Kala: Difference between revisions
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
=== Syllable Structure === | === Syllable Structure === | ||
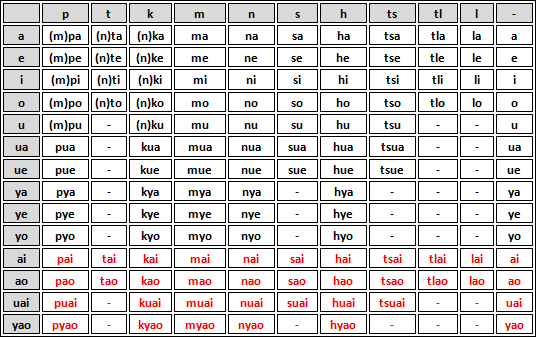
'''Kala''' syllable structure is (('''N''')'''C''')(''y, u'')'''V'''('''F'''). As in most languages, CV is the most common syllable type, accounting for the majority of '''Kala''' lemmas. The finals /n/, /m/, and /k/ are grammatical and indicate adverbs, plurals, and negatives, respectively. They only occur word finally. So, '''nkapa''' (alcohol) is permitted, but ''nakpa'' is not; '''kyopo''' (fear) is acceptable, but ''koypo'' is not, etc. There is a limited set of syllables allowed by '''Kala''' phonotactics, similar to Japanese or Chinese. They are listed here: | '''Kala''' syllable structure is (('''N''')'''C''')(''y, u'')'''V'''('''F'''). As in most languages, CV is the most common syllable type, accounting for the majority of '''Kala''' lemmas. The finals /n/, /m/, and /k/ are grammatical and indicate adverbs, plurals, and negatives, respectively. They only occur word finally. So, '''nkapa''' (alcohol) is permitted, but ''nakpa'' is not; '''kyopo''' (fear) is acceptable, but ''koypo'' is not, etc. There is a limited set of syllables allowed by '''Kala''' phonotactics, similar to Japanese or Chinese. They are listed here: | ||
[[File:Kalasyl.png]] | |||
* Only /l/ cannot occur word initially (except in loan words and toponyms). | * Only /l/ cannot occur word initially (except in loan words and toponyms). | ||
Revision as of 11:36, 20 December 2015
The Kala conlang...
Phonology
Consonants
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| central | lateral | |||||
| Nasal | m (m) | n (n) | ɲ (ny) | |||
| Plosive | p~b (p) | t~d (t) | k~g (k) | ʔ (`) | ||
| Affricate | ts (ts) | t͡ɬ~tl (tl) | t͡ʃ (ts) | |||
| Continuant | s (s) | l~ɾ (l) | ʃ (s) | h~ɦ (h) | ||
| Semivowel | j (y) | w (u) | ||||
- Prenasalized: /ᵐp ⁿt ᵑk/
- Labialized:/pʷ kʷ mʷ nʷ ʃʷ hʷ t͡ʃʷ/
- Palatalized: /pʲ kʲ mʲ hʲ/
Note: Because of its small phoneme inventory, Kala allows for quite a lot of allophonic variation. For example, /p t k/ may be pronounced [b d ɡ] as well as [p t k], /s l h/ as [ʃ ɾ ɦ], and /t͡s t͡ɬ/ as [t͡ʃ t͡l]; also, vowels may be either long or short.
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Close | i | u | |
| Mid | e | o | |
| Open | a |
Kala has five vowels /i/, /e/, /a/, /o/ and /u/. Each occurs in both stressed and unstressed syllables. Phonetic nasalization occurs for vowels occurring between nasal consonants or when preceding a syllable-final nasal, e.g. tsunka [ˈt͡ʃũᵑka] ('bug').
Diphthongs
Phonetically, Kala has only two diphthongs, both falling; [aɪ̯] and [aʊ̯], but there are five syllables that can be analyzed as rising diphthongs; [wa], [we], [ja], [je], and [jo]. The two triphthongs [waɪ̯] and [jaʊ̯] are very rare but should be noted as possible.
Phonotactics
Syllable Structure
Kala syllable structure is ((N)C)(y, u)V(F). As in most languages, CV is the most common syllable type, accounting for the majority of Kala lemmas. The finals /n/, /m/, and /k/ are grammatical and indicate adverbs, plurals, and negatives, respectively. They only occur word finally. So, nkapa (alcohol) is permitted, but nakpa is not; kyopo (fear) is acceptable, but koypo is not, etc. There is a limited set of syllables allowed by Kala phonotactics, similar to Japanese or Chinese. They are listed here:
- Only /l/ cannot occur word initially (except in loan words and toponyms).