Square Kufic: Difference between revisions
From FrathWiki
Jump to navigationJump to search
(→nya) |
m (Reverted edits by Morris2HPv (talk) to last revision by Qang) |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
I have tried to encompass all of the variations of Arabic, including those used to write a variety of languages from around the world. | I have tried to encompass all of the variations of Arabic, including those used to write a variety of languages from around the world. | ||
Please see the [[Square_Kufic/Gallery|Gallery]] for examples. | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 462: | Line 464: | ||
[[Image:1fatHa tanwiin.GIF]] | [[Image:1fatHa tanwiin.GIF]] | ||
*Grammatical ending, used to indicate the [[accusative]] of indefinite nouns, pronounced /an/. | *Grammatical ending, used to indicate the [[wikipedia:accusative|accusative]] of indefinite nouns, pronounced /an/. | ||
==tanwiin aD-Damm== | ==tanwiin aD-Damm== | ||
| Line 468: | Line 470: | ||
[[Image:1Damma tanwiin.GIF]] | [[Image:1Damma tanwiin.GIF]] | ||
*Grammatical ending, used to indicate the [[nominative]] of indefinite nouns, pronounced /un/. | *Grammatical ending, used to indicate the [[wikipedia:nominative|nominative]] of indefinite nouns, pronounced /un/. | ||
==tanwiin al-kasr== | ==tanwiin al-kasr== | ||
| Line 474: | Line 476: | ||
[[Image:1kasra tanwiin.GIF]] | [[Image:1kasra tanwiin.GIF]] | ||
*Grammatical ending, used to indicate the [[genitive]] of indefinite nouns, pronounced /in/. | *Grammatical ending, used to indicate the [[wikipedia:genitive|genitive]] of indefinite nouns, pronounced /in/. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
More to come. --[[User:Qang|Qang]] | More to come. -- [[User:Qang|Qang]] | ||
[[Category:Natscripts]] | [[Category:Natscripts]] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:03, 28 June 2011
This is a presentation of the work I have done on the Kufic version of the Arabic alphabet.
I have tried to encompass all of the variations of Arabic, including those used to write a variety of languages from around the world.
Please see the Gallery for examples.
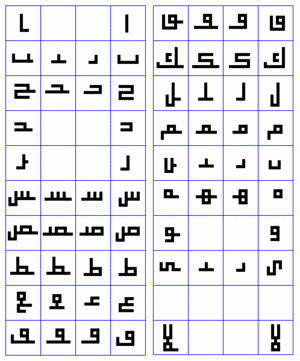
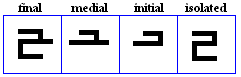
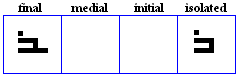
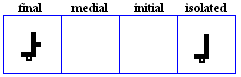
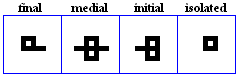
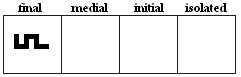
The 19 basic letter forms used in Kufic
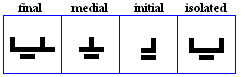
alif
alif
- The basic form of alif, historically vocalized as /a:/ or /?/.
alif hamza
- Used for /a/:
- The alif with hamza above:
- The alif with hamza and fatHa:
- Used for /u/:
- The alif with hamza and Damma:
- Used for /i/:
- The alif with hamza below:
- The alif with hamza and kasra:
- The alif with hamza above a fatHa:
- The alif hamza is used in cases when a short vowel begins a word.
alif madda
- The alif madda, it is used to indicate /?a:/. When two hamza using the alif as a seat follow each other, or when a hamza is followed by a long vowel, then a madda is used instead.
alif waSla
- The alif waSla is used to indicate that the alif is not to be pronounced and that the preceding vowel is elidable.
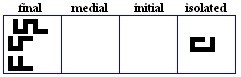
baa, taa, thaa
variations
baa
- The baa, used for /b/.
- The pe used in Perso-Arabic for /p/.
taa
- The taa, used for /t/.
- The Te, used in Urdu for /t`/.
thaa
- The thaa, used for /T/.
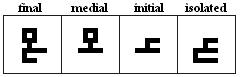
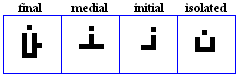
jiim, Haa, khaa
variations
jiim
Haa
- The Haa, used for specifically for /X\/.
khaa
- The khaa, used specifically for /x/.
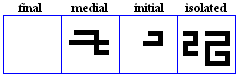
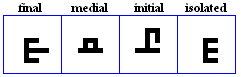
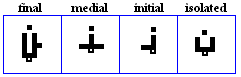
daal, dhaal
variations
daal
- The daal, used for /d/.
- The Daal, used in Urdu to represent /d`/.
- Used in Pashto to represent /d`/.
dhaal
- The dhaal, used for /D/.
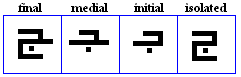
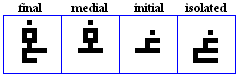
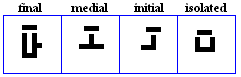
raa, zaay
variations
raa
- The raa, used for /r/.
- The Urdu aar, used for /r`/.
- Used in Pashto to represent /r`/.
zaay
- The zaay or zaa, used for /z/.
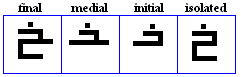
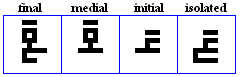
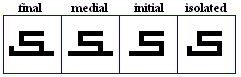
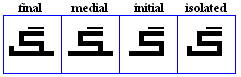
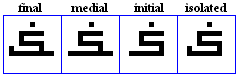
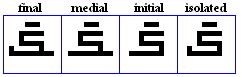
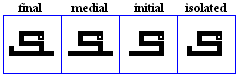
siin, shiin
variations
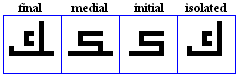
siin
- The siin, used for /s/.
- The xiin, used for /x/ in Pashto.
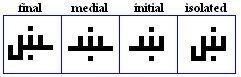
shīn
- The shiin, used for /S/.
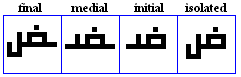
Saad, Daad
variations
Saad
- The Saad, used for /s?\/
Daad
- The Daad, used for /d?\/
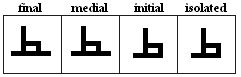
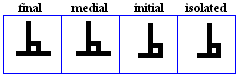
Taa, DHaa
variations
Taa
- The Taa, used for /t?\/.
DHaa
- The DHaa, used for /D?\/ or /z?\/.
ʿayn, ghayn
variations
ʿayn
- The ʿayn, used for /?\/.
ghayn
- The ghayn, used for /G/.
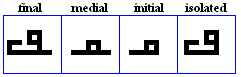
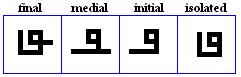
nga
- The nga, used specifically by the Jawi alphabet for /N/.
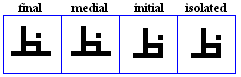
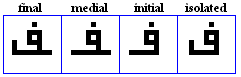
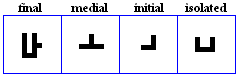
faa
variations
faa
- The faa, used for /f/.
paa
- The paa, used specifically by the Jawi alphabet for /p/.
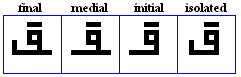
qaaf
- The qaaf, used for /q/ or /g/ in Gulf Arabic.
kaaf
- The kaaf, used for /k/.
- A secondary version of kaaf used by many languages, most prominently those that use the Perso-Arabic alphabet.
- The gaaf, used for /g/ in the Perso-Arabic alphabet and the Jawi alphabet.
- Another version of the gaaf, not used as frequently as the former.
- This version is used unofficially in Moroccan Arabic for /g/ and in some languages as /N/. The use of the initial, medial and final forms vary widely.
- Used specifically in the Pashto Alphabet for /g/.
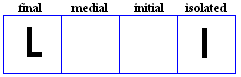
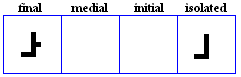
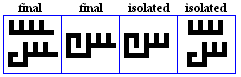
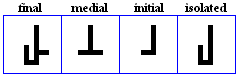
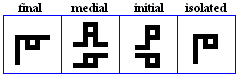
laam
- The laam, used for /l/.
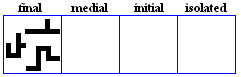
laam-alif
- The laam-alif is a ligature used to represent /la:/.
- Variations.
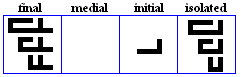
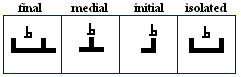
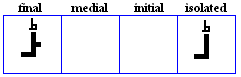
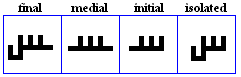
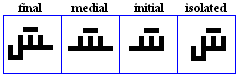
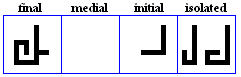
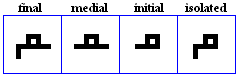
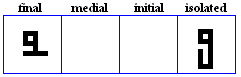
miim
- The miim, used for /m/.
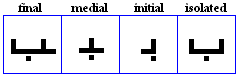
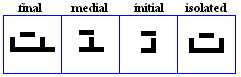
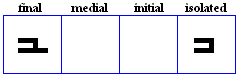
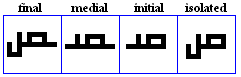
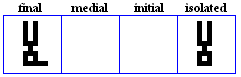
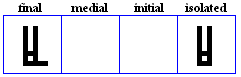
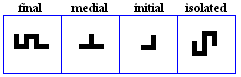
nuun
- The nuun, used for /n/.
- Used specifically in the Pashto Alphabet for /n`/.
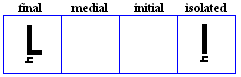
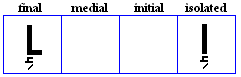
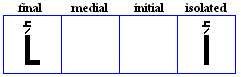
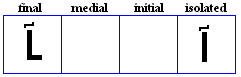
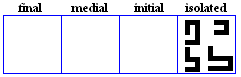
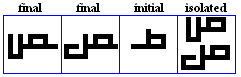
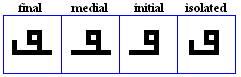
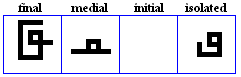
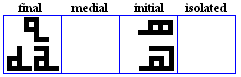
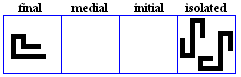
nya
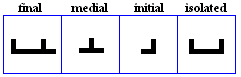
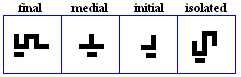
haa
- The haa, used for /h/.
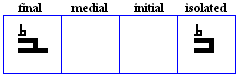
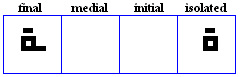
taa marbuuTa
- The taa marbuuTa, a variation of the taa, used grammatically to indicate the feminine gender. It can be vocalized as /h/, /t/ or it can be silent, depending on the semantic role of the morpheme.
waaw
- The waaw, used as /w/ and /u:/.
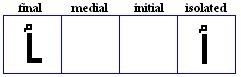
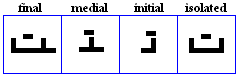
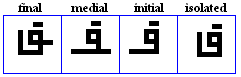
yaa
- The yaa, used as /j/ and /i:/.
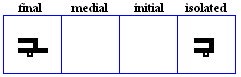
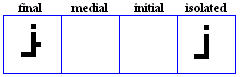
alif maqSuura
- The alif maqSuura, used only in the final position to represent /a:/.
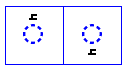
Harakaat
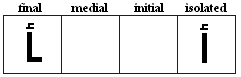
fatHa
- Placed over consonants for /a/.
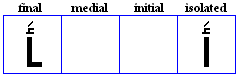
Damma
- Placed over consonants for /u/.
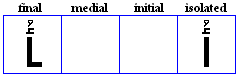
kasra
- Placed below consonants for /i/.
sukuun
- Placed over consonants to indicate the absence of a vowel.
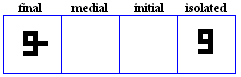
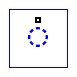
hamza
- Free standing hamza, used for /?/.
- The hamza used as harakaat.
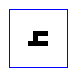
shadda
- Used to indicate gemination.
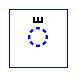
dagger alif
- Used only in completely vocalized text.
tanwiin al-fatH
- Grammatical ending, used to indicate the accusative of indefinite nouns, pronounced /an/.
tanwiin aD-Damm
- Grammatical ending, used to indicate the nominative of indefinite nouns, pronounced /un/.
tanwiin al-kasr
- Grammatical ending, used to indicate the genitive of indefinite nouns, pronounced /in/.
More to come. -- Qang