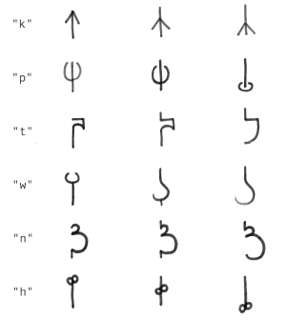
béu has 17 consonants.
For some of these the form differs slightly, depending upon whether the letter is at word initial, word medial or word final.
The three forms are shown below.
béu has 5 vowels and 6 diphthongs.
The form of these doesn't change with their position.
These are shown below.
To give you better idea of what thread writing looks like, I have listed below the 12 colours of béu.
Nice, eh ... sort of organic
..
..... Saying the letters
..
When speaking out the letters, each letter has a word associated with it. This is a bit like when we say "sierra tango echo ..." to spell out a name over the telephone.
| letter | associated name | meaning |
| ʔ | ʔusʔa | a giraffe |
| m | moŋgo | a gibbon |
| y | yeme | a frog/toad |
| j | jamba | a pelican |
| f | fanfa | a horse |
| b | biabia | a butterfly |
| g | gaifai | a flamenco |
| d | duzu | an oryx |
| l | lata | a cow |
| c | compa | a palm tree |
| s | sadu | an elephant |
| k | kiŋki | a fir tree |
| p | pikau | a peacock |
| t | tauta | a hammerhead shark |
| w | wenye | a scorpion |
| n | nùa | a mouse/rat |
| h | habis* | a bee |
We use a different system for the vowels. We add the vowel to san to speak out the vowels. For example ...
To spell naike (sharp) we would say nùa sanai kiŋki sane dù
To spell a vowel that has left.dot (high tone) you substitute dit for san. For example ...
wías (we) would be spelt wenye ditia sadu dù
r is designated by huka (which means hook)
dù is a particle, used with numbers and when spelling, that indicates you have finished a word.
Note ... there is a word dito which means "dot" or "point". Also there is a word santai which means vowel.
táu = letter, character, "symbol used to represent a sound, syllable, word or number"
When a letter is mentioned by itself ( i.e. not as part of a string) it takes the form produced by word building with the above. For example ...
táu gaifai = the symbol given to the sound "g" in béu
táu nùa = the symbol given to the sound "n" in béu
..
* This word has an interesting etymology. alha = flower : alhabis = attracted to flowers
So habis can be seen to be a rubbed down version of alhabis
..
..... The numbers
... The Standard Set
..
The standard set comprises of the numbers from 1 to 172710 (which is 1 to 100012 in base twelve). Every number in the standard set has a unique form.
Five random numbers are given below to demonstrate ...
| ila | = 6 |
| icaufa | = 7212 |
| ildaimba | = 50312 |
| ildaigaumba | = 54312 |
| alaigau | = 64012 |
..
And below is how these numbers are written within a body of text.
..
Within a body of text ("textblock" from now on) a number written vertically and is headed up by a special three sided bracket. The only use of this bracket is to indicate a number within a textblock.
Below this bracket, the number is written with a letter representing each digit of the number
Under the bracket the number is written using a letter symbol.
| letter | digit | ..... | letter | digit | ..... | letter | digit | |||
| J | => | 1 | D | => | 5 | K | => | 9 | ||
| F | => | 2 | L | => | 6 | P | => | 10 | ||
| B | => | 3 | C | => | 7 | T | => | 11 | ||
| G | => | 4 | S | => | 8 |
You can see that base 12 is being used. (just for explanatory purposes I will use "T" for 10 and "E" for 11)
More or less the same symbols is used for the number digit as for the letter. They take their initial, medial or final form, depending on whether the are the first, second or third number of the three digit group. táu ʔusʔa is used for inserting zeroes. táu ʔusʔa is never pronounced, it is only a place holder as number magnitude depends on position.
Although there is a unique word for 1727 numbers, it is not necessary to memorize 1727 unique forms. The 1727 numbers are built up from smaller elements. These elements are shown below ...
..
| 10012 = | anjai | 1012 = | anjau | one = | anja |
| 20012 = | aufai | 2012 = | aufau | two = | aufa |
| 30012 = | aimbai | 3012 = | aimbau | three = | aimba |
| 40012 = | ugai | 4012 = | ugau | four = | uga |
| 50012 = | ildai | 5012 = | ildau | five = | ilda |
| 60012 = | alai | 6012 = | ulau | six = | ila |
| 70012 = | oicai | 7012 = | oicau | seven = | oica |
| 80012 = | ezai | 8012 = | ezau | eight = | eza |
| 90012 = | okai | 9012 = | okau | nine = | oka |
| T0012 = | yapai | T012 = | yapau | T = | yapa |
| E0012 = | watai | E012 = | watau | E = | wata |
..
To construct a number from the above ...
1) Select which elements you need. For example, for 54312, you will need the elements ildai + ugau + aimba
2) If the element is non-initial, delete the initial vowel of the element => ildai + gau + mba ... (note that ya and wa were originally ia and ua ... they should be deleted)
3) Join the elements up => ildaigaumba
..
There is a soecial form for 1, 2 and 3 ... anja, aufa and aimba, while used for building up larger numbers, are never used by themselves. Instead we use ...
..
| ʔà | one |
| hói | two |
| léu | three |
..
ʔà along with its plural form ʔài are also used to code indefiniteness.
..
Numbers are never written out in full. Always the method given above is used. It is as if in a body of English text you never came across the "seven" but only "7".
With fractions, cardinal numbers and numbers denoting group size, there is the choice of writing 7th or seventh. That is you can either use the symbols given below or you can write out in full ... in this example suga, nuga and buga.
..
..
Note ... If you had a leading zero you would use the word jù. 007 would be jù jù oica (three words). To deal with a telephone number, you would lump the numbers in threes (any leading zero or zeroes by themselves though) and outspeak the numbers. If you were left with a single digit (say 4) it would be pronounced ugai. If you were to pronounce it uga, it would of course mean 004. Also you would probably add the particle dù at the end.
..
... The Extended Set
..
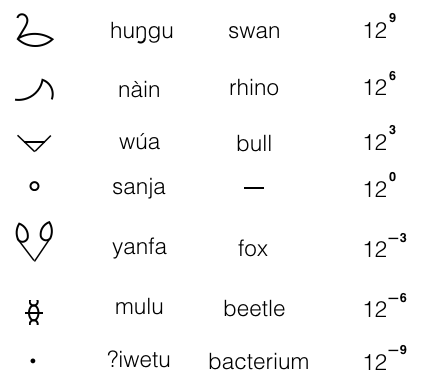
So far we have covered the standard set (1 -> 1727). To expand this into "the extended set" we use "magnitude" words. There are seven of these.
..
..
The first column gives the magnitude symbol, the second ... how the symbol is pronounced, the third ... the meaning*, and the last ... the magnifier that the symbol represents.
.* Yes all the magnitude words double up as animal names. But actually this never causes any problem. If you hear huŋgu huŋgu you know it means "5,159,780,352 Swans" ... there is no ambiguity.
To demonstrate the use of the magnitude words, let's take a long number ... 1,206,8E3,051.58T,630,559
Which is written as ...
and pronounced as ... anja huŋgu aufaila nàin ezaitaumba wúa ildaunja sanja ildaizaupa yanfa alaimbau mulu ildaildauka ʔiwetu dù
You can see that the digits are still grouped into bunches of three. Within the triplets, leading zeros can be dropped ... giving doublets or even singletons.
All the magnitude words are spoken out. Notice the final dù. This means "exactly". You usually add this when pronouncing numbers from the extended set.
When you write an extended set number, you must finish the number off with a bracket. (in contrast the final bracket is never used if the number is from the standard set)
Anyway ... the above is only an example. You are unlikely to find something with so big a dynamic range within a textblock.
Below are examples of numbers which you would more typically find in a text block ...
Pronounced aimba wúa ildaunja dù and ildaunja sanja ildaizau respectively.
(a) aimba wúa ildaunja dù is an whole number.
ildaunja sanja ildaizau is not a whole number. Notice that the 4 versions of ildaunja sanja ildaizau have been given different kinds of final brackets.
(b) This one shows that 51.5812 is an approximation to the actual value. (pronounced daula)
(c) This one shows that 51.5812 has been rounded down. That is .. if A = "actual value", then 51.59 =< A =< 51.58
(d) This one shows that 51.5812 has been rounded up. That is .... if A = "actual value", then 51.58 =< A =< 51.57
(e) This one shows that 51.5812 has been rounded up or down to the nearest digit. That is .... if A = "actual value", then 51.585 =< A =< 51.575
..
dù and daula ( plus ? plus ? plus ?) as well as giving information about the accuracy of the number, also lets the listener know that the speaker has finished.
..
... The free form of the numbers / mathematical notation
..
The numbers considered above were all in what is called "block form". That is ... the form they appear as within a body of text. There is also a way to write numbers when they are not inside a text block. That would happen on a page given over to mathematical formula. In this environment the numbers are written horizontally ... from left to right. There are some slight differences between the free form version of the numbers and the block form versions. The free form version of the numbers are ...
As with the block form, they always occur in triplets. However their form doesn't vary depending on which one of the triplets the character is ... the digits are always exactly the same. There is a special egg-shape symbol for zero (actually called táu kyái, where kyái means "egg"). In free form it is not permitted to drop leading zero's ... well not triplet leading zero's, word leading zero's can of course be dropped.
Below is how the five numbers given previously appear in free form ...
And that long number mentioned in the previous section (a number from the extended set) ...
It is, of course, pronounced exactly as the block form number. That is ... anja huŋgu aufaila nàin ezaitaumba wúa ildaunja sanja ildaizaupa yanfa alaimbau mulu ildaildauka ʔiwetu dù
..
Below are some more symbols used in mathematics. These would appear in a free form page (or part of a page).
..
..
The top 3 symbols in the leftmost column designate "operations". These modify a number and are placed immediately left of the number they modify. If a number has more than one operator they come in the order "minus sign", then "i", then the inverse ("1/x") symbol.
..
And below is a few examples of equations written in this notation.
..
..
... Index
- Introduction to Béu
- Béu : Chapter 1 : The Sounds
- Béu : Chapter 2 : The Noun
- Béu : Chapter 3 : The Verb
- Béu : Chapter 4 : Adjective
- Béu : Chapter 5 : Questions
- Béu : Chapter 6 : Derivations
- Béu : Chapter 7 : Way of Life 1
- Béu : Chapter 8 : Way of life 2
- Béu : Chapter 9 : Word Building
- Béu : Chapter 10 : Gerund Phrase
- Béu : Discarded Stuff
- A statistical explanation for the counter-factual/past-tense conflation in conditional sentences